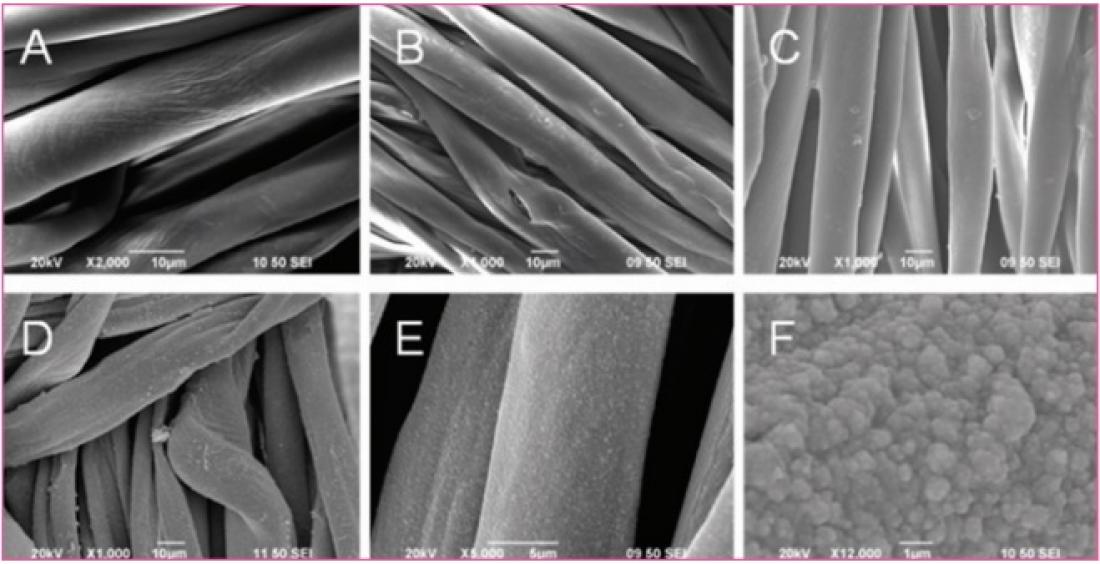
SEM images of the surface morphologies of cotton fiber with different modifications. (A) Pristine cotton. (B) VTMS-modified cotton. (C) PMANa-coated cotton. (D-F) Copper-coated cotton.
In this new method for preparing electrically conductive textiles, the textile surface is modified with a negativelycharged polyelectrolyte poly(methacrylic acid sodium salt) (PMANa) or poly(acrylic acid sodium salt) (PAANa) by in-situ free radical polymerization, and then treated with electroless metal deposition. The as-fabricated conductive textiles preserve robust mechanical and electrical stability under repeated cycles of rubbing, stretching and washing. They can be integrated into wearable electronics to replace the conventional rigid conductive electrodes and wires.
Special features and advantages
• The negatively charged polymer interfacial layer that bridged the deposited metal and the textile surface provides the metal layer with outstanding adhesion properties and good washing durability.
• The method is low cost (without expensive catalyst) and readily applicable to the industry to develop scale production of high performance conductive textiles.
Applications
• Flexible electronic interconnects, contacts and electrodes, especially for wearable electronics, smart textile and fashion
• EMI shielding, electrostatic discharge, thermal control materials
Awards
• Sliver Medal - 43rd International Exhibition of Inventions of Geneva, Switzerland (April 2015)
Principal Investigator
Dr Zijian ZHENG
Institute of Textiles and Clothing
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Contact Details
Institute for Entrepreneurship
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Tel: (852) 3400 2929 Fax: (852) 2333 2410 Email: [email protected]