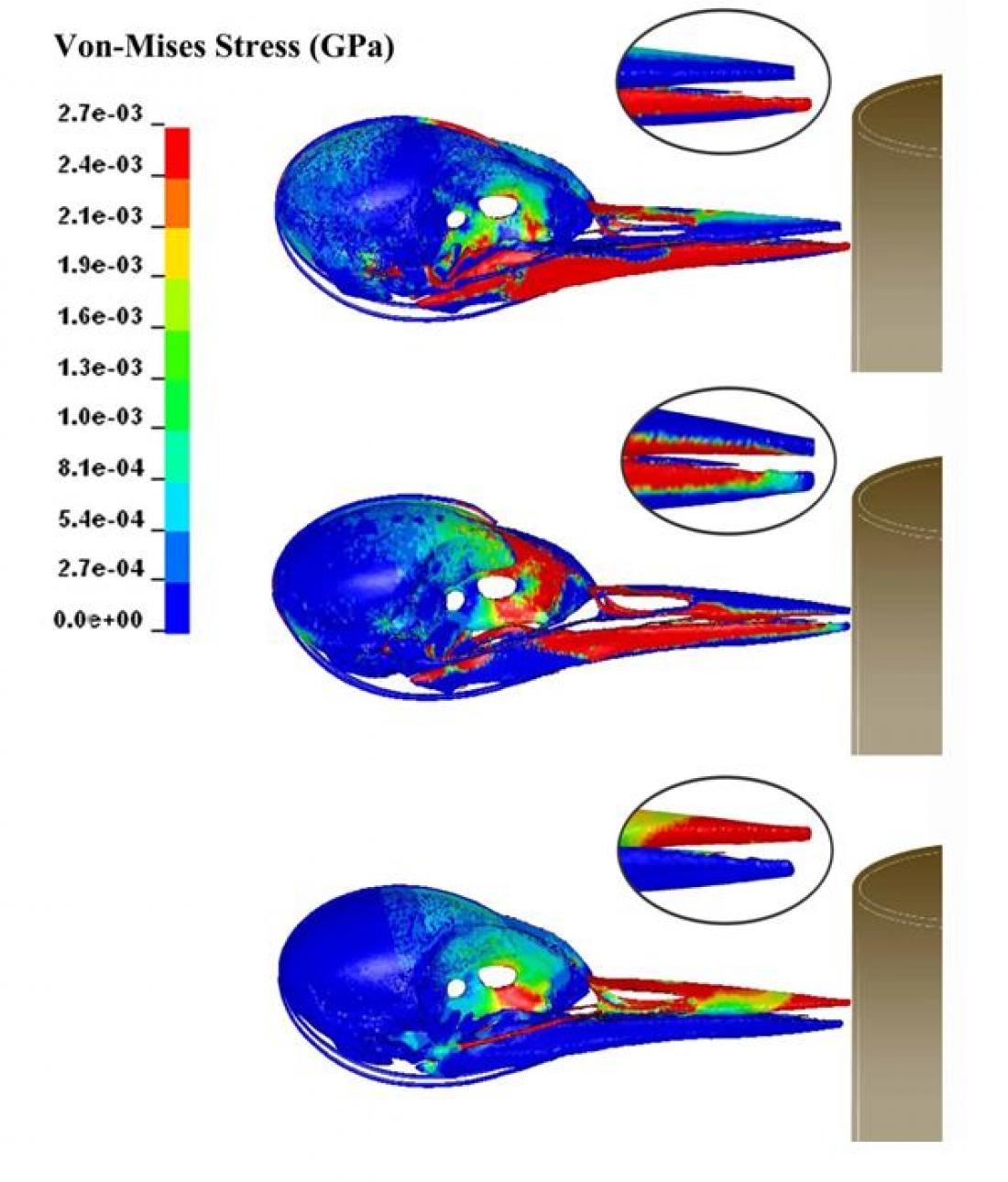
Comuptation models were developed by the researchers to show the stress distributions with different lengths of beaks.
A pioneering study by researchers of The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) and the Beihang University in Beijing has unravelled the mystery of why woodpeckers don't hurt themselves in the act of pecking on the trees. This finding is expected to provide fresh insights on the safety design of helmets and other related products.
The research was jointly led by Professor Ming Zhang of PolyU's Department of Health Technology and Informatics and Professor Yubo Fan of Beihang University. A series of experimental studies and computer simulation were conducted. Two synchronous high-speed video systems were used to observe the pecking motion, and a force sensor was used to measure the pecking force. The mechanical properties and macro/micro morphological structure in the woodpecker's head were investigated using a mechanical testing system and micro-CT scanning. Computational models of the woodpecker's head were established to study the dynamic intracranial responses.
Based on the result of this study, the research team has come up with answers on why the repeated daily head-banging motion of woodpeckers does not sustain any brain injury. The experimental data and simulation showed that three factors are at work in sparing the injury.
Firstly, the skulls of woodpeckers are protected by hyoid bone's looping structures which acts as a kind of "safety belt". Secondly, the upper and lower halves of the birds' beaks are uneven in length - this asymmetry lowers the impact of pecking force transmitted from the tip of the beak onto the brain. Last but not least, the "spongy" bone structure at different points in the skull helps distribute the incoming force, thereby protecting the brain.
The team says it's the combination of these three features that allows woodpeckers to peck without injury. It is anticipated that more quantitative studies will take place before applying the bio-mechanism to human protective device design and probably industry design.
The study was published in the online edition of PloS ONE journal.
Press Contacts
Professor Ming Zhang
Department of Health Technology and Informatics
Tel: (852) 2766 4939
Email: [email protected]