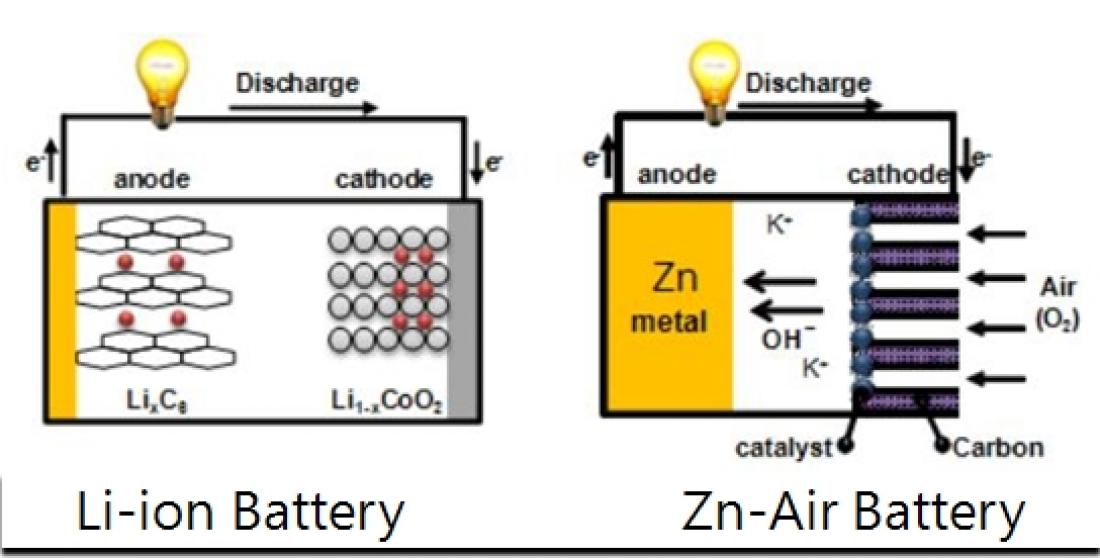
Li-ion battery and Zn-air battery
Ulsan, S. Korea, July 2, 2013 – Korean researchers from Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) have developed a novel bio-inspired composite electrocatalyst outperforming platinum.
This research work was published on June 25, in the journal Nature Communications.
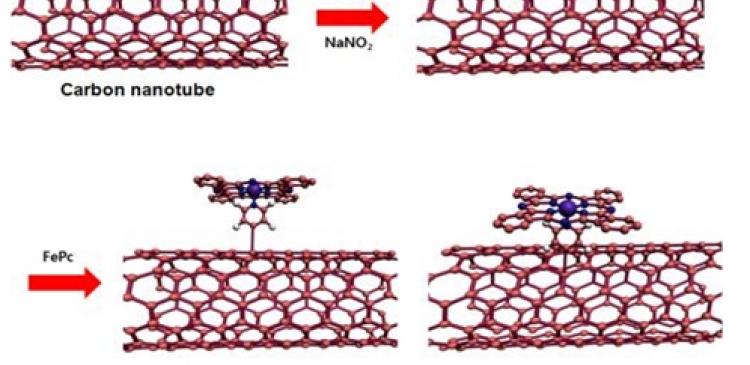
The research team developed an inexpensive and scalable bio-inspired composite electrocatalyst, iron phthalocyanine with an axial ligand anchored on single-walled carbon nanotubes, demonstrating a higher electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction than the state-of-the-art Pt/C catalysts as well as an exceptional durability during cycling in an alkaline media.
Electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction are critical components that may dramatically enhance the performance of fuel cells and metal-air batteries, which are perceived to be the power for future electric vehicles.
Currently Pt and its alloy are known as the most efficient catalysts for activation of the oxygen reduction reaction. However, their application is limited due to high costs and scarce reserves.
Scientists worldwide are looking for better catalysts which outperforms platinum, costs less and has a simpler production process.
The UNIST research team led by Prof. Jaephil Cho, dean of the Interdisciplinary School of Green Energy, UNIST, demonstrated a new strategy to rationally design inexpensive and durable electrochemical oxygen reduction catalysts for metal-air batteries and fuel cells.
The research team designed a new class of ORR catalysts using pyridine-functionalized carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to anchor FePc molecules and provide the axial ligand for the iron centre. At the same time, the CNTs provide an easy pathway for fast electron transfer from the current collector to the ORR active sites.
The resulting material, bio-inspired FePc-Py-CNTs catalyst has shown outstanding durability and electrocatalytic activity for ORR in an alkaline media, offering better performance than a commercial Pt/C catalyst. Compared to other unpyrilysed metal macrocycles catalysts, this bio inspired FePc-Py-CNTs catalyst has achieved a much longer cycle life , reaching more than 1,000 cycles in a durability test.
“I believe the FePc-Py-CNTs catalysts is a technologically promising candidate for practical applications in metal-air batteries and alkaline fuel cells,” said Prof. Cho. “The origin of the enhanced performance for this bio-inspired catalysts in aromatic macrocycle, provides important insight into rational design of metal macrocycles catalysts for other applications such as solar harvesting and catalysts for other redox reactions.”
The fellow researchers include Ruiguo Cao, Ranjit Thapa, Hyejung Kim, Xioadong Xu, and Prof. Noejung Park from UNIST and researchers from Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL), Loa Alamos National Laboratory and Georgia Institute of Technology.
The research was supported by the Converging Research Centre Program through the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST), Korea. The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP), Korea is also acknowledged.
###