Differences in surface air temperatures (in June–August) between the 1980s and 2000s. The summer temperatures steeply rose in Europe and Northeast Asia, while the margin of the temperature rise in Western Russia is minor, showing a heterogeneous pattern of temperature changes from the east to west. (Sato T. and Nakamura T., Scientific Reports, July 26, 2019)
Persistent abnormally hot weather can cause negative impacts on human health, agriculture, and natural environments. A heat wave — a spell of hot days with the mercury rising much higher than the average temperature — has been reported more frequently in Europe and Northeast Asia in recent years.
“Internal atmosphere–land interactions in Eurasia are believed to be an important factor in triggering abnormal summer temperatures. However, the exact reasons for such interactions causing heat waves remain largely unclear,” says Associate Professor Tomonori Sato of the research team.
In the present study published in Scientific Reports, Tomonori Sato and Tetsu Nakamura of Hokkaido University examined a large dataset derived from the “database for Policy Decision making for Future climate change” (d4PDF). The database comprises data spanning over a 60-year period (1951–2010) which incorporates observed sea surface temperature, sea ice, and natural and anthropogenic forcing.
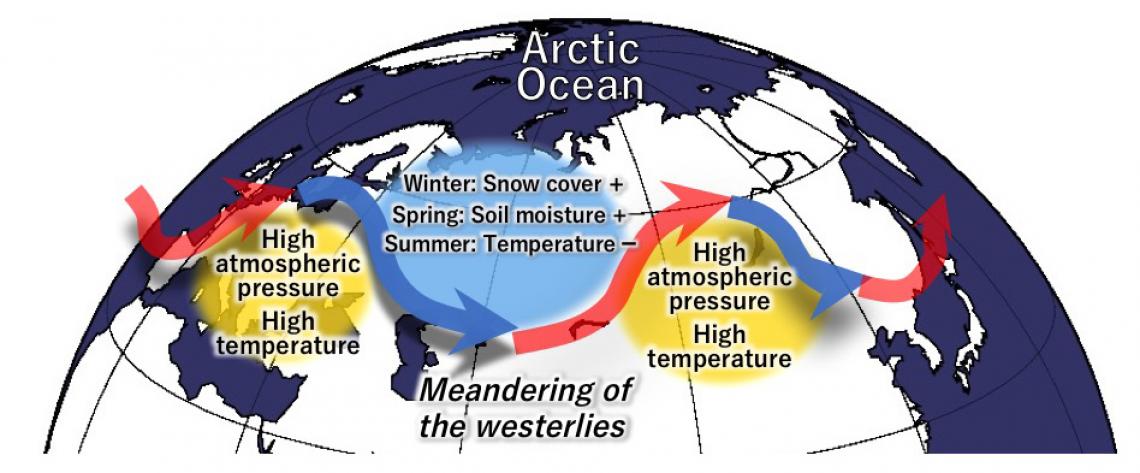
More snow cover in winter will be reflected in the level of moisture in the soil in spring, which will cause lower summer temperatures. The low summer temperatures will facilitate the meandering of the westerlies, which tend to cause high temperatures in the surrounding regions.
The researchers analyzed 6,000 patterns in the spatial distribution of summer temperatures in Eurasia, and succeeded in dividing past summer temperature variations into two groups—one attributable to global warming and the other attributable to natural changes. The former exhibited the rising temperatures in Eurasia since around 1990, while the latter showed the spatial distribution of low and high temperatures that correspond to the meandering of the westerlies. The distribution shows a wave train-like structure – which demonstrates that when some regions experienced abnormally high temperatures, the surrounding areas were hit by abnormally low temperatures.
The researchers then discovered that when Western Russia had a deeper-than-usual snow cover in late winter and spring, the wave train-like distribution of temperatures appeared. When deeper snow accumulation occurs, more moisture retains in the soil after snowmelt. The soil moisture then prevents the summer temperature from rising, which is a likely cause for making the westerlies meander, thus causing the surrounding regions to experience high temperatures.
“Our finding could help improve the accuracy of summer weather forecasting and help mitigate the adverse impacts from abnormal weather in the future,” says Tomonori Sato.
Tetsu Nakamura (left) and Tomonori Sato (right) of Hokkaido University.
Contacts:
Associate Professor Tomonori Sato
Graduate School of Environmental Science
Hokkaido University
Email: t_sato[at]ees.hokudai.ac.jp
Tetsu Nakamura (Ph.D. researcher)
Graduate School of Environmental Science
Hokkaido University
Email: nakamura.tetsu[at]ees.hokudai.ac.jp
Naoki Namba (Media Officer)
Institute for International Collaboration
Hokkaido University
Tel: +81-11-706-2185
Email: en-press[at]oia.hokudai.ac.jp