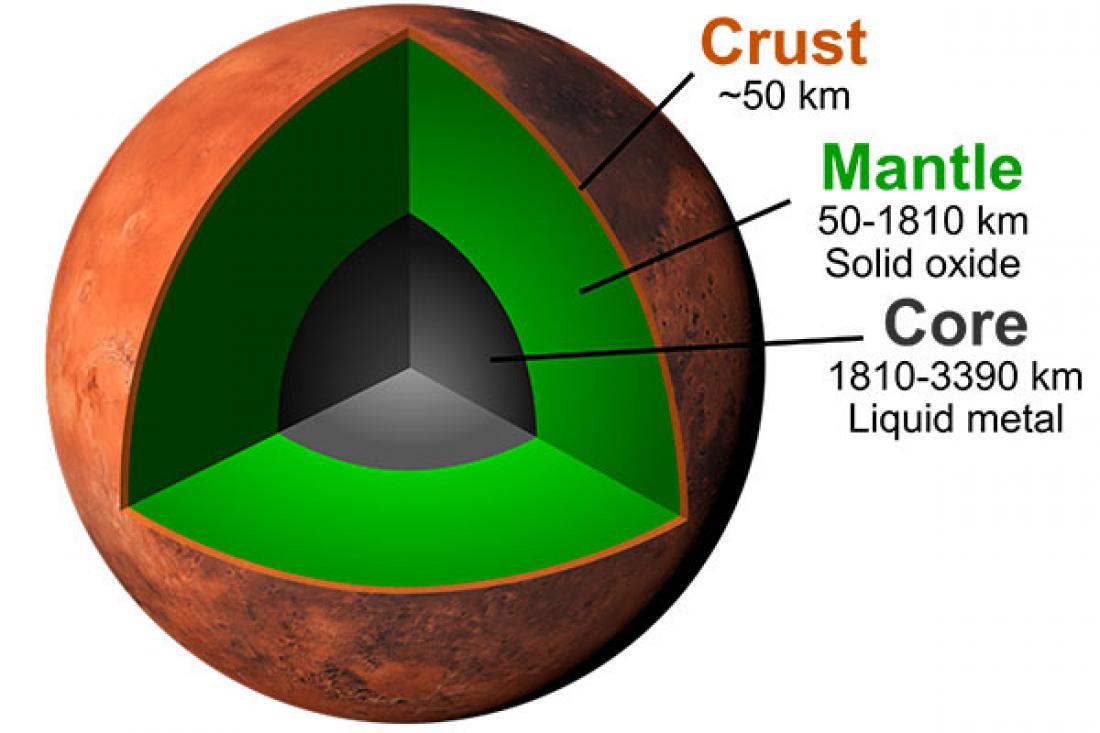
Interior structure of Mars
Yoshizaki explains, "Knowing the composition and interior structure of rocky planets tells us about formation conditions, how and when the core separated from the mantle, and the timing and amount of crust extracted from the mantle." Early astronomers used the separation distances and orbital periods of planets and their moons to determine the size, mass and density of these bodies. Today's orbiting spacecrafts provide greater details about a planet's shape and density, but the distribution of density in its interior has remained unknown. The seismic profile of a planet supplies this critical insight. When a quake rocks a planet, sound waves travel through its interior at speeds controlled by its internal composition and temperature. Strong contrasts in density, for example, rock versus steel, cause sound waves to respond differently, revealing the core-mantle boundary depth and details of the likely composition of these different layers.
By the end of the 19th century, scientists hypothesized a metallic core inside the Earth, but it was not until 1914 that seismologists demonstrated its existence at a depth of 2,900 km. Seismologists revealed the structure of the planet's interior, which helps us to locate sources and understand the nature of earthquakes. The 4 lunar seismometers brought by Apollo astronauts, defined the Moon's core-mantle-crust structure. Mars, the second-best explored planet, received in mid-2018 its first seismometer from the InSight mission.
Compositional models for a planet are developed by bringing together data from surface rocks, physical observations, and chondritic meteorites, the primitive building blocks of the planets. These meteorites are mixtures of rock and metal, like the planets, that are composed of solids accreted from the early solar nebula. Different proportions of oxides of magnesium, silicon and iron and alloys of iron and nickel make up these solids.
Yoshizaki adds that " we found that Mar's core is only about one-sixth of its mass, whereas for the Earth it is one-third of its mass." These findings are consistent with Mars having more oxygen atoms than Earth, a smaller core and a rusty red surface. They also found higher volatile element abundances, for example sulfur and potassium, in Mars than the Earth, but less of these elements than in the chondritic meteorites.
The seismometer on NASA's InSight mission will directly test this new model of Mars when it defines the depth to the Martian core-mantle boundary. Such compositional models for Mars and Earth provide clues to the origin and nature of planets and conditions for their habitability.
Contact:
Takashi Yoshizaki
Department of Earth Science, Graduate School of Science,
Tohoku University
Email: [email protected]