A group of researchers has recently unveiled a novel mechanism that leads to further suppression of thermal conductivity in thermoelectric materials, something that will help develop new guidelines for producing high-performance thermoelectric materials.
Details of their research were published in the journal Advanced Materials on December 17, 2022.
Controlling the ease with which heat is transmitted through a material, i.e., thermal conductivity, has a wide range of applications to our everyday lives: from insulating our homes, to improving the performance of electronic devices, as well as enhancing the energy conservation of automobiles and aviation and generating greater power efficiency.
Scientists are increasingly interested in thermal management technology as a means to solve various heat-related problems and to effectively utilize thermal energy.
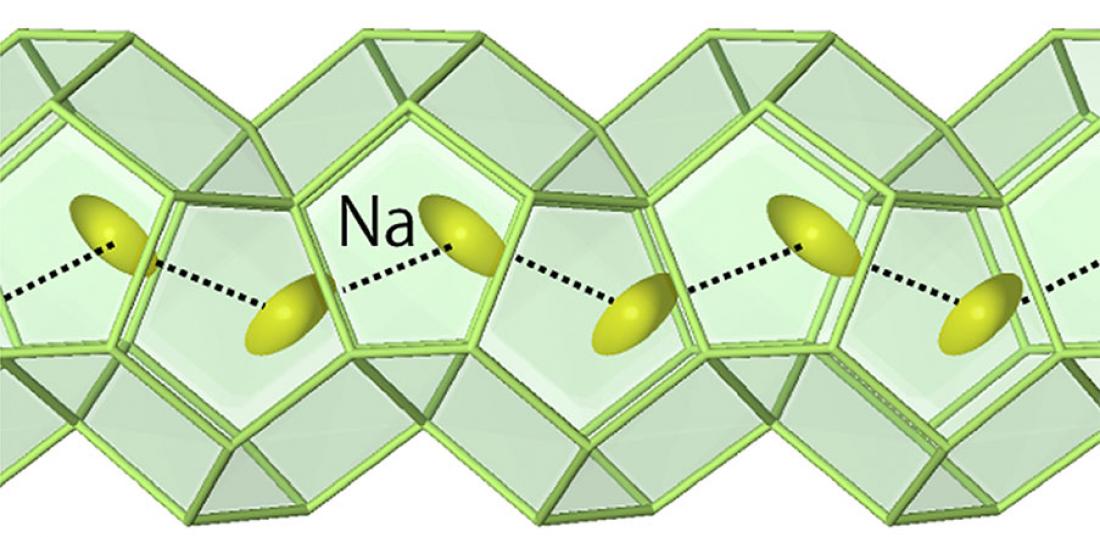
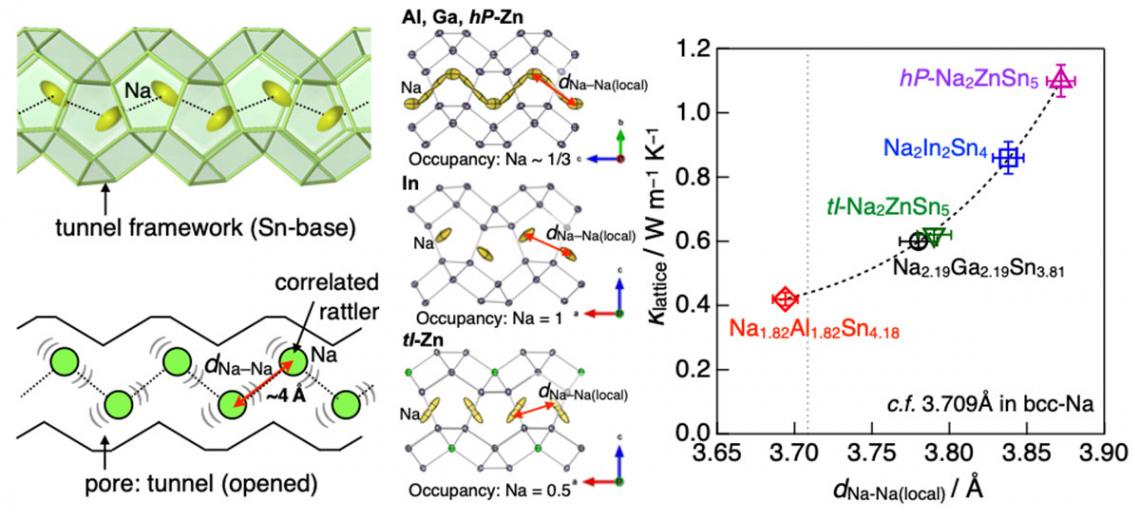
When the research group placed atomic chains into tunnel spaces within intermetallic compound crystal structures, the atoms strongly correlated with each other in large amplitude vibrations, or "rattling." Vigorous experiments and theoretical calculations demonstrated that the stronger the correlation between rattling atoms, the greater the decrease in thermal conductivity.
"Since advancements in thermoelectric materials require lower thermal conductivity, our discovery can provide new guidelines for engineering improved thermoelectric materials," states Takahiro Yamada, professor at Tohoku University's Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials (IMRAM) and co-author of the paper.
Also involved in the group was Professor Hisanori Yamane, also from IMRAM, Dr Masahiro Kanno from Tohoku University's Graduate School of Engineering (at the time of research), Professor Masato Yoshiya from Osaka University's Graduate School of Engineering, Associate Professor Hiroshi Takatsu and Professor Hiroshi Kageyama from Kyoto University's Graduate School of Engineering, Chief Senior Research Scientist Dr Takuji Ikeda from the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology's (AIST) Research Institute for Chemical Process Technology, and Senior Research Scientist Dr Hideaki Nagai from AIST's Research Institute for Energy Conservation.
A schematic diagram. In intermetallic compounds with tunnel spaces in the crystal structure (Na-X-Sn compounds, where X is Al, Ga, In, or Zn), Na atoms in the tunnel vibrate (rattling) with large amplitude along the elongation direction of the tunnel, and the local interatomic distance of these Na atoms. It was found that the lattice thermal conductivity decreases in compounds where the local interatomic distance (dNa-Na) of these Na atoms is closer. This is a new mechanism of thermal conductivity reduction caused by the strong correlation of the atomic chain-like rattling atoms in the tunnel with each other.