Mechanism of type 2 diabetes mellitus improvement by gargling with mouthwash
Researchers from Osaka University find that gargling with an antiseptic mouthwash can reduce ‘bad’ bacteria in the mouths of people with type 2 diabetes, and may lead to better control of their blood sugar
Osaka, Japan – More than bad breath, there is growing evidence that ongoing inflammation in the mouth, like with gum disease, is associated with serious diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease or type 2 diabetes. Now, researchers from Osaka University have identified an easy way to fight bacteria that might cause such problems.
In a study published this month in Scientific Reports, the researchers reported that when people with type 2 diabetes gargled with an antiseptic mouthwash, the numbers of periodontitis-related bacteria decreased. Excitingly, some patients with reduced bacteria also achieved much better control of their blood sugar, hinting at promising future clinical applications.
“There are three highly virulent bacterial species that are linked to periodontitis, or diseases of the tissues surrounding the teeth,” explains lead author of the study Saaya Matayoshi. “We decided to see if we could reduce these three species—Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Tannerella forsythia—in patients with type 2 diabetes using a mouthwash containing the antiseptic chlorhexidine gluconate.”
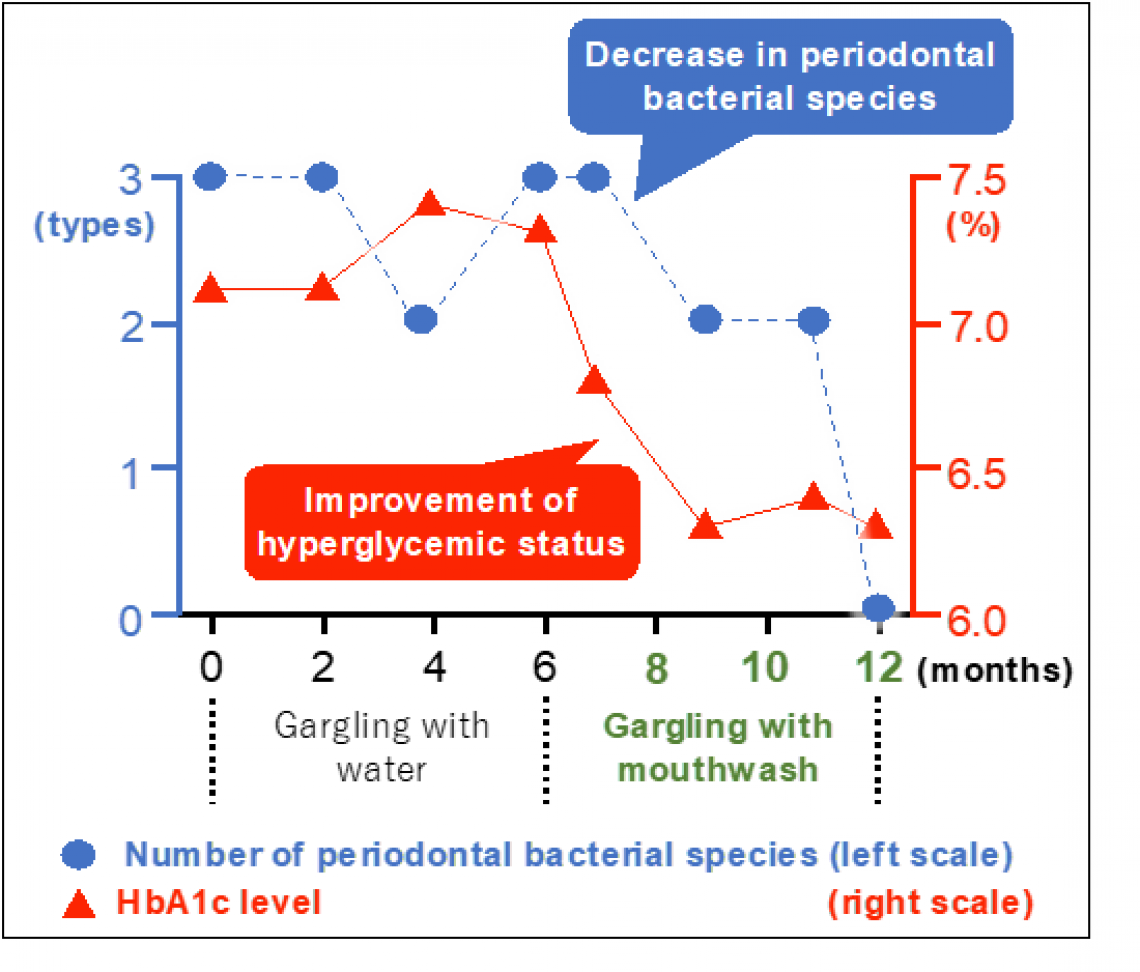
To do this, the researchers took monthly or bimonthly saliva and blood samples from 173 patients over an entire year. With the saliva, the researchers noted the presence or absence of the three bacterial species, and with the blood samples, they measured HbA1c levels as a marker of blood-sugar control. Importantly, for the first 6 months of the study, the patients gargled with water, whereas for the second 6 months they gargled with the antiseptic mouthwash. In this way, the research team could see whether gargling itself was effective for reducing bacteria, or whether mouthwash was more effective.
“We were unsurprised to see that gargling with water had no effects on bacterial species or HbA1c levels,” explains Kazuhiko Nakano, senior author of the study. “However, there was an overall reduction in bacterial species when the patients switched to mouthwash, as long as they were gargling at least twice a day.”
The researchers also found that, although there were no overall changes in HbA1c levels when patients gargled with the antiseptic mouthwash, there appeared to be large variations in individual responses. For example, when they split the group into younger and older patients, younger patients had greater reductions in bacterial species and significantly better blood-sugar control with the mouthwash compared with water.
Given that poor oral health is linked to serious disease, simple methods to improve oral hygiene have important ramifications. If researchers can identify patients who are likely to respond well to antiseptic mouthwash, this easy-to-use treatment may improve the lives of people with periodontitis-linked diseases such as diabetes, dementia, cardiovascular disease, and respiratory tract infections.
###
The article, “Effects of mouthwash on periodontal pathogens and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus,” was published in Scientific Reports at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-53213-x
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
A remarkably effective case of decrease in virulent periodontal bacterial species and improvement of hyperglycemic status by gargling with mouthwash containing chlorhexidine