Fig.1
Selective formose reaction under microwave irradiation
Researchers from Osaka University have used environmentally friendly chemistry to selectively produce sugars from formaldehyde. This work will help minimize use of fossil resources in industrial chemicals production
Osaka, Japan – Much of what the chemicals industry produces, except for metals, is derived from fossil resources. Using renewable biomass and even one-carbon sources—such as formaldehyde—is necessary to increase the sustainability of the chemicals industry.
In a study recently published in RSC Advances, researchers from Osaka University have used microwave irradiation to increase the suitability of the formose reaction as a source of precursors for industrial chemicals production.
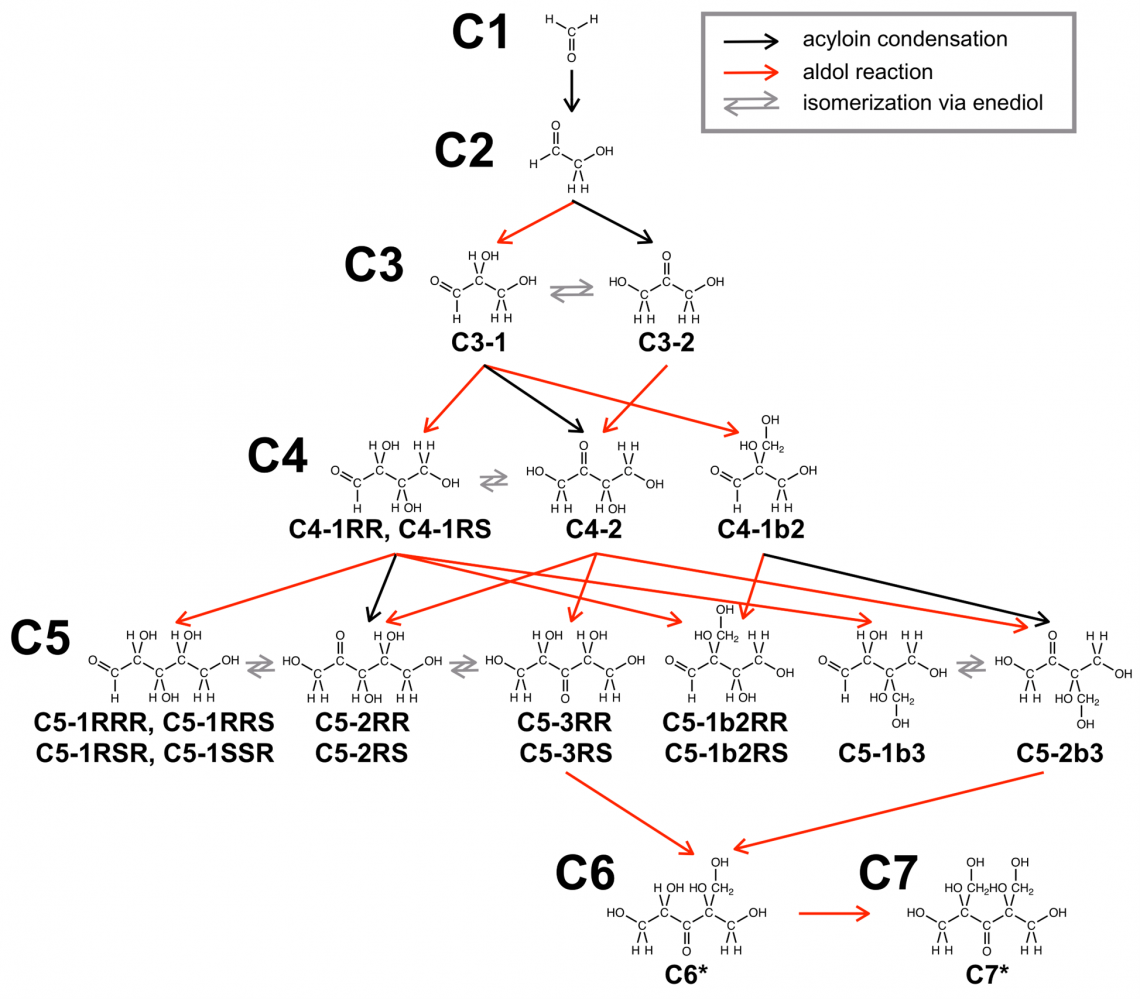
A classic chemical synthesis from formaldehyde is the formose reaction, which produces a complex mixture of sugars and sugar alcohols. Complex product mixtures aren't necessarily useful for chemists, who often need a pure substance, e.g., a single sugar, for subsequent chemical reactions. There are few reports of using the formose reaction to produce pure sugars or sugar alcohols that contain a large number—e.g., six or more—of carbon atoms. There are no reports that clearly describe doing so using microwave irradiation, a common and environmentally friendly means of speeding up and increasing the selectivity of chemical reactions. Using microwave irradiation to enhance the utility of the formose reaction in the chemicals industry is the goal that the researchers sought to achieve.
"The chemicals industry has a sustainability problem, and using formaldehyde as a chemical synthesis precursor can help solve this problem," explains Akihito Hashidzume, lead author of the study. "Our updates to the formose reaction add substantial value to its utility in subsequent chemical syntheses."
The researchers are the first to report the outcome of when a formaldehyde solution reactant and calcium hydroxide catalyst are exposed to 1 minute of microwave irradiation at 150°C. Five milliliters of reactant was converted into a mixture consisting of two sugars: one containing six carbons (hexose) and the other containing seven carbon atoms (heptose). Without decomposition into smaller products, the reaction yield was nearly 100%.
"We hypothesize that the formose reaction in our system proceeds substantially on the surface of calcium hydroxide crystallites in the reaction mixture," says Hashidzume. "Given that the formose reaction can also proceed on mineral or meteorite surfaces, our work also has intriguing possible implications for understanding the prebiotic synthesis of sugars."
This work succeeded in expanding the utility of the formose reaction for the chemicals industry, speeding up the reaction and producing a mixture of only two products that can be readily purified. The straightforward reaction design reported here will help researchers improve the sustainability of chemical feedstock production, which will prove invaluable if scaling up to larger reaction volumes can be achieved.
###
The article, “Preferential formation of specific hexose and heptose in the formose reaction under microwave irradiation,” was published in RSC Advances at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra07249a
Fig.2
Plausible reaction pathways for the selective formose reaction
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en