Medicine & Healthcare Dermatology
News
26 Mar 2024
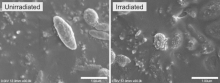
Numerical basis found for picosecond laser endpoints in effective clinical treatments with fewer complications
15 Mar 2024
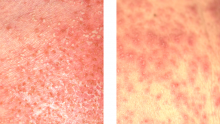
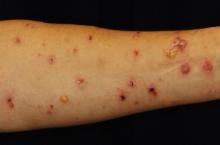
Two rare skin conditions with similar symptoms can be mistaken for each other, so a scoring system has been formulated to aid physicians in distinguishing two diseases
04 Sep 2023
Researchers from Osaka University have revealed that the expression of a specific isoform of GREB1 Is4 is induced in malignant melanoma cells by the melanocyte-specific transcription factor, MITF. They revealed that GREB1 Is4 stimulates pyrimidine biosynthesis and promotes cancer cell proliferation. Furthermore, the anti-tumor effect of antisense nucleic acids against GREB1 showed a potential new modality for malignant melanoma.
27 Mar 2023
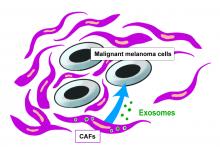
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are key factors in the tumor microenvironment, which have been implicated in cancer cell progression. It has also been reported that vesicles called exosomes produced by these CAFs play an important role in cancer progression. An Osaka Metropolitan University research group investigated the effect of CAF-derived exosomes on the growth of malignant melanoma cells. They found that CAF-derived exosomes express CD9 and CD63 transmembrane proteins, and that the CD9-positive exosomes may inhibit the growth of malignant melanoma cells.
14 Mar 2023
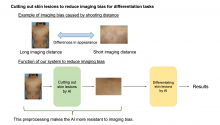
Atopic dermatitis skin lesions and the lesions produced by infectious complications of the disease look so similar that it makes it impossible for patients to spot the difference and know when to visit their doctor for treatment. But an AI-powered mobile app developed by dermatologists now puts the power of diagnosis in the hands of patients.
29 Jun 2022
The skin’s top layer contains a diverse set of hundreds of lipid molecules called ceramides with varying chain lengths that play a vital role in its barrier function.
23 Dec 2021
By searching for the protein transglutaminase 1 (TGM1) among patients with various autoimmune skin diseases, researchers have successfully identified a separate disease that
can be linked to autoimmunity against TGM1. This backward method
demonstrates a new way of identifying autoantigens as markers for various
diseases. By letting autoantigens point to the disease, diagnosis and
treatment can be facilitated, according to the study now published in PNAS.
27 Oct 2021
Researchers reveal correlation between ribotype (RT) strains of Cutibacterium acnes, which are found in human skin, and the lifespan of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Strains RT4 and 8, which are associated with acne in human skin, shortened the lifespan of the nematode, while RT6, which are predominantly found in healthy human skin, did not. Also, it was found that the healthy skin-related RT6 strain of C. acnes improved C. elegans resistance to the pathogenic organism Staphylococcus aureus.
14 Jun 2021
A team of scientists has shown that the healing of skin blisters is driven by hair follicle stem cells, which delay their own development in the process.
25 Mar 2021
Through a series of experiments using nasal polyp organ culture and mouse models of restraint stress, researchers unveil relationship between presence of corticotropin-releasing stress hormone and increase in and degranulation of allergy-causing mast cells.
20 Feb 2020
A faculty startup, based at South Korea's Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) has attracted 7 Billion KRW investment.

22 Jan 2018
A new method for controlling pigmentation in fabricated human skin has been developed by researchers from A*STAR’s Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology (SIMTech) and the Singapore Centre for 3D Printing (SC3DP) at Nanyang Technological University.
06 Dec 2017
Researchers have identified a type of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) that is associated with the skin disease bullous pemphigoid (BP) in diabetic patients administered with DPP-4 inhibitory drugs.
13 Jul 2017
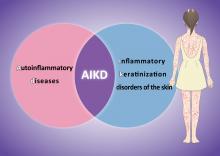
Nagoya University-led team reviews skin diseases to define a new type of genetic-based inflammation for improving diagnosis and treatment of rare skin conditions.
07 Jul 2017
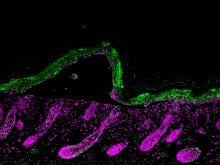
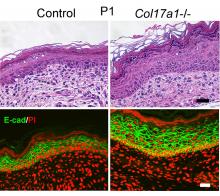
Type XVII collagen (COL17) is found to regulate the proliferation of epidermal cells and therefore the thickness of juvenile and aged skin, suggesting COL17 can potentially be used for future anti-aging strategies.
16 Jun 2017
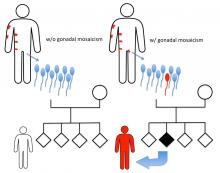
A Nagoya University research collaboration reveals the father–daughter inheritance of a mosaic skin disease as a sperm cell mutation causing a whole-body skin disorder: relevance to genetic counseling.

06 Jun 2017
Scientists in South Korea have come up with a new method for 3D printing human skin, which both shortens the process and reduces the cost.
Events
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline
Researchers
Dr. Ozawa is a Specially Appointed Professor at the Department of Dermatology, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka Metropolitan University (formerly Osaka City University). His specialized field is skin malignant tumor and surgery.
Takashi Hashimoto's major expertise is clinical and basic research for both autoimmune bullous diseases and hereditary skin diseases.
Giants in history
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline