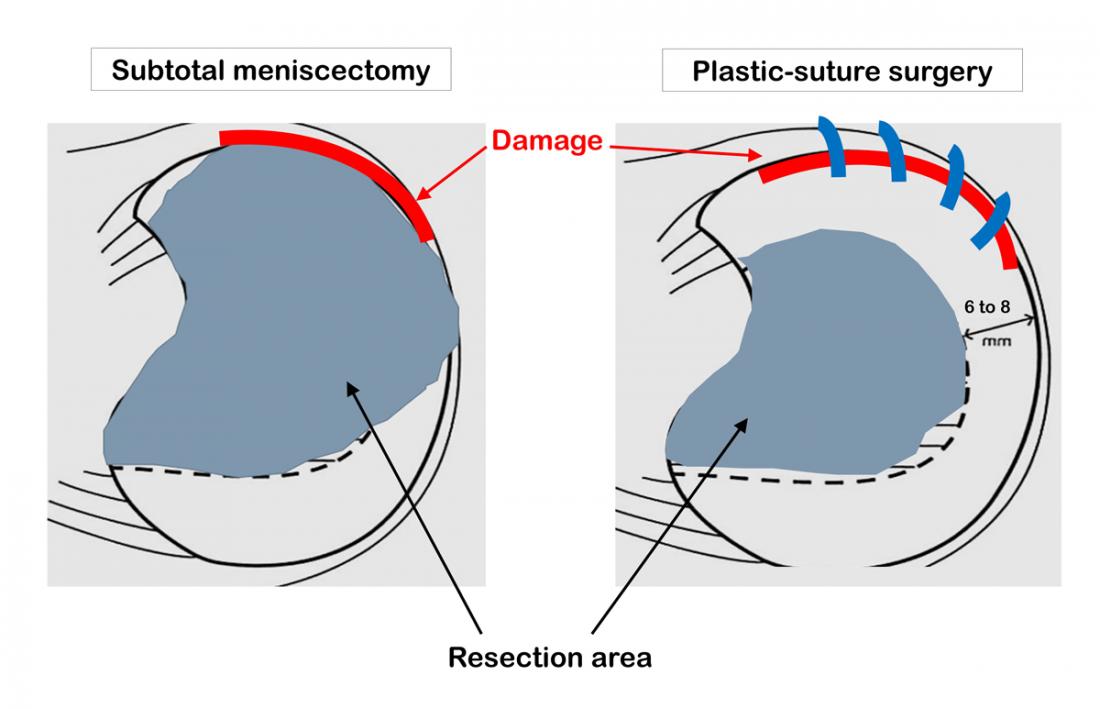
Surgical procedures for repairing a meniscus showing the resection area and tear (red). Left: subtotal resection to remove the damaged portion. Right: plastic suture to repair the tear and allow the meniscus to retain its normal shape.
Osaka, Japan― Tearing their meniscus—a crescent-shaped piece of a soft cushion of cartilage located between the femur and tibia—can be devastating for young athletes. It is easily damaged in people with congenital lateral discoid meniscus or those that are physically active and once damaged, the meniscus cannot repair itself. The most common method has been to remove the damaged portion of the meniscus, but in recent years meniscus-sparing surgeries, that suture the margins of the meniscus at the tear, have begun to spread.
Researchers led by Lecturer Yusuke Hashimoto, and Professor Hiroaki Nakamura, from Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Medicine, conducted a 5-year study of cartilage degeneration, following up on 41 young patients (initially aged 15 or younger), with lateral disc meniscus injuries who received different treatments. The subtotal resection group, where more than half of the meniscus was removed; and the plastic suture group, in which the torn margin of the meniscus was sutured leading to a smaller resection.
The researchers observed that subtotal meniscectomies were more likely to progress cartilage degeneration, the worst being when the posterior segment was dissected for those with lateral disc meniscus injuries. In addition, they found that in younger patients, even if there was more damage to the meniscus, preserving the meniscus with sutures was more effective in protecting cartilage from future damage.
“By performing surgical procedures to preserve the meniscus as much as possible, we found that it is important—especially in the posterior segment—to preserve knee function to prevent the progression of age-related cartilage degeneration. In the future, we would like to promote the use of surgical techniques that preserve the posterior segment,” concluded Dr. Hashimoto.
The results were published in the Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established in April 2022, formed by merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University. For more research news visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow @OsakaMetUniv_en and #OMUScience.