iScience
News
14 Jul 2023
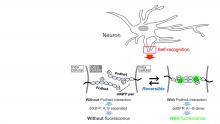
Researchers from Osaka University have developed a fluorescent sensor that may be useful for understanding how cells recognize themselves versus other cells when making connections in the brain. Specifically, their sensor can be used to visualize not only connections between cells, but also the disassociation of these interactions. Because neuronal self-connectivity has been implicated in brain disorders like epilepsy and autism, a better understanding of this process may result in improved therapies.
11 Jul 2023
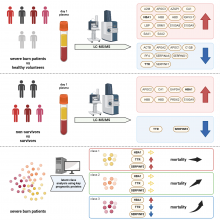
The physiological mechanisms underlying severe burns are not well understood. Researchers at Osaka University used mass spectrometry to identify key blood proteins associated with burn mortality. Ultimately, three proteins (HBA1, TTR, SERPINF2) were very highly correlated with morality rates. Further research into these proteins and their pathways may lead to better drugs to treat people with life-threatening burns.
07 Nov 2022
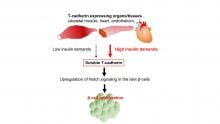
Researchers led by Osaka University show that a molecule called T-cadherin can be secreted in a soluble form. Soluble T-cadherin interacts with pancreatic insulin-producing β cells via the Notch signaling pathway to promote their proliferation and increase the production of insulin. Recombinant T-cadherin stimulated Notch signaling in isolated mouse pancreatic islets, which contain β cells, indicating that T-cadherin may have therapeutic potential for diabetes.
17 Oct 2022
Researchers from Osaka University have shown that deficiency of the protein Favine can lead to accelerated development of atherosclerosis. Loss of Favine in a mouse atherosclerosis model also led to calcification and thrombus development in the blood vessels of the mice. Prior to this, no mouse models for calcification or thrombus formation existed, hindering atherosclerosis research. This work also identifies Favine and its downstream signaling pathway, known as MEF2C-KLF2, as potential therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis.
07 Sep 2022
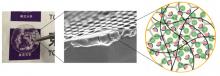
Crucial to our everyday use the Li-ion battery can be found everywhere. Research at Tohoku University has resulted in a hybrid electrolyte that is both more stable while also retaining excellent conductivity. This will pave the way to a safer polymeric solid electrolyte for Li-ion batteries with a myriad of applications.
23 Aug 2022
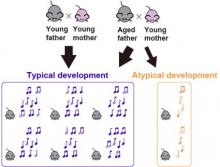
A baby’s cry is a form of communication used to attract attention from adult caregivers, and every baby cries in a similar but distinct way. An international research team has studied the vocal behavior of baby mice, called pups, to determine how the age of the father affects the pups’ vocal communication and body weight development. Their study will help them better understand vocal development in human babies.
05 Aug 2022
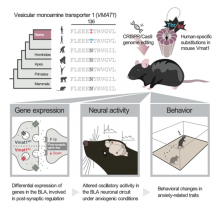
New research using genome editing technology has allowed scientists to create a model and assess a gene mutation associated with neuropsychiatric disorders in humans. The study has revealed how the mutation functions in the brain and affects anxiety and sociality.
18 Mar 2022
Tohoku University scientists in Japan have developed a virus-based approach for measuring variations in gene regulatory elements, called transcription factors, as conditions change in live organisms.
22 Feb 2022
A Japanese research team created a new way to sort living cells suspended in fluid using an all-in-one operation in a lab-on-chip that required only 30 minutes for the entire separation process.
15 Feb 2022
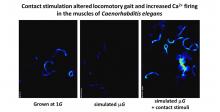
A new study on nematode worms reveals physical contact with objects can help prevent neuromuscular decline in simulated microgravity. The research provides new insights into maintaining human health in space.
15 Apr 2021
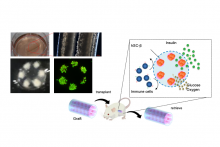
Researchers from The University of Tokyo develop a novel device for the safe and effective transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived pancreatic beta-cells in type I diabetes mellitus
04 Feb 2021
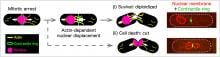
Cells replicate their genetic material and divide into two identical clones to perpetuate life. Some cells pause in the process with a single, undivided nucleus. When the cell resumes division after such a pause, the nucleus can become caught in the fissure, splitting violently, and killing both cells. But that is not always the case. Researchers from Hiroshima University in Japan are starting to understand how active nuclear displacement rescues cell death.
25 Dec 2019
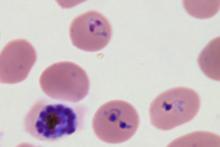
Malaria parasites transform healthy red blood cells into rigid versions of themselves that clump together, hindering the transportation of oxygen. The infectious disease affects more than 200 million people across the world and causes nearly half a million deaths every year, according to the World Health Organization’s 2018 report on malaria. Until now, however, researchers did not have a strong understanding of how the parasite so effectively infiltrated a system’s red blood cells.
21 Jan 2019
A team of researchers has developed a system that produces electricity and hydrogen (H2) while eliminating carbon dioxide (CO2).
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.