Genetics
News
14 Jul 2021
Researchers have found a way to enhance radiation therapy using novel iodine nanoparticles.
17 Jun 2021
Researchers from Hiroshima University now have a better understanding of the mechanism underlying how certain bacteria can transfer genetic material across taxonomic kingdoms, including to fungi and protists. Their work, published in Frontiers in Microbiology, could have applications in changing how bacteria perform certain functions or react to changes in their environment.
09 Jun 2021
Publication bias, or the tendency of researchers and journals to not publish uninteresting findings, plagues much of the natural sciences and especially biomedical research. Hiroshima University researchers have developed a meta-analytic technique exploiting publicly available transcriptome databases that avoids the problem—and in so doing, discovered four genes previously unknown to be associated with responding to low-oxygen stress.
31 May 2021
High-resolution genome structural analyses combined with large-scale simulations show the arrangements of the genome’s spool-like structures affecting gene expression.
28 May 2021
Scientists from Japan, Europe and the USA have described a pathway leading to the accelerated flowering of plants in low-nitrogen soils. These findings could eventually lead to increases in agricultural production.
21 May 2021
Single-cell gene studies are clarifying the roles of the brain’s specialised immune cell in Alzheimer’s disease and offer new avenues for treatment of this incurable condition.
13 May 2021
A simple tool allows researchers to track how different subpopulations of the Plasmodium knowlesi parasite are changing over time.
13 Apr 2021
The O. swinhoana frog species is the first vertebrate known to retain descendant genes that now determine sex in mammals, birds, and fishes inherited from a common ancestor.
07 Apr 2021
New national body established to further research insights, improve patient outcomes and create new economic opportunities for the biomedical technology industry.
26 Mar 2021
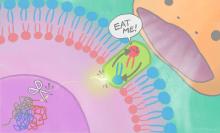
An ‘eat-me’ signal displayed on cell surfaces requires activation of a lipid-scrambling protein by a nuclear protein fragment.

24 Feb 2021
Many genetic variants have been found to have a linkage with genetic diseases, but the understanding of their functional roles in causing diseases are still limited. An international research team, including a biomedical scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU), has developed a high-throughput biological assay technique which enabled them to conduct a systematic analysis on the impact of nearly 100,000 genetic variants on the binding of transcription factors to DNA. Their findings provided valuable data for finding key biomarkers of type 2 diabetes for diagnostics and treatments. And they believe that the new technique can be applied to studies of variants associated with other genetic diseases.
17 Feb 2021
Researchers from DGIST have now found a way to keep living, wet cells viable in an ultra-high-vacuum environment, using graphene, allowing—like never before—accurate high-resolution visualization of the undistorted molecular structure and distribution of lipids in cell membranes. This could enhance our bioimaging abilities considerably, improving our understanding of mechanisms underlying complex diseases such as cancers and Alzheimer’s
11 Feb 2021
A brain enzyme activates dormant neural stem cells, revealing how defects in its gene could lead to neurodevelopmental disorders.
04 Feb 2021
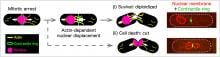
Cells replicate their genetic material and divide into two identical clones to perpetuate life. Some cells pause in the process with a single, undivided nucleus. When the cell resumes division after such a pause, the nucleus can become caught in the fissure, splitting violently, and killing both cells. But that is not always the case. Researchers from Hiroshima University in Japan are starting to understand how active nuclear displacement rescues cell death.
23 Dec 2020
A joint research team co-led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has developed a novel computational tool that can reconstruct and visualise three-dimensional (3D) shapes and temporal changes of cells, speeding up the analysing process from hundreds of hours by hand to a few hours by computer. Revolutionising the way biologists analyse image data, this tool can advance further studies in developmental and cell biology, such as the growth of cancer cells.
23 Dec 2020
A transporter protein that regulates cell membrane cholesterol likely played an important role in vertebrate evolution, according to a review published by iCeMS researchers in the journal FEBS Letters.
21 Dec 2020
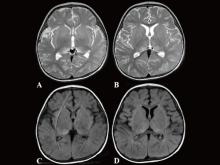
Researchers baffled by an infant’s rare encephalitis case unusual in children found unheard-of mutations and a new way to examine the “immunity gene.”
04 Dec 2020
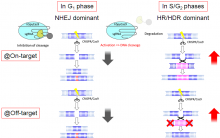
Turning off gene-editing until it reaches cell cycle phases where more accurate repairs are likely to happen offers a promising fix to CRISPR-Cas9’s problem with unwanted genetic changes.
20 Nov 2020
A research team, affiliated with South Korea's Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) has presented the whole-genome sequence and analyses of the endangered whale shark (Rhincodon typus), the largest extant fish on Earth.
20 Nov 2020
A research team, affiliated with the Korea Genomics Center (KOGIC) at UNIST has released data from the initial phase of the Korean Genome Project (Korea1K), including information describing 1,094 whole genomes, along with 79 quantitative clinical traits.
19 Nov 2020
A research team, affiliated with South Korea's Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) established an advanced direct conversion strategy to generate iMNs from human fibroblasts in large-scale with high purity, thereby providing a cell source for treatment of SCI.
19 Nov 2020
A repetitive DNA sequence that causes health risks when it malfunctions can now be watched inside living cells using a synthetic tool
04 Nov 2020
Innovative research by scientists at Duke-NUS Medical School has shed light on the mysterious role of long non-coding RNAs in the development of pancreatic cancer and suggests potential new targets for precision cancer therapies.
03 Oct 2020
A new apparatus improves how we study the effects of aiming high-field terahertz radiation at cells, with implications for regenerative medicine.
02 Oct 2020
Marine biologists studying the genetic structure of the Humboldt squid population found it is vulnerable to overfishing by fleets on its migration path.
01 Oct 2020
Scientists have found an ingredient that makes a vaccine more effective through an approach more often seen in materials science – testing molecules that self-assemble into larger structures.
01 Oct 2020
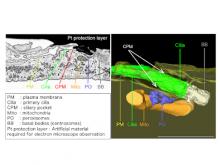
Scientists found out why people with Zellweger syndrome also get sick with genetic disorders linked to dysfunctions of the cilia or the cell’s “antenna.”
31 Aug 2020
A research team from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE) at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) has developed a new Gene Expression Embedding frameworK (GEEK), which uses artificial intelligence technologies in machine learning and natural language processing to study the regulation of gene expression. In contrast to previous works that focused on one or a few regulatory mechanisms at a time, this new framework can study the joint effects of many mechanisms simultaneously. A research article describing this new study has been published in the renowned international science journal Nature Machine Intelligence. The framework may help study the causes of cancers and treatment methods.
04 Aug 2020
Recurrent miscarriages (RM) cause frustration and trauma to couples who want to have a child. However, not all couples can find out about the underlying reasons because of medical constraints. The Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (O&G) of the Faculty of Medicine at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CU Medicine) has successfully developed a new genome sequencing test called ChromoSeq to identify the genetic defects for married couples, who suffered from RM. When compared with the conventional karyotyping analysis, ChromoSeq offers greater accuracy in detecting potential genetic abnormalities associated with RM in affected couples. The team conducted a study on the innovation and the findings were recently published in the international journal American Journal of Human Genetics.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Pakistani botanist Azra Quraishi (22 September 1945 – 22 November 2002) is recognised for developing virus-free seed potatoes that increased potato production in Pakistan by an estimated five per cent.
Indian botanist Shipra Guha-Mukherjee (13 July 1938 – 15 September 2007) made a breakthrough discovery that enabled the genetic study of plants and, by extension, the development of improved varieties of rice, wheat, potatoes, and other crops.
Irene Ayako Uchida’s (8 April 1917 – 30 July 2013) strides to understand genetic diseases such as Down syndrome paved the way for early screening of chromosomal abnormalities in foetuses.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
In his over 30 year career in rice research, Munshi Siddique Ahmad (1924 – 19 October 2011) developed more than 30 varieties of high-yielding rice, including the BRRI Shail strain, which was responsible for increasing the rice production of Bangladesh from 8 million tonnes in 1965 to 20 million tonnes in 1975.
Eminent Filipina scientist and educator Clara Lim-Sylianco (18 August 1925 – 23 July 2013) is remembered for her extensive research on mutagens – often-carcinogenic agents that permanently alter genetic materials such as DNA – antimutagens and bioorganic mechanisms.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Janaki Ammal Edavalath Kakkat (4 November 1897 – 7 February 1984) was an Indian botanist who studied plant chromosomes and genetics.
Maqsudul Alam (14 December 1954 – 20 December 2014) was a biologist from Bangladesh who is renowned for his research on genome sequencing
Barry Paw (29 August 1962 – 28 December 2017) was a biologist and oncologist who discovered several novel genes and their functions in red blood cells.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Syed Qasim Mehdi (13 February 1941 – 28 September 2016) was a Pakistani molecular biologist who was a founding member of the Human Genome Diversity Project (HGDP), which assessed human diversity by studying human migration, mutation rates, relationships between different populations, genes involved in height and selective pressure.