□ An announcement was made on December 12 (Tuesday) that Professor Sunghoon Im's team from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, DGIST (President Kun Woo Lee), had developed depth-sensing deep learning technology that enables safe autonomous driving in diverse environments, irrespective of location or weather conditions. The technology is expected to be applied to many fields, including indoor and outdoor robot vision and 3D object detection, in which depth-sensing technology is essential.
□ In the realm of autonomous driving, depth-sensing technology is crucial in detecting distances around the vehicle to accurately perceive the surrounding environment. Hence, research on deep learning-based depth-sensing technologies for autonomous driving is being actively conducted both domestically and internationally. While existing technologies have demonstrated acceptable performance in test data under specific conditions, they have produced errors in detection and shown low-quality performance with the addition of variables such as fog or rain, which limits their practical use.
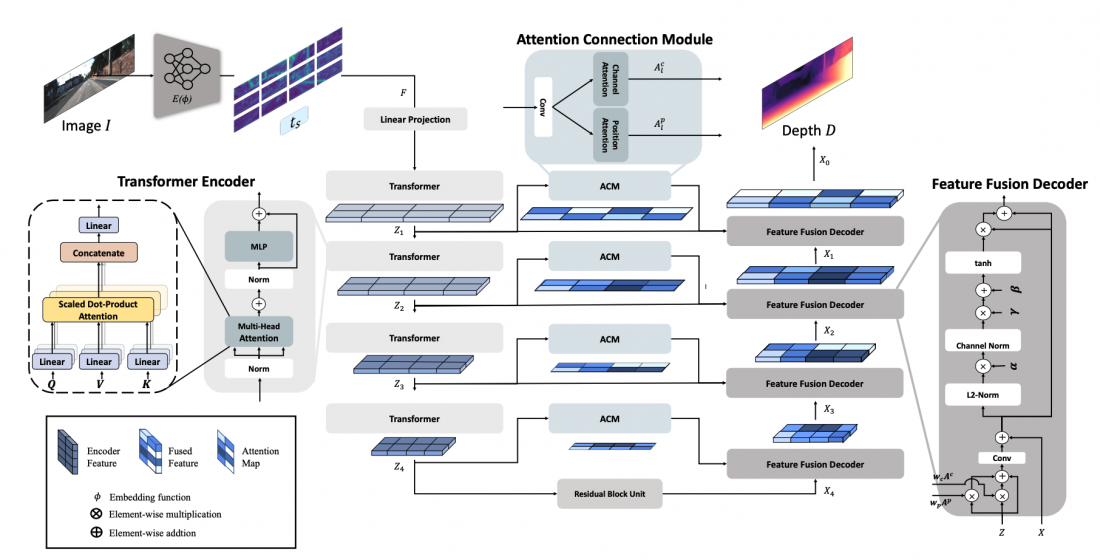
□ In response to these challenges, Professor Im's team focused on generalizing the technology to operate consistently under any condition, while analyzing the relationship between various neural network structures and depth-sensing issues. With this approach, they developed depth-sensing technology with high accuracy and reliability through concentrated feature extraction for the entire input image and effective feature matching. Additionally, they conducted preliminary research on autonomous driving data in various environments, including diverse locations and weather conditions, and evaluated the proposed technology to assess its generalization performance.
□ Furthermore, the research team evaluated previous studies and the proposed technology with regard to various environments and depth-sensing benchmarks. They analyzed the generalization performance of depth-sensing technologies based on neural network structures. By doing so, they proposed neural network structures and evaluation indices to enhance generalization performance.
□ Professor Sunghoon Im from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at DGIST commented, "Through this research, the proposed generalization research on monocular camera depth-sensing moves one step closer to building autonomous driving artificial intelligence that people can trust and use, moving away from biased autonomous driving AI models." He added, "The application of these related technologies to various fields is expected to have a significant influence on the development of reliable artificial intelligence technology."
□ The results of this study were published in November 2023 in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, a prestigious international journal that ranks among the top 1% in the fields of electrical engineering and computer science/AI.
- Corresponding author e-mail Address : [email protected]