Peer Reviewed
News
27 Oct 2023
- A research team led by Professor Jong-min Choi at the Department of Energy Science and Engineering, DGIST, has successfully developed stable quantum dot thin films, which can improve efficiency and stability in perovskite quantum dot solar cells.
- Suggests a new quantum dot surface stabilization strategy based on a non-polar solvent and covalent ligands
27 Oct 2023
- This educational institution held a ceremony at the DGIST Convention Hall on September 6 to commemorate the 19th anniversary of its foundation.
27 Oct 2023
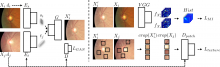
- The developed image translation model can yield accurate classification results despite the use of biased data for the training of a deep learning model.
- This solution is expected to be applied in various fields, such as self-driving, content creation, and medicine.
27 Oct 2023
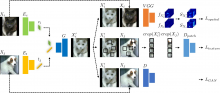
- This team developed the PAINT technology that controls the adhesive properties of new organic materials, analyzes melanin formation processes, and facilitates selective melanin formation.
- A research paper on the technology, which fabricates local patterns based on melanin-like pigments, was published in Nature Communications, an international academic journal.
26 Oct 2023
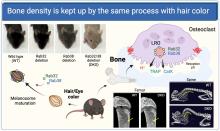
Research out of Osaka University finds an overlap in the mechanism of hair color determination and bone resorption, which is associated with bone related diseases like osteoporosis. The findings revealed that proteins named Rab32 and Rab38 play pivotal roles in bone resorption in osteoclast, cell specialized in the process. These proteins are also crucial for pigmentation of hair and skins.
26 Oct 2023
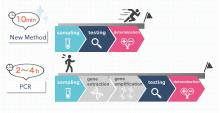
Research from Osaka University demonstrates a nanopore-based technique that can detect different variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. The method was very effective in detecting the Omicron variant of the virus in the saliva of people with COVID-19.
25 Oct 2023
Pair-bonded Java sparrows show enlarged eye rings to signal breeding readiness.
24 Oct 2023
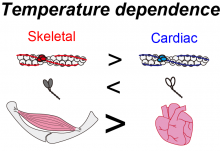
Research out of Osaka University investigated the effect of increased cell temperature on the contractility of skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle by heating the muscle proteins using advanced microscopical techniques. The findings indicated that skeletal muscle is more sensitive to increases in temperature than cardiac muscle, and that heating can rapidly activate the contractile proteins of skeletal muscle, thereby improving muscle performance.
24 Oct 2023
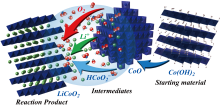
Layered lithium cobalt oxide, a key component of lithium-ion batteries, has been synthesized at temperatures as low as 300°C and durations as short as 30 minutes.
20 Oct 2023
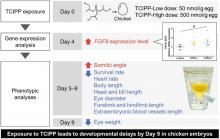
Evaluation of developmental toxicity in early chicken embryos exposed to tris(2-chloroisopropyl) phosphate

20 Oct 2023
This study examined how the origin (wild or hatchery-reared), feeding area (Baltic Sea mainstem, Bosnian Sea, and Gulf of Finland), and organic halogen compound (OHC) concentrations of Baltic Sea Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) affect the salmon liver proteome, transcriptome, and oxidative stress markers. Results suggest that the Baltic salmon liver proteome, together with the transcriptome, is influenced more by OHC concentrations and oxidative stress levels in the feeding area than by their origin.
20 Oct 2023
Structural characteristics of environmental pollutants and computer simulations predict effects on the endocrine system of seals
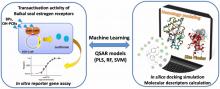
20 Oct 2023
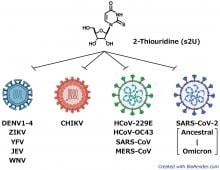
A broad-spectrum antiviral drug candidate, 2-thiouridine, that targets positive-strand RNA viruses has been identified and characterized.
20 Oct 2023
A research team from Osaka Metropolitan University has found that polysulfides are abundant in broccoli sprouts. They found that the amount of polysulfides increased dramatically during growth, by an approximately 20-fold in seeds by the fifth day of germination. Furthermore, a comprehensive analysis of the polysulfides detected a number of polysulfide candidates whose structures have not yet been determined. The identification of these unknown polysulfides and detailed analysis of their pharmacological activities are expected to enable the development of new preventive and therapeutic strategies and medicines for cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, inflammation, and other diseases.
20 Oct 2023
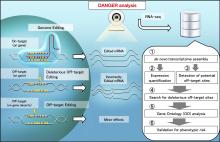
Risk-averse on/off-target assessment for CRISPR editing without reference genome
20 Oct 2023
New perspective argues pursuing fair AI for healthcare requires cross-disciplinary collaboration to translate methods into real-world benefits.
16 Oct 2023
New research reveals how disrupted energy production in the kidneys contributes to progressive kidney disease in diabetes.
16 Oct 2023
The latest ‘large language model’ artificial intelligence system, GPT-4, could aid chemistry researchers, but limitations reveal the need for improvements.
16 Oct 2023
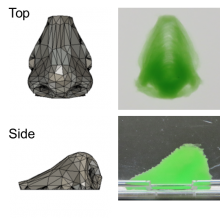
Researchers from Osaka University developed a cell-friendly means of bioprinting at high fidelity. By successive injection of a cell-based ink and a printing support, the ink solidified into defined geometries, even into the shape of a human nose. Printed cells remained viable for at least two weeks. This work is an important milestone toward developing lab-grown tissues and organs, and eventually advancing regenerative medicine as well as animal-free drug safety testing.
13 Oct 2023
A new amphipod species thrives at record temperatures in nearby hot spring pools of an ancient Inca city, defying norms for these typically cold-dwelling animals. Unraveling its key adaptations can give clues for the survival of other freshwater creatures in our warming world.
12 Oct 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists, in cooperation with researchers from the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, have captured cosmic-ray extensive air showers with unprecedented precision using the prime-focus wide field camera mounted on the Subaru Telescope, situated atop Mauna Kea in Hawaii. Analyzing approximately 17,000 images captured between 2014 and 2020, they pinpointed 13 images containing extensive air showers, with a number of particle tracks far exceeding the usual count.
12 Oct 2023
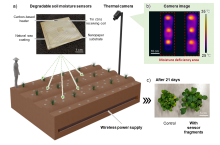
Researchers from Osaka University developed wirelessly powered soil moisture sensing technology that will help meet the needs of sustainable precision agriculture. Both the soil moisture content and the position of each sensor are readily detected and transmitted, even at high sensor densities. The sensors are largely biodegradable and can be tilled into the soil at the end of the crop season. This work might help farmers allocate resources to cropland in a timely, targeted manner.
12 Oct 2023
Researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, synthesize a two-center zinc complex that absorbs visible light as a solid and in solution.
11 Oct 2023
In a recent publication in EPJ Quantum Technology, Le Bin Ho from Tohoku University’s Frontier Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences has developed a technique called "Time-dependent Stochastic Parameter Shift" in the realm of quantum computing and quantum machine learning. This breakthrough method revolutionizes the estimation of gradients or derivatives of functions, a crucial step in many computational tasks.
11 Oct 2023
A research team led by Osaka University developed a theranostics approach to both diagnose and treat certain pancreatic cancer cases. They radioactively labeled a monoclonal antibody targeting glypican-1, which is highly expressed in pancreatic cancer, then administered it to disease model mice. One label, 89Zr, showed high uptake in tumors, which would allow early detection of pancreatic cancer with PET scans. Another label, 211At, was used with alpha therapy to significantly slow tumor growth.
11 Oct 2023
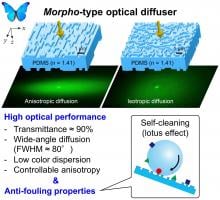
Researchers at Osaka University developed a nanostructured light diffuser that provides balanced lighting by diffracting blue and red light, and can be cleaned by simple rinsing with water. The diffuser consists of cheap materials and can be shaped with common tools. A protective glass coating maintains the diffuser’s optical performance yet adds durability. This work might improve the visual performance of everyday lighting displays.
11 Oct 2023
The International Symposium on Triglyceride/Neutral Lipid and Rare Diseases will be held at the Kyoto International Conference Center on October 21 and 22, 2023. The symposium is organized by the International Symposium on Triglyceride/Neutral Lipid and Rare Diseases Conference Committee, which is led by Dr. Ken-ichi Hirano (Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University) and the Japan Intractable Diseases (Nanbyo) Research Foundation.
10 Oct 2023
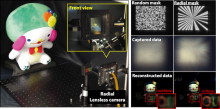
To extend the depth of field in mask-based lensless cameras, researchers from Osaka University replaced conventionally coded masks with a radial-coded mask optimized to balance the frequency response. As a result, the point spread function depends less on distance, and subjects at various depths can be clearly imaged. Experiments in simulation and on a prototype show that the depth of field of the camera is extended when the proposed radial mask is used.
05 Oct 2023
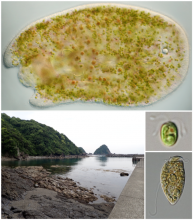
Acoels have been found to host a wide diversity of symbiotic, photosynthetic microalgae.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.