Nucleic Acids Research
News
15 Apr 2024
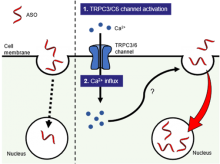
Researchers from Osaka University found that a new activator called L687 induces cancer cells to accept delivery of antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) drugs. These drugs can treat cancer by blocking the transfer of messages from genes that encourage cancer growth. Previous methods to deliver ASOs into cells had only limited success. This research will help accelerate the development and delivery of novel ASO cancer therapies.
02 Feb 2023
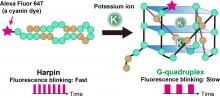
A new microscopic technique allows for the real-time study of RNA G-quadruplexes in living cells, with implications for the fight against amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
24 Jun 2021
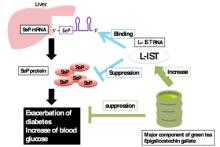
A research group has discovered a new gene that aids in the fight against type 2 diabetes. The gene, known as L-IST, reduces Selenoprotein P, too much of which increases insulin resistance, and can be increased through drinking tea.
06 Nov 2019
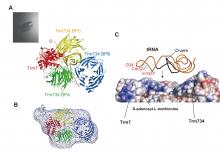
Groups in Ehime University, Japan and the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK), Japan have solved the crystal structure of the eukaryotic Trm7-TRm734 complex, which methylates the ribose at the first position of anticodon in tRNA. They have clarified the tRNA recognition mechanism of this complex and the functions of its subunits based on the crystal structure. This study was published in Nucleic Acids Research on October 5, 2019.
26 Aug 2019
A recent study, affiliated with South Korea's Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) has presented a novel approach to identify cancer suppressing microRNA (miRNA) targets and relevant cellular signaling pathways through large-scale gene-expression data analysis.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.