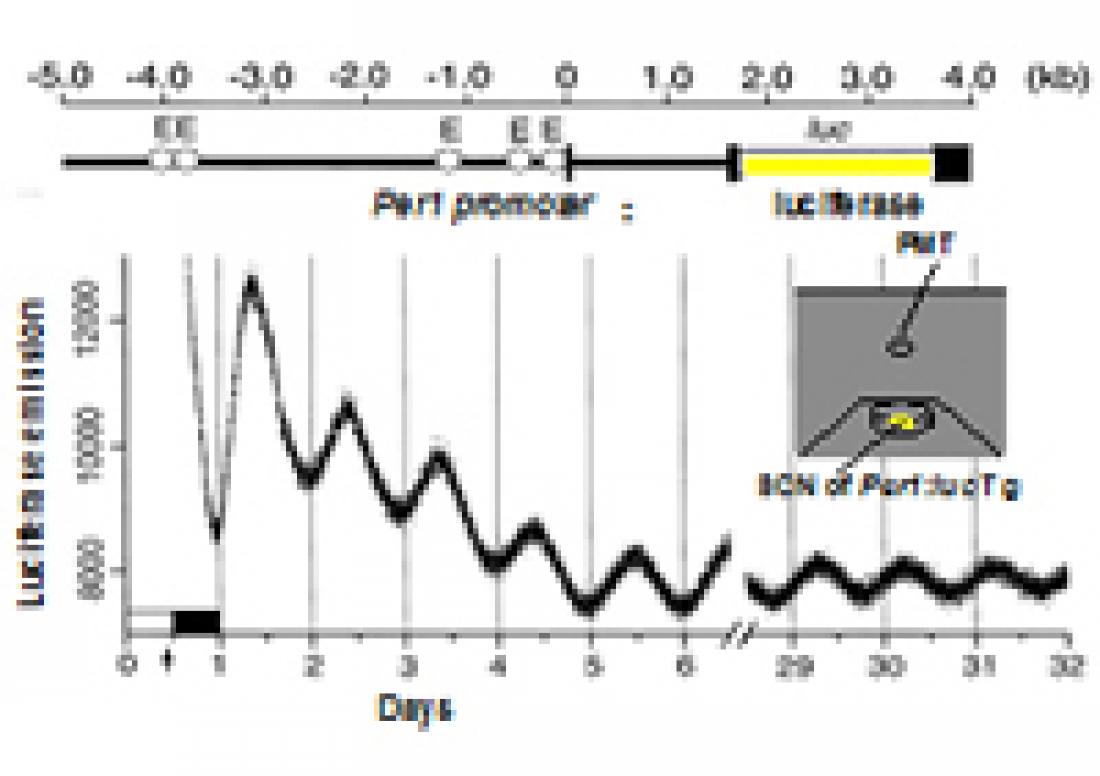
Rhythmic emission in the SCN of Per1:luc Tg rats
Human biochemical processes are controlled by internal body clocks with an approximately 24 h period—circadian rhythms. In mammals, the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) contains self-sustained circadian oscillator as master pacemakers. The expression of clock gene Period1 (Per1) oscillates autonomously in the SCN and is induced immediately after a light pulse. Per1 is an indispensable member of the central clock system, since the constitutive expression of Per1 in the SCN modifies physiological and behavioral rhythms [1]. The SCN and peripheral tissues are compared about the ability of phase shift using realtime monitoring system from same animal.
Now, Shin Yamazaki, Rika Numano, Michikazu Abe and colleagues at University of Virginia and University of Tokyo constructed Per1:luc Tg rats in which firefly luciferase was rhythmically expressed under the control of the mouse Per1 promoter [2].
Rhythmic emission from the cultured Per1:luc SCN slices persisted for some months in vitro, while those from peripheral tissues such as the liver damped after two to seven cycles. These results show that a self-sustained circadian pacemaker in the SCN entrains circadian oscillators in the periphery.
Next, the researchers compared the phase shift ability of light and dark (LD) cycles between the SCN and peripheral tissues. The phase-shifting paradigm is closely analogous to trans-Atlantic flights from west to east (6 h advance) and from east to west (6 h delay).
The emissional rhythms in the SCN shifted 6 h most rapidly within one day, while those in peripheral tissues took more than two days. Circadian oscillators in the periphery were temporarily lost following large and abrupt shifts in the environmental light cycle.
Notably, jetlag can be explained as a condition where the rhythms in the SCN and peripheral tissues are desynchronized.
[1] Rika Numano et.al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A, 103, 3716, (2006)
[2] Shin Yamazaki1*, Rika Numano2*, Michikazu Abe1*, Akiko Hida2, Ri-ichi Takahashi3, Masatsugu Ueda3, Gene D. Block1, Yoshiyuki Sakaki2, Michael Menaker1, Hajime Tei2 *These authors contributed equally to this work.
Resetting central and peripheral circadian oscillators in transgenic rats.
Science, 288, 682, (2000).
DOI: 10.1126/science.288.5466.682
1NSF Center, Univ. of Virginia, 2Inst. of Medical Science, Univ. of Tokyo,3Y.S. New Technology Institute Inc.