(Starting from left) Professor Jae Youn Hwang; Integrated M.S&Ph.D. student, Kyungsu Lee; and Juhum Park, Chief Executive Officer of Dabeeo Inc.
The artificial intelligence network and extracted buildings from aerial photographs
The team of Prof. Jae Youn Hwang from the Department of Information and Communication Engineering, DGIST, developed an artificial intelligence neural network module for creating digital maps using deep learning-based technology. The module can accurately extract buildings from aerial photographs for remote sensing. This research is closely related to various follow-up studies, such as developing core artificial intelligence technology, with Dabeeo Inc., a technology company specializing in map data. It is anticipated that this accomplishment will have a positive impact in related fields in the future.
With the recent advances and performance improvement in deep learning technology, a type of artificial intelligence technology, applied research is conducted actively in this field. Among them, the technology to accurately segment objects, such as buildings, from aerial images is important for creating digital maps that are used in military, logistics, and autonomous driving. However, existing technologies could not accurately locate objects in low-quality or low-resolution aerial images. Therefore, digital maps were created manually, which was time-consuming and costly.
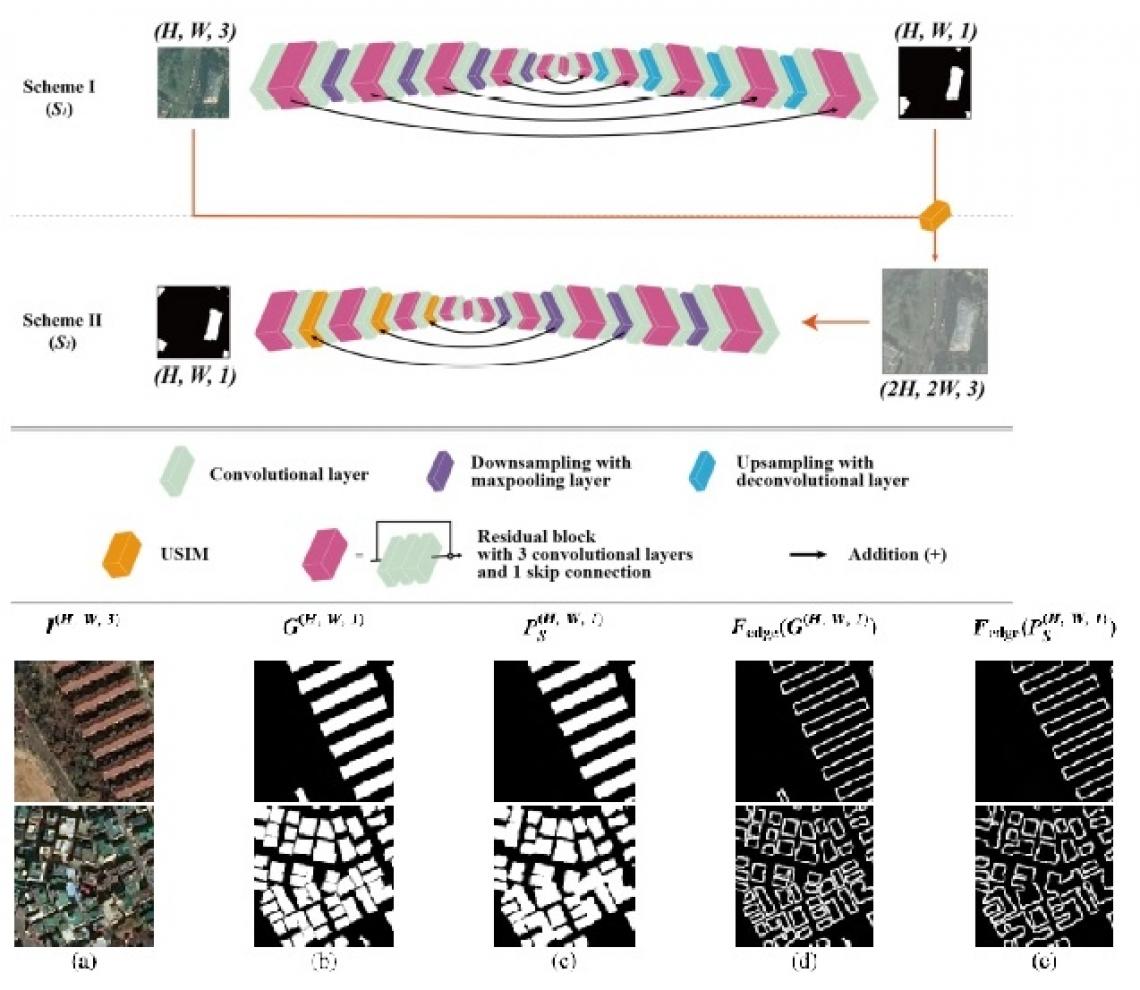
Therefore, Prof. Jae Youn Hwang thought it would be possible to improve the performance of building detection by focusing on the boundaries of the buildings in aerial images while detecting objects that are required for automatic creation of digital maps. Based on this concept, they began developing an artificial intelligence model, which can segment the boundaries accurately and detect the precise boundaries of buildings.
Furthermore, the research team designed a new learning pipeline and an operator to analyze the association between the boundary of the building and entropy. By doing so, they developed a new neural network structure that segmented the boundaries accurately. The developed novel neural network has the advantage of extracting the exact shapes and boundaries of buildings from aerial images. Therefore, compared with the existing neural networks, it can significantly improve the performance of extracting buildings from various aerial image domains. This development maximized efficiency to the extent that a digital map, which a person would require over a month to create, can be produced in a few seconds.
This achievement is the result of the industry-academia collaboration that continued since the Artificial Intelligence Lab was co-founded by DGIST and Dabeeo in 2019. With the technological advances it made through the industry-academia collaboration with DGIST, Dabeeo was selected for the future unicorn nurturing project by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and now growing into a global IT company. Moreover, the artificial intelligence technology based on extracting objects from images, DGIST and Dabeeo are currently recognized for their technological prowess in the field of object analysis. Additionally, DGIST and Dabeeo are working on various studies and commercialization activities, such as spatial data analysis using satellite and aerial images and enhancing the automatic data extraction platform.
Professor Jae Youn Hwang of the Department of Information and Communication Engineering at DGIST said, "the neural network we developed in this study is a novel neural network that can extract objects from aerial and satellite images with high accuracy. If this technology is further improved in the future, it is expected to be applied to various fields, such as medical imaging, and have a positive impact on the development of artificial intelligence technology."
□ Kyungsu Lee, a graduate student in the integrated MS & Ph.D. Program of the Department of Information and Communication Engineering, DGIST, participated in this study as the first author. Additionally, Prof. Jihwan P. Choi from KAIST participated in this study as the co-corresponding author. The results of this study were published on Monday, July 26th in ‘Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,’ a top journal in the related field within the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in the United States.