Health
News
11 May 2021
Researchers from Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU), in collaboration with Cornell University, have developed a novel targeted therapy for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) that uses a specially-designed nano-carrier to deliver the Chinese medicine compound gambogic acid (GA). The invention enhances the anti-cancer effect of GA and reduces its damage to off-target organs. The invention has the potential to become a more effective therapeutic option for TNBC.
07 May 2021
A new mouthwash developed in Malaysia, called Microencapsulated OroSYNTM, is expected to protect against oral diseases.
The mouthwash made from banana skin and a bacterium promotes a healthy microbiome in the oral cavity to protect against diseases
03 May 2021
• Only 20% of primary liver cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are diagnosed at an early stage, which makes early detection an urgent, unmet healthcare need.
• Study aims to develop more accurate diagnostics for early HCC, an AI algorithm to predict an individual’s risk of developing HCC, and discover novel molecular targets to prevent the development of HCC.
• Study aims to recruit 2,000 participants at high risk of developing HCC from six healthcare institutions and eight polyclinics across Singapore.
29 Apr 2021
The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted personal lives and created a great deal of uncertainty, imposing additional pressure as well as new challenges at work. However, a survey of healthcare professionals in Wuhan during the COVID-19 lockdown conducted by the Faculty of Business of Lingnan University in Hong Kong (LU) found that individual employees with proactive personality do well in the face of challenging circumstances. The research suggests that individual employees also play critical roles in managing crisis and uncertainty, thus maintaining effective organisational functions.
27 Apr 2021
Article by Rosalia Sciortino* originally published in The Jakarta Post, Thursday, 22 April 2021
15 Apr 2021
Researchers from the Department of Neurology at Tohoku University have developed a new taxonomy for a rare autoimmune disease known as neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. The disease was previously thought to be a form of multiple sclerosis (MS) and had, until now, borrowed its taxonomy from MS.

15 Apr 2021
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive type of breast cancer with a high fatality rate. Currently, chemotherapy is the major treatment option, but the clinical result is unsatisfactory. A research team led by biologists at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has identified and characterised a set of specific super-enhancers that stimulate the activity of the related critical cancer genes. The research has also discovered that the deletion of certain specific super-enhancers could reduce tumour cell growth. The latest findings may help discover new effective drug targets for TNBC patients to improve their survival chance.

14 Apr 2021
On April 15, 2021, Hokkaido University and Shionogi & Co., Ltd. will start to monitor COVID-19 in Osaka Prefecture based on wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE), with the cooperation of the Prefectural Government.
13 Apr 2021
Researchers from Osaka University and Hokkaido University develop a system for analyzing mutations in SARS-CoV-2 that is much simpler and faster than existing methods.
01 Apr 2021
COVID-19 has had a massive impact on both our physical health and psychological health. Using data from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami, researchers at Tohoku University have sought to find ways to mitigate the mental health impacts of COVID-19 on adolescents.
31 Mar 2021
Researchers reveal through a systematic review of 158 articles detailing quality improvements in pediatric intensive care units mainly throughout North America and the U.K. that despite having a median score of 11.0 on the Quality Improvement Minimum Quality Criteria Set, only 17% of them were considered high quality by achieving a 14-16 score, and only 5% cited Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE) guidelines for reporting quality improvement works.
29 Mar 2021
A hydrogel, a type of soft matter, developed at Hokkaido University successfully reverted cancer cells back to cancer stem cells within 24 hours, in six different human cancer types. This could lead to the development of anti-cancer stem cell drugs and personalized medicines.
29 Mar 2021
Multi-country trial finds low-cost intervention to improve hypertension management in rural communities is cost-effective. Consisting of home visits by community healthcare workers, physician training and coordination with public health care infrastructure, the intervention can be scaled up in low- and middle-income countries.
29 Mar 2021
Researchers from the University of Tsukuba find that vigorous exercise causes imperceptible improvements in sleep quality
Tsukuba, Japan—Physical exercise has long been prescribed as a way to improve the quality of sleep. But now, researchers from Japan have found that even when exercise causes objectively measured changes in sleep quality, these changes may not be subjectively perceptible.
In a study published this month in Scientific Reports, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that vigorous exercise was able to modulate various sleep parameters associated with improved sleep, without affecting subjective reports regarding sleep quality.
26 Mar 2021
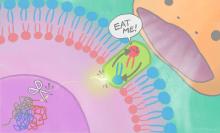
An ‘eat-me’ signal displayed on cell surfaces requires activation of a lipid-scrambling protein by a nuclear protein fragment.
25 Mar 2021
Professor David Matchar and his team from the Health Services and Systems Research (HSSR) Programme at Duke-NUS bagged two prestigious awards at the International Stroke Conference 2021, held virtually on 17-19 March, 2021.
25 Mar 2021
Through a series of experiments using nasal polyp organ culture and mouse models of restraint stress, researchers unveil relationship between presence of corticotropin-releasing stress hormone and increase in and degranulation of allergy-causing mast cells.
24 Mar 2021
Study shows that antibody longevity varies widely from 40 days to as long as several decades and not everyone who has recovered from COVID-19 is immune from reinfection. Individuals with low levels of neutralising antibodies may still be protected if they have robust T-cell immunity. Blood tests and a computer algorithm suggest annual vaccinations might be needed for some individuals to prevent future outbreaks of COVID-19.
11 Mar 2021
Scientists at Tohoku University looked into the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of pregnant women in Japan.
11 Mar 2021
Scientists have discovered a route of introduction for High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus (HPAIV) H5N8 into Japan and, in parallel, have investigated the potential of two human anti-influenza drugs for the control of HPAI in birds.
07 Mar 2021
In honour of International Women's Day, we are highlighting women in research. More than 50 experts across a wide range of disciplines are prepared to speak with international media about their research and women in STEM.
04 Mar 2021
This article is an excerpt from the Hokkaido University research magazine “Tackling Global Issues vol.3 Fighting the menace of zoonosis" (link below).
04 Mar 2021
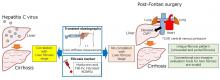
Collecting liver tissue from 22 postoperative patients with long-term post-Fontan surgery, researchers have found a specific liver fibrosis to develop from the sinusoidal region which is difficult to accurately assess by conventional examination methods (ultrasound elastography and blood tests).
03 Mar 2021
Osaka City University finds that the chemical sesaminol, naturally occurring in sesame seeds, protects against Parkinson’s disease by preventing neuronal damage that decreases the production of dopamine. In vitro experiments show sesaminol handle oxidative stress in cells by regulating the production of reactive oxygen species and the movement of antioxidants. In vivo experiments reveal that a diet of sesaminol increases production of dopamine and significantly improve motor functions in mice.
02 Mar 2021
A Hong Kong Baptist University-led (HKBU) research team has developed a novel drug which has the potential to become a next-generation treatment for cancers associated with Epstein–Barr virus (EBV).
26 Feb 2021
Vitamin B6 may help calm cytokine storms and unclog blood clots linked to COVID-19's lethality. But research on it is lacking. A Hiroshima University researcher calls on fellow scientists to study its potential role.
25 Feb 2021
This article is an excerpt from the Hokkaido University research magazine “Tackling Global Issues vol.3 Fighting the menace of zoonosis" (link below).
25 Feb 2021
Medical staff and researchers from Tohoku University and Fukushima Medical University conducted a collaborative, multifaceted training program for healthcare workers to better prepare them for disasters. The training incorporated a wide range of subjects such as data analysis, cultural revitalization in the wake of disasters, and post-disaster psychological and physical well-being.
19 Feb 2021
A research team implemented a study based on a program that encouraged elderly patients at care homes in Adachi Ward, Tokyo to participate in activities such as park cleaning, gardening, and shopping. Their results revealed a surprising behavioral change.
18 Feb 2021
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis enables high-resolution separation of proteins extracted from biological samples, but it requires more than one day of pretreatment to recover the separated proteins trapped inside the gel for detection by mass spectrometry. BAC-DROP, our novel electrophoresis technology, uses a dissolvable form of polyacrylamide gel, which allows sample pretreatment to be completed in about 5 hours. The developed technology will enable the rapid diagnosis of viruses and disease protein markers.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Giants in history
Chinese biochemist Chi Che Wang (1894 - 1979), one of the first Chinese women to study abroad, advanced to prominent research positions at American institutions including the University of Chicago and the Northwestern University Medical School.
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Flora Zaibun Majid ( 1939–2018) was an accomplished Bangladeshi researcher in botany and nutrition science and the first female chairperson of the Bangladesh Council of Scientific and Industrial Research.
Iranian physician and bacteriologist Azar Andami (8 December 1926 – 19 August 1984) developed a cholera vaccine to combat an outbreak that swept through the Middle East, India, Southeast Asia, and Africa in 1937.
Irene Ayako Uchida’s (8 April 1917 – 30 July 2013) strides to understand genetic diseases such as Down syndrome paved the way for early screening of chromosomal abnormalities in foetuses.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
Maggie Lim (5 January 1913 – November 1995) was a Singaporean physician who promoted family planning and expanded the access to clinics to improve the quality of life for mothers and children in Singapore’s early days.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
The founder of the Adyar Cancer Institute in India, Muthulakshmi Reddy (30 July 1886 – 22 July 1968), fought to uplift women and girls from impoverished situations.
Chinese-American virologist and molecular biologist Flossie Wong-Staal (27 August 1946 – 8 July 2020) was the first scientist to clone HIV and determine the function of its genes.
Maharani Chakravorty (1937 – 2015) was one of India’s earliest molecular biologists whose research paved the way for advances in the treatment of bacterial and viral infections.
Archana Sharma (16 February 1932 - 14 January 2008) conducted research into plant and human genetics that expanded the understanding of both botany and human health. In relation to botany, she uncovered the means by which asexually-reproducing plants evolve into new species.
The first Thai woman to receive a degree in medicine, Margaret Lin Xavier (29 May 1898 – 6 December 1932), is best remembered for her compassion towards her less privileged patients.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Filipino chemist and pharmacist Manuel A. Zamora (29 March 1870 – 9 July 1929) is best remembered for his discovery of the tiki-tiki formula to combat beriberi, a disease caused by Vitamin B1 deficiency.
After witnessing death and suffering as a youth in his home village during World War II, Nguyễn Tài Thu (6 April 1931 – 14 February 2021) set his sights on alleviating pain by becoming a doctor. After studying Traditional Chinese Medicine in China in the 1950s, Thu returned to Vietnam to serve in military hospitals. Eventually, he became the country’s foremost practitioner of acupuncture, a technique he first learned by inserting needles into himself.
David T. Wong (born 1936) is a Hong Kong-born American neuroscientist who is best known for discovering the antidepressant drug fluoxetine, better known as Prozac.
Indian organic chemist Asima Chatterjee (1917 to 2006) studied the medicinal properties of plant products, especially compounds known as vinca alkaloids.
Hsien Wu (24 November 1893 – 8 August 1959) is widely regarded as the founder of biochemistry and nutrition science in China. He was the first to propose that protein denaturation was caused by the unfolding of the protein, instead of chemical alteration.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Syed Qasim Mehdi (13 February 1941 – 28 September 2016) was a Pakistani molecular biologist who was a founding member of the Human Genome Diversity Project (HGDP), which assessed human diversity by studying human migration, mutation rates, relationships between different populations, genes involved in height and selective pressure.
Tsai-Fan Yu (1911 – 2 March 2007) was a Chinese-American physician and researcher who was the first female full professor at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. She discovered that gout, a condition characterized by the painful inflammation of joints, was caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the bloodstream.
Min Chueh Chang (10 October 1908 – 5 June 1991) was a Chinese-American biologist who studied fertilization in mammalian reproduction.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.