PLOS Computational Biology
News
18 Oct 2022
Researchers develop a ground-breaking model to estimate bait vaccination effectiveness in wild animals based on the proportion of immunized animals in a population and the number of vaccine applications.
22 Sep 2022
Chaos theory improves understanding of Arctic narwhal behavior, with the aim of helping efforts to protect this vulnerable species.
20 Jun 2022
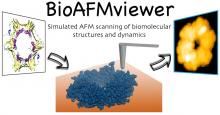
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) allows to visualize the dynamics of single biomolecules during their functional activity. All observations are, however, restricted to regions accessible by a fairly big probing tip during scanning. Hence, AFM images only the biomolecular surface with limited spatial resolution, missing important information required for a detailed understanding of the observed phenomena.
22 Dec 2020
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) allows to obtain images and movies showing proteins at work, however with limited resolution. The developed BioAFMviewer software opens the opportunity to use the enormous amount of available high-resolution protein data to better understand experiments. Within an interactive interface with rich functionality, the BioAFMviewer computationally emulates tip-scanning of any biomolecular structure to generate simulated AFM graphics and movies. They greatly help in the interpretation of e.g., high-speed AFM observations.

28 Jan 2020
In a recent study from Hiroshima University, researchers turned to mathematics to predict hive patterns in humans.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.