Peer Reviewed
News
15 Feb 2023
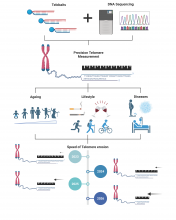
To clarify the mechanism of serial dependence in number perception, a research team from Osaka Metropolitan University conducted two tests, independently asking subjects to estimate the number of coins, or to estimate the value of those coins, shown on-screen for half a second. The results showed that serial dependence was confirmed in both tasks and that the most significant effect on serial dependence was not caused by the last stimuli, but the subjects last response. These results indicate that higher-order cognitive processing has a greater influence on the occurrence of serial dependence.
14 Feb 2023
- Dr. Yun established open innovation theory (dynamics, business model, political economics) as the first corresponding author, collaborating with global scholars
14 Feb 2023
- An overview of the methodology for using holography in precision medicine
14 Feb 2023
- He is to lead the Korean Society for Brain and Neural Sciences for a period of two years, from January 2023 to December 2024
14 Feb 2023
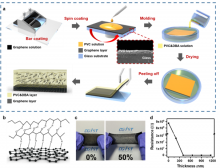
- Elastic Triboelectric Tactile Sensor Development Using Graphene Electrode Unaffected by Elasticity
- Published in 'Nano Energy' as a Technology to Produce Precise Sensors by Supplementing the Output Change Problem of Sensors Deformed by Human Activity
13 Feb 2023
Team studies discrimination, mental distress, and work impairment in COVID-19 survivors.
13 Feb 2023
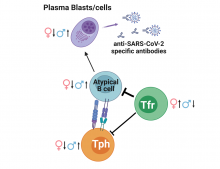
Researchers from Osaka University have shown sex-specific differences in the immune response to COVID-19 infection. By identifying and analyzing the immune cell population in COVID-19 patients, they showed that infection results in a reduced ratio of circulating follicular T regulatory (cTfr) cells to a network of antibody-producing proteins, correlated with dysregulated antibody production. This cTfr cell reduction is more significant in males, providing cellular evidence for the observed association between increased risk and male sex.
13 Feb 2023
A research group from the Graduate School of Engineering at Osaka Metropolitan University has shown that 3C-SiC exhibits high thermal conductivity equivalent to the theoretical value, based on thermal conductivity evaluation and atomic-level analysis, for the first time. They demonstrated that a 3C-SiC film on silicon substrate had a high thermal conductivity and expect that fabricating large-diameter wafers can be achieved at a low cost. The discovery should lead to improved heat dissipation in everyday electronic devices.
10 Feb 2023
Hydrothermal vents have been identified as a previously undiscovered source of dissolved black carbon in the oceans, furthering the understanding of the role of oceans as a carbon sink.
10 Feb 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have demonstrated that fish can recognize “it’s me” when they themselves in a picture for the first time in non-human animals. Further testing made it clear that the fish recognize their own face in the pictures like humans.
09 Feb 2023
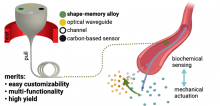
A research team led by an associate professor at Tohoku University has developed a microscopic fiber equipped with actuators and biochemical sensors. The breakthrough could be used to develop smart catheters and lead to further advancement in robotics.
08 Feb 2023
Hokkaido University researchers have developed a novel method to design and develop peptide antibiotics in large numbers, which will prove critical to controlling antibiotic resistance.
07 Feb 2023
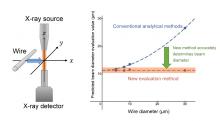
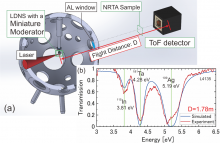
A research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has derived a new evaluation method for the measuring the size X-ray microbeams (diameter) through mathematical analysis. The group then verified the validity of the mathematically derived evaluation method by measuring the diameter of X-ray microbeams using metal wires of various diameters with an X-ray fluorescence analysis system for small areas and found that it was possible to calculate the beam diameter more accurately than the previous conventional evaluation method.
07 Feb 2023
Two catalysts working in tandem enable inexpensive formate salts to perform difficult dearomative reactions, giving products potentially useful for drug development.
06 Feb 2023
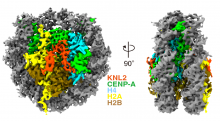
Researchers led by Osaka University used cryogenic electron microscopy to analyze the atomic structure of the centromeric region of the chromosome, essential for cell division. A protein called CENP-A marks the centromere; the researchers showed that during interphase, CENP-A is bound by a protein called KNL2 to maintain the location of the centromere. During mitosis, KNL2 is replaced by CENP-C, allowing correct formation of the kinetochore complex for cell division.
06 Feb 2023
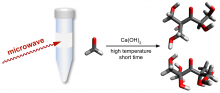
Researchers from Osaka University expanded the synthetic toolkit for preparing valuable chemical precursors from renewable feedstocks. They used microwave irradiation to dramatically improve the selectivity of the formose reaction, forming a simple six- and seven-carbon mixture that can be readily purified. These findings will help the chemicals industry minimize the use of fossil resources and improve the sustainability of manufacturing processes.
03 Feb 2023
Researchers used the James Webb Space Telescope to identify the precise location of a powerful energy source hidden by cosmic dust in the luminous merging galaxy IIZw096.
03 Feb 2023
Traditional hydrogen peroxide production is energy and emission intensive, and so scientists have sought to synthesize it electrochemically. But tailoring the cobalt-nitrogen-carbon (Co-N-C) catalyst has been challenging. Using a theoretical prediction, which was then experimentally verified, an international research group has designed a Co-N-C catalyst that alleviates this problem.
03 Feb 2023
Researchers used a chemical synthesis robot and computationally cost effective A.I. model to successfully predict and validate highly selective catalysts.
02 Feb 2023
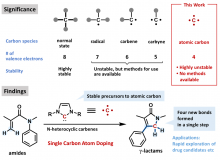
Researchers from Osaka University have used single carbon atom doping to form four chemical bonds in one step. Gamma-lactams (cyclic molecules that are common in antibiotics) were easily synthetically accessible from alpha, beta-unsaturated amides (an important molecule in cancer progression). The team chemically modified an anti-seizure medication in 96% yield, highlighting the work's utility to otherwise synthetically complex aspects of pharmaceutical development. The results of this work could become foundational to drug discovery and development.
02 Feb 2023
Blocking an immune-regulating protein reverses the damage caused by acute and chronic kidney disease, a preclinical study suggests.
02 Feb 2023
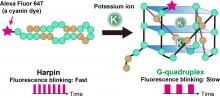
A new microscopic technique allows for the real-time study of RNA G-quadruplexes in living cells, with implications for the fight against amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
01 Feb 2023
Osaka University researchers investigated the physics of laser-driven neutron sources, and found the relationship between the power and the neutrons generated. They were able to decrease the exposure time needed for neutron absorption experiments, which may be employed in biomedical research.
31 Jan 2023
The study is an important step towards the understanding of long-term changes in the water cycle and will aid in more informed decisions when assessing and managing regional water systems.
31 Jan 2023
A research group at the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Informatics has developed a new learning method for artificial intelligence that combines classification performance for data with multiple labels with the ability to learn continually from data. Numerical experiments on real-world multi-label data indicate that the new method outperforms conventional approaches. The simplicity of this algorithm makes it easy to integrate it with other algorithms to devise new ones.
31 Jan 2023
Data stored in ice cores dating back 55 years bring new insight into atmospheric levels of a molecule that can significantly affect weather and climate.
31 Jan 2023
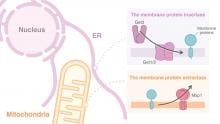
Researchers from Osaka University have shown that a system known as the GET pathway is essential for efficient mitophagy, the process by which mitochondria are removed from cells. The GET pathway targets a protein assembly called the Ppg1–Far complex, which inhibits mitophagy, to the membrane of a part of the cell called the endoplasmic reticulum. When the GET pathway is defective, this complex instead becomes targeted to mitochondria, where it acts to suppress mitophagy.
30 Jan 2023
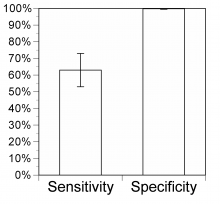
Researchers from Osaka University compared the sensitivity of rapid antigen tests (RATs) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests for the Omicron variant of COVID-19 using data produced by the Japan Professional Football League. They found the comparative sensitivity of RATs for Omicron was not affected by the duration from the onset of symptoms to testing.
30 Jan 2023
Everyday electronics, such as our phones, employ surface acoustic wave devices for frequency filtering and sensing. But this consumes a lot of energy, serving as a drain on battery life. Now, a team of researchers has developed a new acoustic waveguide based on the mathematical concept of topology, which will help alleviate this problem.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.