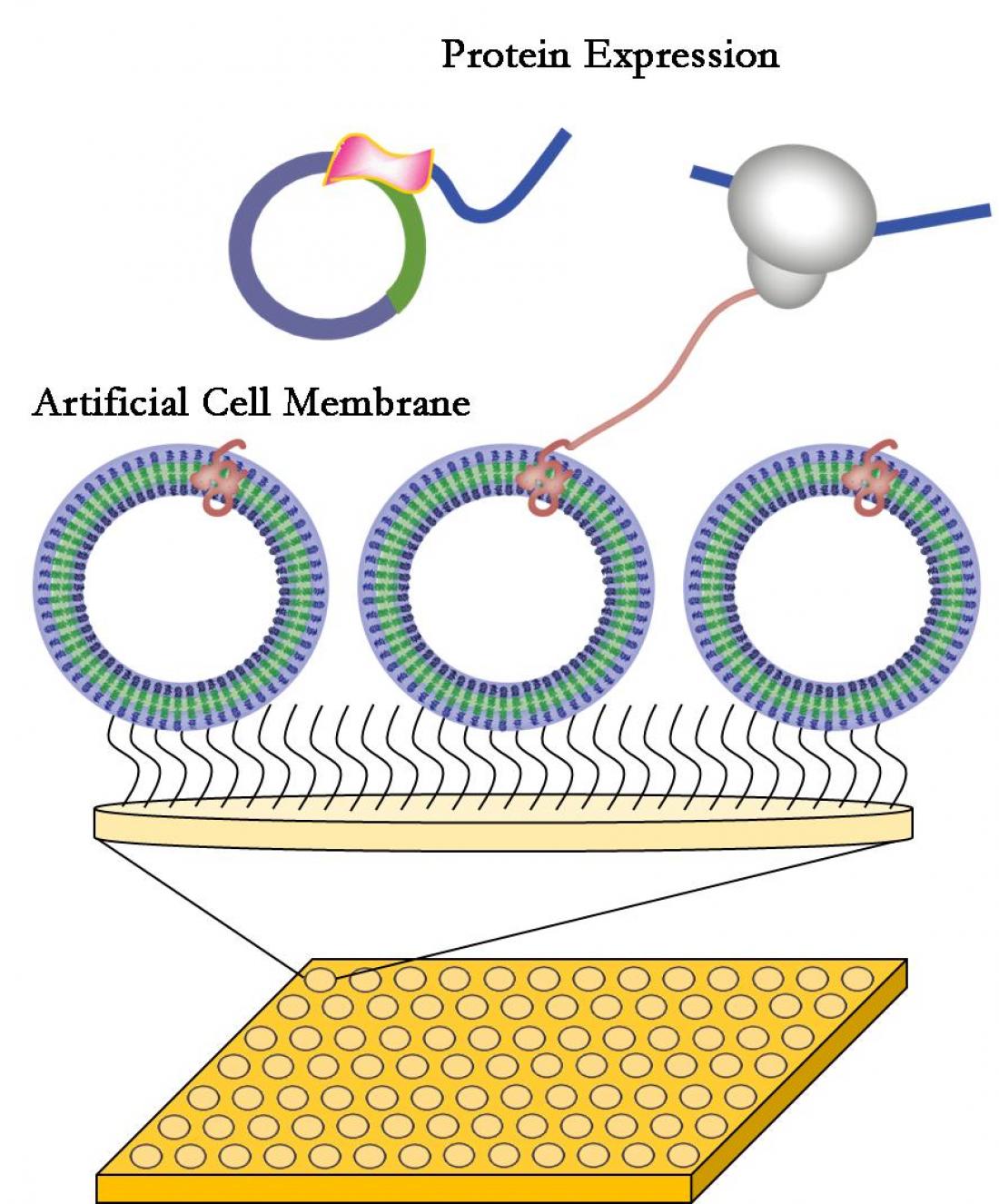
A membrane protein is directly produced and incorporated into the polymer membrane.
Synthetic cell membranes invented at the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE), a research institute of Singapore’s Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), may improve the way we identify and develop drugs by speeding up and reducing the cost of the drug screening process. The technology earned a spot as one of the twelve finalists in the Asian Innovation Awards 2011 organised by the Wall Street Journal Asia.
Singapore, 30 June 2011 – They may look and act like natural human cell membranes but the synthetic cell membranes invented by A*STAR’s IMRE have more advantages. IMRE’s patented synthetic cell membranes can be made-to-order, are easier to maintain in a laboratory environment and do not require the lengthy preparation that comes with working on live cell membranes. The synthetic cell membranes mimic the natural functions of cell membranes, such as interacting with drug molecules and antibodies, which is crucial in the drug discovery process. The innovation also provides a more stable membrane model for a better understanding of the mechanisms of diseases that affect human cells.
A team of researchers led by IMRE’s Dr Madhavan Nallani successfully used synthetic materials to mimic biological processes. “We have harnessed natural cellular processes to fabricate a simple yet functional system using engineered materials to mimic the cell membrane and its proteins,” said Dr Nallani, the IMRE scientist who invented the synthetic cell membranes. “These artificial cell membranes allow researchers to study interactions between membrane proteins, drugs and other compounds without the hassle of using living materials.”
“Cells communicate with each other through membrane proteins. The disruption of this communication mechanism causes diseases like cancer, diabetes and even Parkinson’s disease. Understanding the workings of membrane proteins is very crucial in creating medicines to combat these diseases,” explained Professor Eva Sinner, a visiting scientist at IMRE who works on biomaterials and is involved in the project.
Current methods of drug testing require living cells, which entail high capital and maintenance costs, as well as specialists to operate sophisticated equipment. IMRE’s patented synthetic cell membranes, which are essentially membrane proteins inserted into a stable polymer matrix outside a cellular environment, creates a platform for researchers to work on that both simple to use and easy to maintain.
“This innovation is a classic example of how materials R&D can be applied to biomedical technologies,” said Prof Andy Hor, Executive Director of IMRE. “The success of this technology will be a great boost in helping create better drugs faster and more cost effectively.”
Dr Nallani is currently looking for partners to commercialise the technology. The invention has direct impact and application in fields like drug discovery, antibody and therapeutics development, and drug delivery, which are collectively worth some US$170 billion dollars .
– END –
Encl. Annex A: A*STAR Corporate Profiles
Annex B: Schematic representation of an artificial membrane
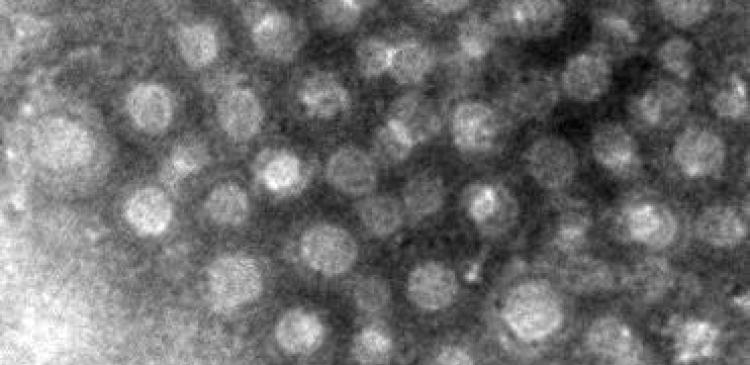
Annex C: Transmission electron microscope (TEM) image of artificial membranes
For media enquiries, please contact:
Mr Eugene Low
Manager, Corporate Communications
for Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE)
3, Research Link
Singapore 117602
DID +65 6874 8491
Mobile +65 9230 9235
Email [email protected]
For technical enquiries, please contact:
Dr Madhavan Nallani
Scientist II
Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE)
3, Research Link
Singapore 117602
DID +65 6872 7541
Email [email protected]
________________________________________
Annex A - A*STAR Corporate Profiles
About the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE)
The Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE) is a research institute of the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR). The Institute has capabilities in materials analysis & characterisation, design & growth, patterning & fabrication, and synthesis & integration. We house a range of state-of-the-art equipment for materials research including development, processing and characterisation. IMRE conducts a wide range of research, which includes novel materials for organic solar cells, photovoltaics, printed electronics, catalysis, bio-mimetics, microfluidics, quantum dots, heterostructures, sustainable materials, atom technology, etc. We collaborate actively with other research institutes, universities, public bodies, and a wide spectrum of industrial companies, both globally and locally. For more information about IMRE, please visit www.imre.a-star.edu.sg
About the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
The Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) is the lead agency for fostering world-class scientific research and talent for a vibrant knowledge-based and innovation-driven Singapore. A*STAR oversees 14 biomedical sciences and physical sciences and engineering research institutes, and six consortia & centres, located in Biopolis and Fusionopolis as well as their immediate vicinity.
A*STAR supports Singapore's key economic clusters by providing intellectual, human and industrial capital to its partners in industry. It also supports extramural research in the universities, hospitals, research centres, and with other local and international partners. For more information about A*STAR, please visit www.a-star.edu.sg.