"In the pancreas, the Kir6.2 channel blockade increases the insulin signaling, and insulin signaling decreases the blood glucose levels," says Dr. Shigeki Moriguchi. "In the brain, insulin signaling increases the acquisition of memory through CaM kinase II activation by Kir6.2 channel blockade."
The research group, led by Dr. Moriguchi and Professor Kohji Fukunaga of the Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, thus concluded that Alzheimer's disease can be described as a diabetic disorder of the brain.
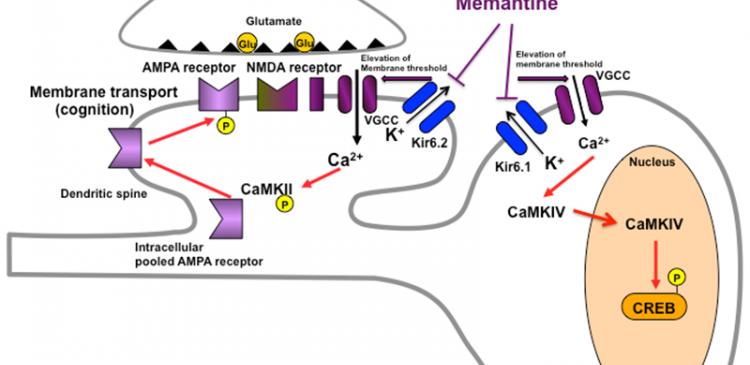
Memantine, a drug widely used to treat Alzheimer's disease, is a well known inhibitor of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors that prevent excessive glutamate transmission in the brain. Researchers have now found that memantine also inhibits the ATP-sensitive potassium channel (Kir6.2 channel), improving insulin signal dysfunction in the brain.
In their experiment with mice, the researchers found that memantine treatment improved impaired hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) and memory-related behaviors in the mice through the inhibition of KATP channel Kir6.2.
"Since KATP channels Kir6.1 or Kir6.2 are critical components of sulfonylurea receptors (SURs) which is downstream insulin receptor signaling, the KATP channel inhibition by Memantine mediates the anti-diabetic drug action in peripheral tissues," says Dr. Moriguchi. "And this leads to improved cognitive functions and improved memory retention among Alzheimer's patients."
The researchers now hope that results of their study and the parallels drawn with diabetes, will lead to new treatments for Alzheimer's disease, using the inhibition of Kir6.2 channel.
Contact:
Shigeki Moriguchi Email: [email protected]
Kohji Fukunaga Email: [email protected]
Department of Pharmacology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Proposed model for blockade of Kir6.1 or Kir6.2 by memantine in hippocampus. Our results suggest that Kir6.2 blockade in dendritic spines by memantine regulates CaMKII activity by increasing intracellular Ca2+ mobilization, which in turn improves cognitive function by promoting AMPAR trafficking into the postsynaptic membrane.