DGIST Professor Jaeheung Cho of Emerging Materials Science
There are various metal enzymes in the human body. Metal enzymes interact with active oxygen, which is chemically more reactive than normal, to form metal-reactive oxygen species. These metal-reactive oxygen species participate in the synthesis and degradation of biological materials and drug metabolism through oxidation, which is the reaction that combines with oxygen or the reaction that loses hydrogen. Therefore, many research teams study enzymatic reactions in-vivo by synthesizing substances mimicking metal-reactive oxygen. However, there has not been any metal-reactive oxygen species reacting with nitrile found or developed.
Nitrile is a type of organic compound consisting of a triple bond of carbon (C) and nitrogen (N). It is chemically diverse and used as a material to synthesize certain compounds. In spite of its diverse applications as intermediates in biochemistry and physiology, however, there has been minimal yields of the synthesis using nitrile due to its chemical properties requiring very strong acid or base, or high temperature to proceed the reactions.
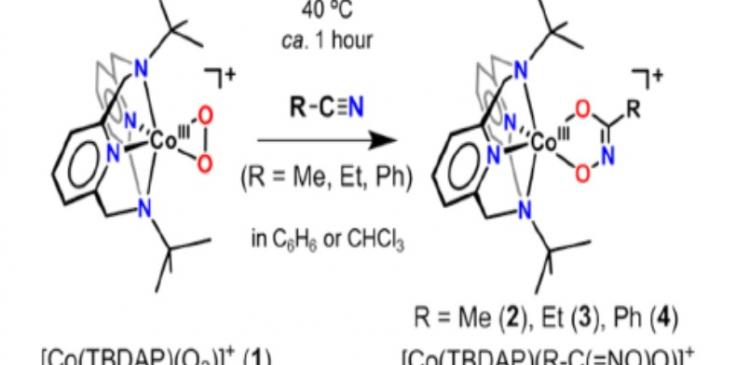
Despite the limitations, a research team led by DGIST Professor Jaeheung Cho of Emerging Materials Science has recently succeeded in synthesizing the metal-reactive oxygen species (cobalt-peroxo species), a biomimetic material that reacts with nitrile, for the first time.
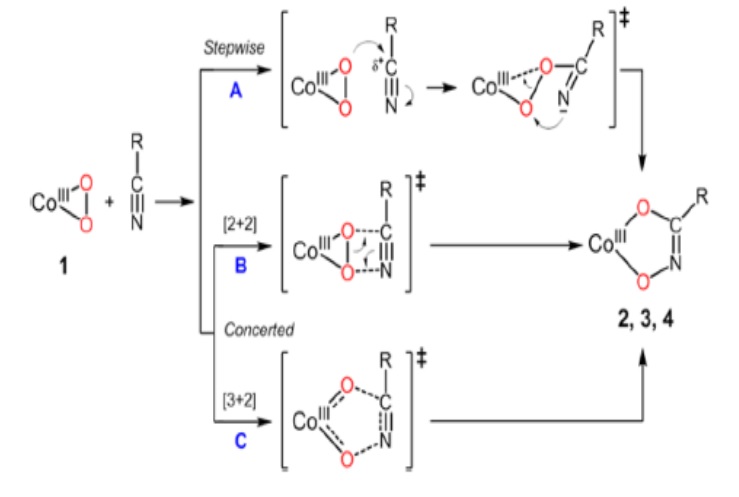
The research team has found that the cobalt-peroxo species (peroxo : one of the reactive oxygen with two electrons added to an oxygen molecule) which is synthesized using an oxidizing agent on a metal cobalt compound reacts with nitrile under the conditions of high temperature and pressure. This is the first confirmation that the metal-reactive oxygen species react with the nitrile.
In particular, the hydroximatocobalt (III) complexes that are composites produced by the reaction between cobalt-perox and nitrile, can develop into a prodrug in the future. This is because when the hydroximatocobal (III) complexes are converted into cobalt (Ⅱ) state through in vivo reduction, certain enzymes that are highly expressed in cancer cells can be controlled. The prodrug refers to a medication or compound that shows almost no drug activity by itself, but is metabolized and shows its effect through in-vivo enzymatic or chemical reaction.
Not only that, nitrile plays an important role in the synthesis of plant hormones and compounds. On the other hand, compounds containing nitrile functional groups in herbicides may cause environmental damage by remaining in agricultural wastes and the like. Therefore, the transformation of nitrile functional groups is an environmentally important reaction.
Professor Jaeheung Cho stated the significance of the study “This study demonstrates the new reactivity of metal-reactive oxygen species and it is expected to contribute to the development of catalysts that enable activation of nitrile in the future. Also, synthesized products are expected to be developed as anti-cancer prodrugs.”
This study has been published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, an international journal of chemistry, on August 16. The research was carried out by C1 Gas Refinery Project’ of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Research Foundation.
For more information, contact :
Professor Cho Jaeheung
Department of Emerging Materials Science
Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST)
E-mail : [email protected]