Hokkaido University researchers have devised a unique approach for making nanosized semiconductors on a metal surface. The details of the method were reported in the journal Nano Letters and could further research into the fabrication of nanosized light and energy emitters.
The approach, developed by Hokkaido University’s Research Institute for Electronic Science and Hokkai-Gakuen University, involves generating localized heat on a gold nanoparticle within a butterfly-shaped nanostructure. The heat causes hydrothermal synthesis in which semiconducting zinc oxide crystallizes on the gold nanoparticle.
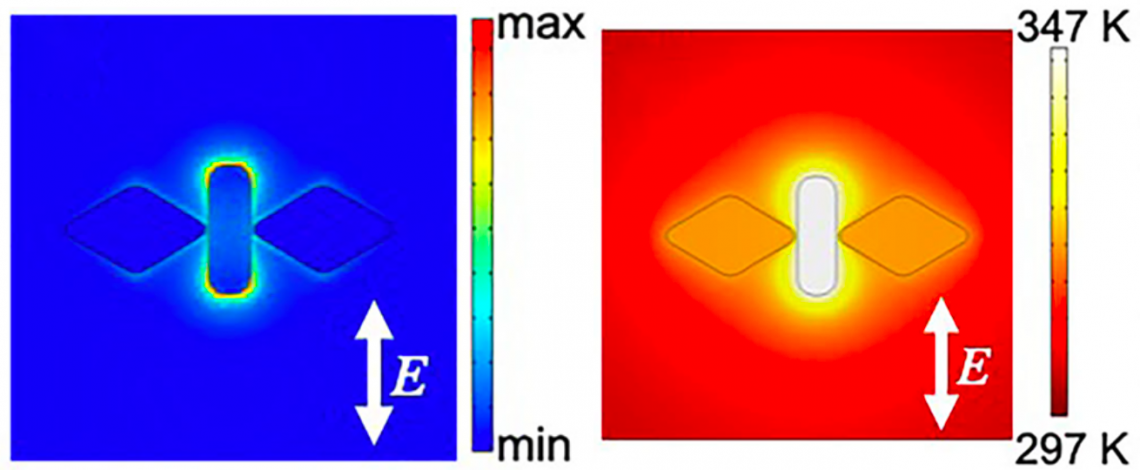
Calculated localized field (left) and temperature distribution (right) of the nano-butterfly structure.
Scientists have been investigating ways to carefully place nano-sized semiconductors on metallic particles to utilize them in nano-lasing and nano-lithography, for example. But current methods lack precision or are too costly.
The approach developed by the Japanese team overcomes these issues.
The team first conducted simulations to determine the optimal conditions for precisely controlling the generation of heat in nanostructures. They utilized a phenomenon called surface plasmon resonance, a process which partly converts light to heat in metallic materials.
According to the simulations, a butterfly-shaped nanostructure consisting of two rhombus gold particles placed on either side of a gold nanorod would lead to optimal conditions. In this system, the nanorod, or the body of the butterfly, works as a nanoheater using a specific polarized light. After rotating the light polarization 90 degrees, the rhombus particles, or the wings of the butterfly, should work as an antenna to gather light at subwavelength spots in the butterfly’s semiconductor skin.
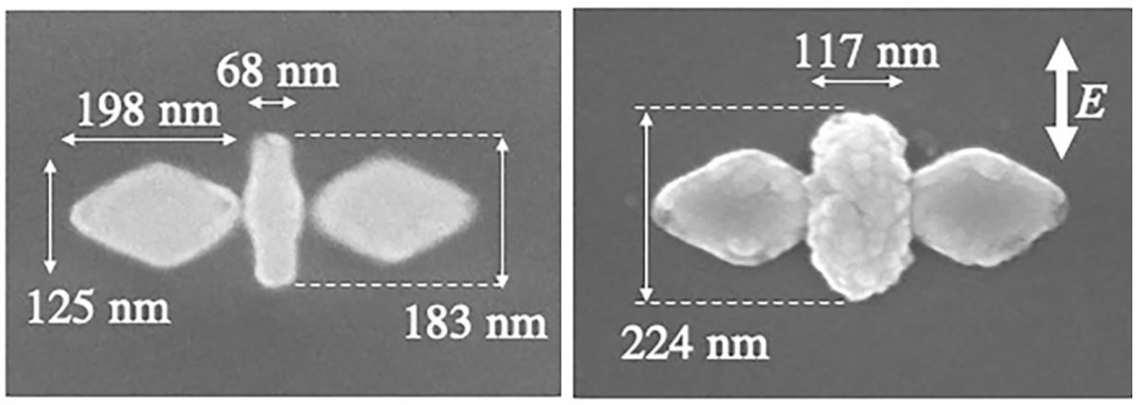
To test this theory, they fabricated the gold butterfly and placed it in water inside a glass chamber. A solution made from equal parts zinc nitrate hexahydrate and hexamethylene tetramine was added to the chamber, which was then sealed and placed on a microscopic stage. When the laser light was shone on the system inside the chamber, the nanorod heated up and semiconducting zinc oxide particles crystallized along its surface as they expected.
This demonstrated that the butterfly-shaped gold nano-antenna can precisely control where plasmon-assisted hydrothermal synthesis occurs, therefore enabling the localized formation of nanosized semiconductors.
Scanning electron microscope images of the nano-butterfly structure before (left) and after (right) laser irradiation. Semiconductor zinc oxide has crystalized on the surface of the gold nanorod.
“Further research is expected to lead to the development of powerful nano-sized light sources, highly efficient photoelectric conversion devices, and photocatalysts,” says Hokkaido University’s Keiji Sasaki of the research team. “It could also lead to applications in semiconductor electronics and optical quantum information processing.”