Researchers at Tohoku University's School of Medicine have found an explanation for the correlation between eating fish during pregnancy, and the health of the baby's brain.
Dietary lipid contains fatty acids such as omega-6 and omega-3, which are essential nutrients for many animals and humans. The research group, led by Professor Noriko Osumi, found that a balanced intake of lipids by pregnant women is necessary for the normal brain formation of the unborn child.
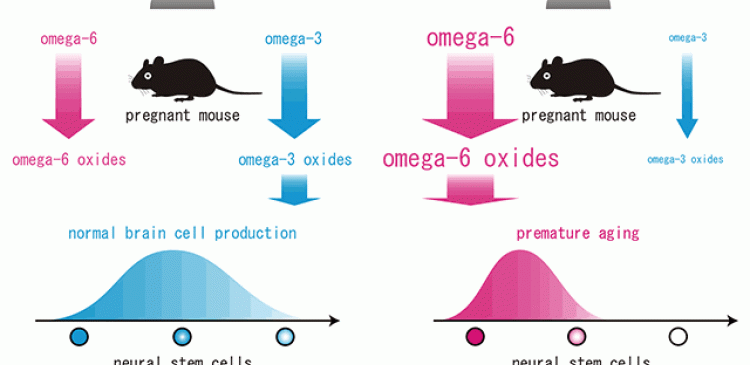
In an animal study, the researchers noticed that when female mice were fed an omega-6-rich/omega-3-poor diet, their offsprings were born with a smaller brain and showed abnormal emotional behavior in adulthood.
This is significant because people in many countries these days have similarly poor dietary patterns and tend to consume more seed oils that are rich in omega-6 fatty acids and less fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
According to Professor Osumi, the brain abnormality found in the offsprings of mice used in the study, was caused by a premature aging of fetal neural stem cells that produce brain cells. The premature aging was promoted by an imbalance of oxides of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. The offsprings also showed higher anxiety levels, even though they were raised on nutritionally optimized diets from an early lactation period.
A diet that contains a good balance of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids is known to improve the development of brain functions; this is based on earlier researches that evaluated the effects of maternal intake of an omega-3-poor diet on brain function in children.
The new study took this premise further and focused on the effects of dietary lipids on the brain formation. The results reveal why omega-6 and omega-3 balance is important for future brain function, and reinforces earlier suggestions that more fish intake by women during pregnancy can advantageously affect the child's health.
This work was supported and made possible by a research fellowship of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science for Young Scientists from the Japan Science and Technology Agency; a grant-in-aid for scientific research (B) from MEXT (Grant 21300115); a scientific research promotion grant from the Mishima Kaiun Memorial Foundation; a research grant from the Asahi Glass Foundation.
Publication Details:
Authors: Nobuyuki Sakayori, Takako Kikkawa, Hisanori Tokuda, Emiko Kiryu, Kaichi Yoshizaki, Hiroshi Kawashima, Tetsuya Yamada, Hiroyuki Arai, Jing X Kang, Hideki Katagiri, Hiroshi Shibata, Sheila M Innis, Makoto Arita and Noriko Osumi
Title: Maternal dietary imbalance between omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids impairs neocortical development via epoxy metabolites
Journal: Stem Cells
DOI: 10.1002/stem.2246
Published online on November 19, 2015 (ahead of print)
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26580686
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/stem.2246/abstract
For enquiries about the research:
Professor Noriko Osumi
Department of Developmental Neuroscience, Center for Neuroscience
United Centers for Advanced Research and Translational Medicine
Tohoku University School of Medicine
Tel: +81-22-717-8203
Email: osumimed.tohoku.ac.jp
For all other enquiries:
Hitoshi Inada
Public Relations Office
Tohoku University School of Medicine
Tel: +81-22-717-7891
Email: hinadamed.tohoku.ac.jp