Space sciences Planetary science
News
28 Feb 2024
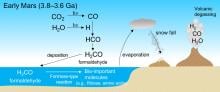
Organic materials discovered on Mars may have originated from atmospheric formaldehyde, according to new research, marking a step forward in our understanding of the possibility of past life on the Red Planet.
23 Jan 2024
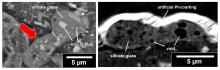
The Hayabusa2 mission that collected samples from the asteroid Ryugu has provided a treasure trove of insights into our solar system. After analyzing samples further, a team of researchers have unearthed evidence that cometary organic matter was transported from space to the near-Earth region.
29 Sep 2023
Observations during two flybys by the Mio spacecraft as part of the BepiColombo International Mercury Exploration Project have revealed that chorus waves occur quite locally in the dawn sector of Mercury. Mercury's magnetic field is about 1% of that of Earth, and it was unclear whether chorus waves would be generated like on Earth. The present study reveals that the chorus waves are the driving source of Mercury’s X-ray auroras, whose mechanism was not understood.
04 Aug 2023
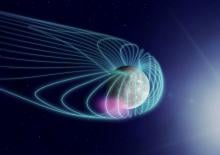
Tohoku University geophysicist Yuto Katoh led a study into the activity of high energy electrons and clarified the unexpected role of the geomagnetic field surrounding the Earth in protecting.
21 Mar 2023
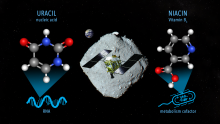
Samples from the asteroid Ryugu collected by the Hayabusa2 mission contain nitrogenous organic compounds, including the nucleobase uracil, which is a part of RNA.
28 Feb 2023
Researchers at Tohoku University have analyzed samples from asteroid Ryugu. They identified some of the oldest solids from the solar system to date, and their findings suggest that the asteroid initially formed in the outer reaches of the solar system.
13 Jan 2023
Understanding how dust grains form in interstellar gas could offer significant insights to astronomers and help materials scientists develop useful nanoparticles.
09 Dec 2021
Using data on electromagnetic (EM) waves and plasma particles measured simultaneously via multiple satellites, an international collaborative research group has discovered the existence of invisible “propagation path” of EM waves and elucidated the mechanism by which EM waves propagate to the ground.
10 Aug 2021
Researchers have developed a novel technique to investigate the dynamics of the early Solar System by analyzing magnetites in meteorites utilizing the wave nature of electrons.
06 Jul 2021
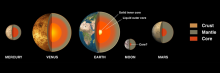
Tohoku University researchers have pinpointed the Sun’s early magnetic field as the reason behind variations in the rock and metal components in the four rocky planets’ cores: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
14 May 2021
Images from the Akatsuki spacecraft unveil why Venus’s atmosphere rotates much faster than its surface.
27 Sep 2020
Researchers have shaken up a once accepted timeline for cataclysmic events in the early solar system. Geological and geochemical records indicate that the Earth-Moon system experienced a period of frequent and cataclysmic impacts from asteroids and other bodies. It was thought that this period had a relatively sudden onset, but the researchers have found evidence that this bombardment period may have started much earlier, and decreased in intensity over time.
20 Feb 2020
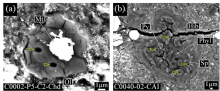
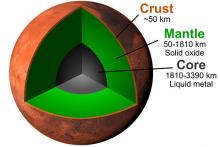
While InSight's seismometer has been patiently waiting for the next big marsquake to illuminate its interior and define its crust-mantle-core structure, two scientists, Takashi Yoshizaki and Bill McDonough have built a new compositional model for Mars. They used rocks from Mars and measurements from orbiting satellites to predict the depth to its core-mantle boundary, some 1,800 km beneath the surface and have been able to suggest that its core contains moderate amounts of sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen as light elements.
17 Dec 2018
A Japan-Spain team has developed a powerful 4-color simultaneous camera named MuSCAT2 for the 1.52-m Telescopio Carlos Sánchez at the Teide Observatory. The instrument aims to find transiting exoplanets, including Earth-like habitable planets orbiting stars near the Sun, in collaboration with NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite.
04 Dec 2018
An international team of astronomers using a combination of ground and space based telescopes have reported more than 100 extrasolar planets (here after, exoplanets) in only three months. These planets are quite diverse and expected to play a large role in developing the research field of exoplanets and life in the Universe.
12 Oct 2018
An international research team discovered the first recorded "ultra-stripped supernova," a rare, faint supernova that is believed to play a role in the formation of binary neutron star systems. These will advance our understanding of a variety of topics ranging from gravitational waves to the origin of precious metals like gold and platinum.
Events
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline
Researchers
Takeshi Horinouchi is a professor at the Faculty of Environmental Earth Science, Hokkaido University, Japan.
Giants in history
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline