PNAS nexus
News
22 Dec 2023
Researchers from Osaka University developed a bio-logger for seabirds that enables long-term observation of rare behaviors. The bio-logger employs low-power depth sensors and accelerometers to identify rare behavior using a light-weight outlier detection model and records the behavior in a 5-min video. Observations using the bio-loggers on Streaked Shearwaters revealed novel aspects of head-shaking and foraging strategies. This approach will enable a wider range of animal behaviors in various environments to be observed.
30 Aug 2022
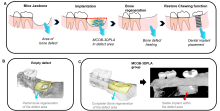
Tohoku University scientists in Japan have made a scaffold that supports the growth of new bone in large jaw defects in mice. Their findings, published in the journal PNAS Nexus, bring scientists one step closer to addressing the issues currently facing the treatment of large jaw bone defects, especially in the elderly.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.