Biology Cell biology
News
25 Mar 2024
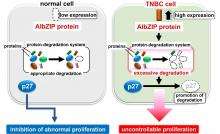
May prove to be therapeutic target in breast cancer treatment
14 Mar 2024
Ancient Mars biomolecules, Gargling away bad bacteria, Molecule glasses magnify life-chemical observations, Cholesterol and cancer link, Quantum electronics leap, Plus our updated Experts for Media: Women list & Asia Research News 2024 is here. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice.
12 Mar 2024
A new study highlights a potential therapeutic target for immune-related disorders, such as multiple sclerosis and asthma.
08 Mar 2024
Scientists from Duke-NUS Medical School have developed a new approach using the Zika virus to destroy brain cancer cells and inhibit tumour growth, while sparing healthy cells.
05 Mar 2024
A novel method for studying genes in testicular cells of living animals could lead to breakthroughs in male contraception and fertility treatments.
28 Feb 2024
A new user-friendly tool helps researchers explore how gene activity is influenced by chemical modifications, providing insights into disease and paths to new treatments.
21 Feb 2024
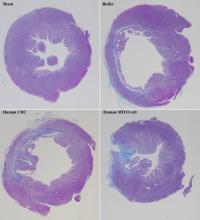
Regenerative therapy to treat heart failure is more effective when the mitochondria of the regenerative cells are activated prior to treatment.
16 Feb 2024
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Journal of Cell Science on a novel role of the small Ca2+-binding protein S100A11 in focal adhesion disassembly.
02 Feb 2024
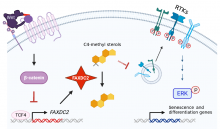
A study led by Duke-NUS Medical School has found an important connection between cancer, stem cells and the building blocks of cholesterol. Specifically, the research reveals how the enzyme FAXDC2 influences cancer cell growth and differentiation through its role in cholesterol synthesis, suggesting possible new approaches to cancer treatment.
15 Jan 2024
Unleashing stem cells from dog urine, Electronic Tongue, Tapping into human motion energy, How neurons network, and A radical use for plastic bags. Plus Communicating science two decades on. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice.
20 Dec 2023
We’re all familiar with our body’s internal clock: it gives us cues on when to wake and when to rest, but it also can determine the rate and time of day at which your body most effectively heals wounds.
13 Dec 2023
Scientists at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed an efficient, non-invasive, and pain-free method to generate canine-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). They identified six reprogramming genes that can boost canine iPSC generation by 120 times compared to conventional methods using fibroblasts. The iPSCs were created from urine-derived cells without the need for feeder cells, an impossible feat until now. Their findings are expected to advance regenerative medicine and genetic disease research in veterinary medicine.
11 Dec 2023
Scientists uncover genetic factors allowing for the early prediction of intestinal metaplasia patients who may have higher risks of developing stomach cancer, enabling early detection, diagnosis and targeted prevention.
20 Nov 2023
A new technique allows researchers to map how the cellular ‘skeleton’ adapts to external stress.
09 Nov 2023
New shrimp species in ancient hot spring, Super sprouts, How "warm-ups" work, New antiviral candidate, Solving voltage decay and from our blog: A sustainable future shines in TIE 2023. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice.
03 Nov 2023
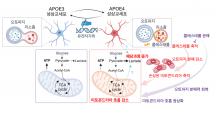
- Confirmed the link between cholesterol accumulated in lysosomes and decreased mitochondrial respiration due to the APOE4 genotype and proposed a possible reason that explains a decline in brain function
- Research results published in Cell Reports
27 Oct 2023
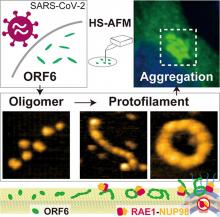
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters high-speed atomic force microscopy studies that shed light on the possible role of the open reading frame 6 (ORF6) protein COVID19 symptoms.
24 Oct 2023
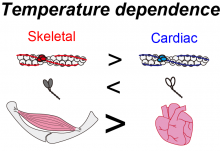
Research out of Osaka University investigated the effect of increased cell temperature on the contractility of skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle by heating the muscle proteins using advanced microscopical techniques. The findings indicated that skeletal muscle is more sensitive to increases in temperature than cardiac muscle, and that heating can rapidly activate the contractile proteins of skeletal muscle, thereby improving muscle performance.
05 Oct 2023
Hunting for supermassive black holes, Coastal survival at risk, Calcium and dead cell clean-up, Two naps are better than one & Pineapple leaf prosthetics. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice.
05 Oct 2023
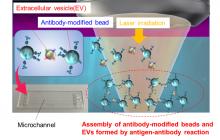
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have used the power of laser light to accelerate the reaction between cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles—a kind of nanoparticle—and antibody-modified microparticles. The three-dimensional structure of the resulting aggregates was then analyzed using a confocal optical system. The results demonstrated the ability to measure, within 5 minutes, approximately 1,000 to 10,000 nanoscale EVs contained in a 500 nL sample.
14 Sep 2023
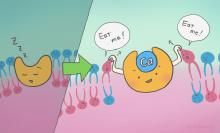
Scientists have found that extracellular calcium mediates the activation of a membrane protein that waves the flag signalling cell death
11 Sep 2023
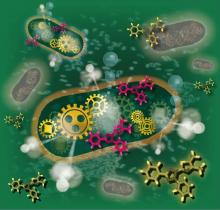
Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a measurement technique that rapidly measures the number of viable bacteria in food products. They have succeeded in drastically reducing the inspection time from 2 days to about 1 hour. With this technology, it will be possible to confirm food safety before shipment from factories and prevent food poisoning.
10 Sep 2023
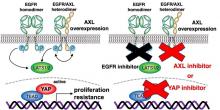
AXL and EGFR inhibitors combined hold promise in fighting certain head, neck, and lung cancers
01 Sep 2023
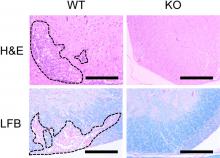
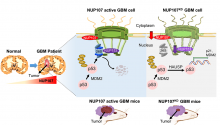
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Cell Reports how alterations in the nuclear pores lead to the degradation of anti-tumor proteins.
04 Jul 2023
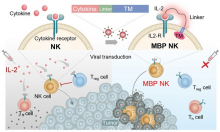
- Professor Minseok Kim’s team at the DGIST confirmed the excellent anticancer effects of the NK cell therapy product that can self-activate in preclinical trials with CT Cells
- This work is expected to be applied in various fields as a next-generation anticancer therapy using NK cells
08 Jun 2023
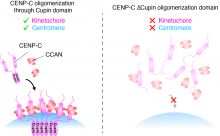
A team led by researchers from Osaka University elucidated a molecular mechanism that is crucial for separating genetic material into daughter cells during cell division. A protein called CENP-C is part of a complex called the kinetochore, which supports the movement of chromosomes. Two portions of CENP-C, the CCAN-binding domain and Cupin domain, are needed for CENP-C to function. The Cupin domain repeats itself through oligomerization, which is essential for proper CENP-C function.
19 May 2023
Mushrooms 🍄get chattier after rainfall 🌧️, Two-organ chip answers fatty liver questions, History maps 🗺️vs future simulations, Restoring vision in blindness. Plus in our blog: Myanmar: Through eyes of leadership. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice.
17 May 2023
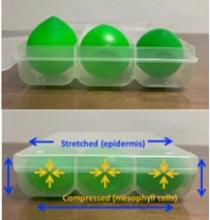
A research group led by Osaka University has found that plant cells may be able to detect mechanical forces to determine their own position within the leaf—whether they are on the surface or in the inner tissues—and therefore differentiate into appropriate cell types after damage. These findings reveal how plants regenerate the correct type of tissues when damaged, and may improve our understanding of the mechanisms underlying the high regeneration potential of plants.
12 May 2023
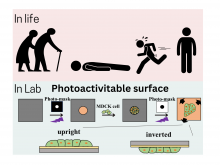
Specially coated surfaces help scientists investigate what happens when cell clusters are turned upside down.
Events

01 Mar 2022 to 02 Mar 2022
The Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI) at Kanazawa University will hold their 5th NanoLSI Symposium 1-2 March 2022, online.
Researchers
Dr. Oehlers leads the Bacterial Pathogenesis Laboratory at A*STAR ID Labs, where he and his colleagues focus on identifying molecular bases of mycobacterial disease and, thus, deploy therapies that address antibiotic resistance in mycobacterial infections.
Dr. Yue Wang is senior principal investigator at the Antifungal Resistance Laboratory of A*STAR ID Labs, where his body of work focuses on virulence mechanisms of the fungal human pathogen Candida albicans.
Prof. Chen’s current research covers research on bacterial antimicrobial resistance, virulence and tolerance in the veterinary, food and medical microbiology fields
Prof. Jinsoo Seo's research focuses on mechanisms of cellular dysfunction and cognitive decline in aging brain, genetic risk factors for neurodegeneration as well as the effect of environmental factors and lifestyle on Alzheimer's disease.
Babita Madan is an assistant professor at the Program in Cancer and Stem Cell Biology, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore.
David Virshup, M.D., is Director of the Programme in Cancer and Stem Cell Biology (CSCB) and Professor at Duke-NUS Medical School and is jointly appointed as Professor of Pediatrics at Duke University in North Carolina.
The prospect of favorably influencing brain health through dietary habits has gained much interest. My research interest explores the therapeutic potential of functional foods and phytonutrients as neuroprotectants against mitochondrial diseases and cerebral toxoplasmosis. The scientific findings support nutritional intervention as a viable strategy for the management of human brain disorders.
My research background covers multidisciplinary fields such as Pharmaceutics, Cancer Nanomedicine, Bioengineering and Organ-on-a-chip platforms. My current research focuses on the development of dynamic biological barriers on a chip such as blinking human cornea on a chip.
Professor Ahmed Al-Haddad, M.Sc., Ph.D. (Germany) is currently Professor of Microbiology and Medical Microbiology at College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Hadhramout University-Yemen.
He is the Founding-Dean of the first Faculty of Nursing in Yemen. He has over fifteen years of research and teaching experience in various domains of life sciences.
Al-Haddad has published many peer reviewed articles and conference papers in the areas of molecular biology, microbiology and antibiotics in National and International journals.
He is reviewer in different national and international Scientific Journals such as Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials, Journal of Microbiology and Antimicrobials, Sultan Qaboos University Medical Journal, British Biotechnology Journal.
He is a member of various national and international scientific organizations.
Toru Kondo is Professor of the Division of Stem Cell Biology at the Institute for Genetic Medicine, Hokkaido University.
Giants in history
Archana Sharma (16 February 1932 - 14 January 2008) conducted research into plant and human genetics that expanded the understanding of both botany and human health. In relation to botany, she uncovered the means by which asexually-reproducing plants evolve into new species.