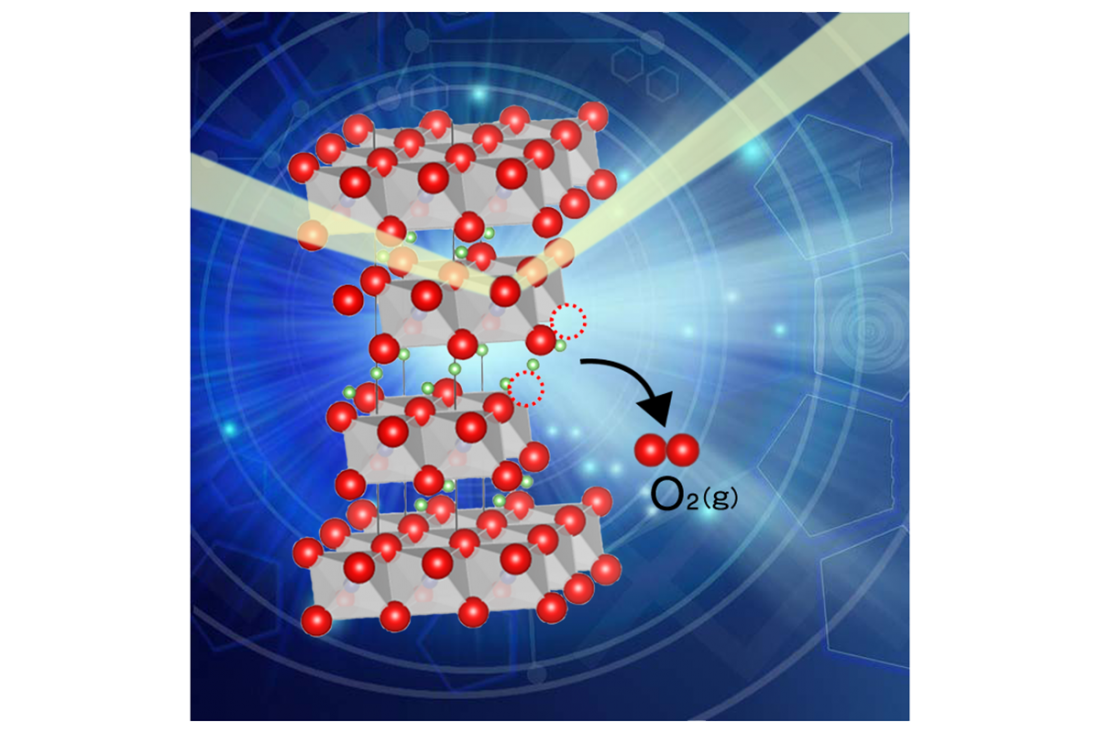
Oxygen release from battery materials which can cause thermal runaway.
A research group has produced fresh insights about the release of oxygen in lithium-ion batteries, paving the way for more robust and safer high-energy-density batteries.
Next-generation batteries that store more energy are critical if society is to achieve the UN's Sustainable Development Goals and realize carbon neutrality. However, the higher the energy density, the higher the likelihood of thermal runaway - the overheating of batteries that can sometimes result in a battery exploding.
Oxygen released from cathode active material is a trigger for thermal runaway, yet our knowledge of this process is insufficient.
Researchers from Tohoku University and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) investigated the oxygen release behavior and relating structural changes of cathode material for lithium-ion batteries LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 (NCM111). NCM111 acted as a model oxide-based battery material through coulometric titration and X-ray diffractions.
The researchers discovered NCM111 accepts 5 mol% of oxygen release without decomposing and that oxygen release induced structural disordering, the exchange of Li and Ni.
When oxygen is released, it reduces the transition metals (Ni, Co and Mn in NCM111), lessening their ability to keep a balanced charge in the materials.
To evaluate this, the research group utilized soft-Xray absorption spectroscopy at BL27SU SPring-8 - a JASRI operated large-scale synchrotron radiation facility in Japan.
They observed selective Ni3+ reduction in NCM111 at the beginning stage of oxygen release. After the Ni reduction finished, Co3+ decreased, while Mn4+ remained invariant during 5 mol% of oxygen release.
"The reduction behaviors strongly suggest that high valent NI (Ni3+) enhances oxygen release significantly," said Takashi Nakamura, coauthor of the paper.
To test this hypothesis, Nakamura and his colleagues prepared modified NCM111 containing more Ni3+ than the original NCM111. To their surprise, they discovered the NCM111 exhibited much severer oxygen release than expected.
Based on this, the research group proposed that the high valent transition metals destabilize lattice oxygen in oxide-based battery materials.
"Our findings will contribute to the further development of high energy density and robust next-generation batteries composed of transition metal oxides," said Nakamura.
Contact:
Takashi Nakamura
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials (IMRAM), Tohoku University
Email: takashi.nakamura.e3@tohoku.ac.jp