Nature Biomedical Engineering
News
04 Dec 2023
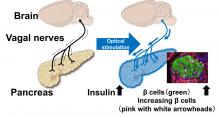
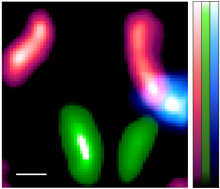
Decreasing pancreatic beta cell numbers – the only cells that produce insulin – is a leading cause of diabetes. In a promising development, a research group has revealed that stimulating autonomic vagal nerves connected to the pancreas can improve the function and also increase the number of pancreatic beta cells in mice.

08 Nov 2022
In a study recently published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering, researchers from Kanazawa University use a method called “lasso-grafting” to design therapeutics with enhanced longevity and brain penetration.
05 Apr 2022
Researchers have captured images of cells in mice using astronomy technology
11 Mar 2022
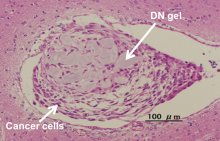
A soft hydrogel could help scientists find treatments for drug-resistant cancer stem cells.
13 May 2021
A spinning toy meets hydrodynamics and sets point-of-care diagnostics in motion.

03 May 2021
A research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) scientists recently developed a new generation of microneedles technology which allows the intradermal delivery of living cells in a minimally invasive manner. Their experiment showed that vaccination using therapeutic cells through this ground-breaking technology elicited robust immune responses against tumours in mice, paving the way for developing an easy-to-use cell therapy and other therapeutics against cancers and other diseases.
29 Mar 2021
A hydrogel, a type of soft matter, developed at Hokkaido University successfully reverted cancer cells back to cancer stem cells within 24 hours, in six different human cancer types. This could lead to the development of anti-cancer stem cell drugs and personalized medicines.
10 Jan 2020
An implantable device has the potential to revolutionize how neuroscientists study the brain and treat diseases.
10 Sep 2019
STAMP technology is a million times more sensitive and comprehensive to accurately detect and classify tumours from a small clinical sample
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.