Host–Endosymbiont Genome Integration in a Deep-Sea Chemosymbiotic Clam
News
29 Mar 2021
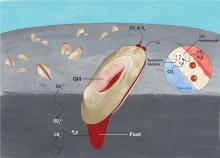
A study led by scientists at Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) has decoded the genomes of the deep-sea clam (Archivesica marissinica) and the chemoautotrophic bacteria (Candidatus Vesicomyosocius marissinica) that live in its gill epithelium cells. Through analysis of their genomic structures and profiling of their gene expression patterns, the research team revealed that symbiosis between the two partners enables the clams to thrive in extreme deep-sea environments.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.