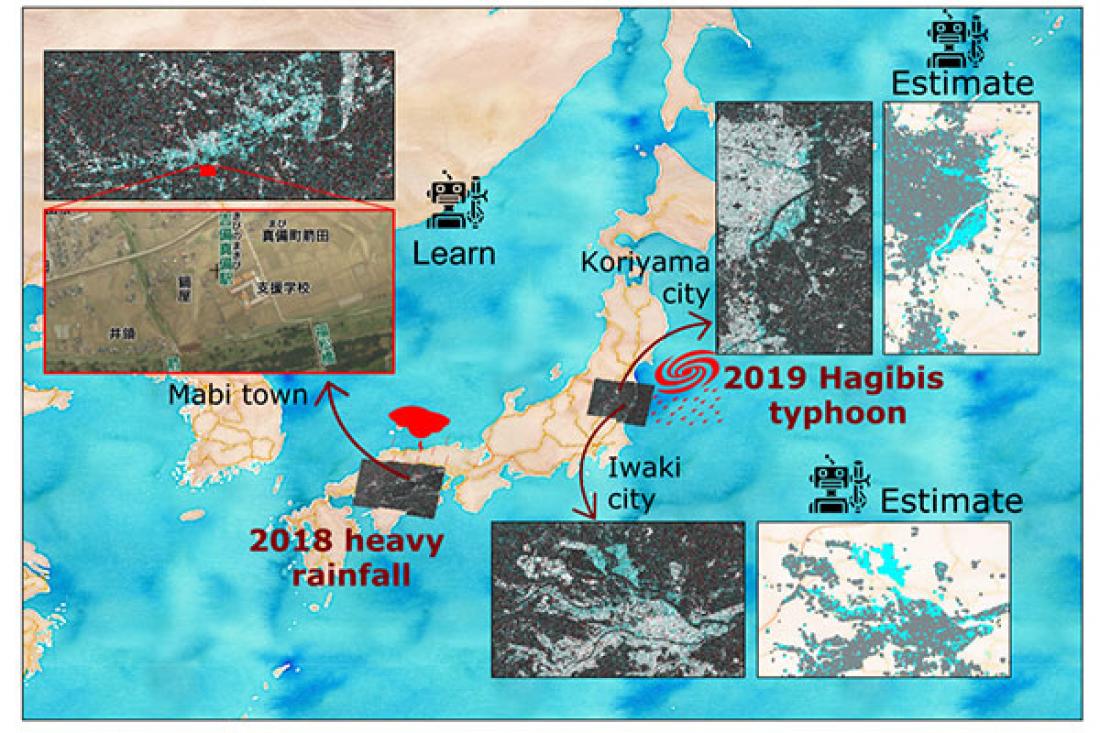
The areas and satellite images used for building the machine learning model (2018 heavy rainfall, Mabi town) and to estimate floods of an unknown event (2019 Hagibis typhoon, Koriyama and Iwaki cities)
Typhoon Hagibis devastated Japan in October 2019, killing 91 people, damaging 85,000 homes, and causing approximately $15 billion in damage. Flooding across the affected regions was profound.
In natural disaster rescue and recovery efforts, real-time flood mapping is crucial. It allows governments to direct relief to the areas that need it most. To aid this effort, satellite images using artificial intelligence (AI) are often employed.
Crucial to this is training data. Training data allows the algorithms to learn data and produce outputs when new inputs arise in a process known as machine learning. However, the amount of training data is limited in many cases. Collecting training data immediately following a disaster is costly, time-consuming and many times impossible.
At IRIDeS and CISMID, authors of the study, evaluated the performance of a model to learn from the 2018 floods that struck southwestern Japan, and to identify the floods induced by the 2019 Typhoon Hagibis. The resulting flood maps were consistent with the results of actual flooding maps released by local governments and public institutions.
The authors note that "Our model successfully identifies the inundated areas and verified that AI can learn from past disasters, ultimately allowing us to better predict flooding in future events." They add that "Our next step in this project would be to incorporate data from the unknown event into a second stage of training for a more accurate estimation."
Contact:
Erick Mas
International Research Institute of Disaster Science, Tohoku University
Tel:+81-22-752-2080
Email: mas@irides.tohoku.ac.jp