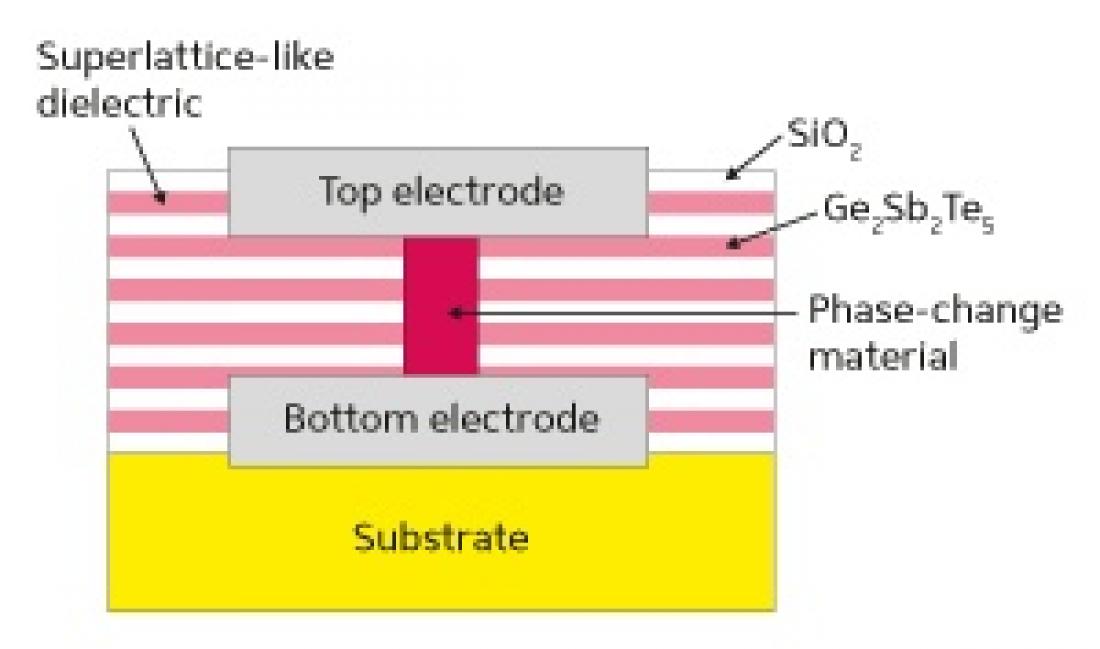
A schematic illustration of a phase-change memory element incorporating a superlattice-like dielectric
The perfect data storage solution should offer fast access to data, maintain data in the absence of external power, and be able to withstand large numbers of read–write cycles. Phase-change random access memory (PCRAM), a type of non-volatile memory that uses the amorphous and crystalline states of phase-change materials for encoding data, can satisfy all of these criteria. Unfortunately, PCRAM also tends to have impractically high power requirements that have impeded its application in many devices. Desmond Loke and co-workers at the A*STAR Data Storage Institute have now demonstrated a technology that could help reduce the power requirements of PCRAM[1].
The high power requirements of PCRAM are a consequence of the high heat levels necessary to drive the transformation between the crystalline and amorphous phases. This heat in turn usually requires relatively large current pulses, which also makes it difficult to integrate with small transistors. Loke and co-workers designed their PCRAM to make the most of this generated heat by replacing the dielectric that surrounds the phase-change material with a material that also acts as a high-performance thermal insulator.
Most dielectric materials, such as silicon dioxide (SiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3), are not particularly good thermal insulators. Conversely, most thermal insulators, such as the amorphous phase-change material germanium antimony telluride (Ge2Sb2Te5), are not very good electrical insulators. The researchers got the best of both worlds by developing a periodic dielectric structure, known as a superlattice-like (SLL), for integration into the PCRAM. The SLL dielectric, which comprises alternating layers of SiO2 and Ge2Sb2Te5 (see image) each just 2–3 nanometers thick, is both a good thermal insulator and a good electrical insulator.
The SLL dielectric in the PCRAM device reduces heat loss from the phase-change material, allowing the phase transition to be driven more efficiently. Consequently, the resulting PCRAM needs smaller currents, less power and less time to switch between the amorphous and the crystalline states. At the same time, the excellent electrical insulation provided by the SLL dielectric prevented current-driven breakdown, leading to a device endurance of more than a billion cycles.
The researchers believe their findings could help accelerate the development of energy-efficient, high-speed PCRAM, which could replace the use of conventional types of RAM, such as flash memory, in electronic devices. “We have already identified techniques to further improve the performance of PCRAM,” says Loke. “For example, by reducing the size of the memory cell, we can expect even higher speeds and lower power consumption levels.”
The A*STAR-affiliated researchers contributing to this research are from the Data Storage Institute