Peer Reviewed
News
31 Mar 2023
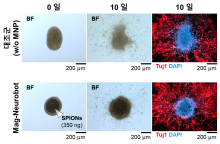
- Research teams led by Professor Hongsoo Choi and Professor Yongseok Oh from DGIST joined the research team led by Dr. Jongcheol Rah from Korea Brain Research Institute to develop the technology for delivering a microrobot to a target point of a hippocampus in an in-vitro environment, connecting neural networks, and measuring neural signals
- The research findings are expected to contribute to neural network research and the verification and analysis of cell therapy products
31 Mar 2023
- DGIST Professor Minseok Kim’s research team has developed an electronic medicine that can restore normal Schwann cell phenotypes in CMT disease models
- It presents the potential of electric stimulation-based treatment for chronic peripheral nerve disorders
31 Mar 2023
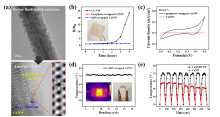
- The world’s first technology for synthesizing high-quality and low-cost copper-graphene nanowire using intense scintillation
- Implementation of high-performance transparent-flexible electronic device based on copper-graphene nanowire and publication in the international journal Nano Energy, which is renowned in the field of energy
29 Mar 2023
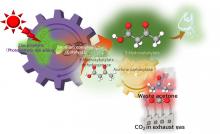
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have developed a process using artificial photosynthesis to successfully convert more than 60% of waste acetone into 3-hydroxybutyrate, a material used to manufacture biodegradable plastic. The results were obtained using low-concentration CO2, equivalent to exhaust gas, and powered by light equivalent to sunlight for 24 hours. The researchers expect that this innovative way of producing biodegradable plastic could not only reduce CO2 emissions but also provide a way of reusing laboratory and industrial waste acetone.
28 Mar 2023
A group including Osaka Metropolitan University researchers discovered that the rhodopsin—a protein in the eye that detects light—of whale sharks has changed to efficiently detect blue light, which penetrates deep-sea water easily. The amino acid substitutions–one of which is counterintuitively associated with congenital stationary night blindness in humans—aid in detecting the low levels of light in the deep-sea. Although these changes make the whale shark rhodopsin less thermally stable the deep-sea temperature, allows their rhodopsin to keep working. This suggests that the unique adaptation evolved to function in the low-light low-temperature environment where whale sharks live.
28 Mar 2023
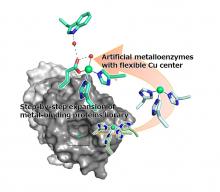
A research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has succeeded in simply creating an artificial metalloenzyme with the common metal-binding motif 2-his-1-carboxylate, which is found in natural non-heme metalloenzymes. They created a library of 12 different proteins and screened the library and found that the H52A/H58E variant had the best stereoselectivity. It is expected that this research can be expanded to produce a variety of biocatalysts that work under mild conditions.
28 Mar 2023
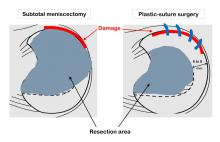
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Medicine conducted an interoperative comparison of lateral disc meniscus injuries of young patients (aged 15 or less), that were treated with plastic sutures or subtotal resection, to see if there was a difference in postoperative cartilage degeneration. The research group observed that sub-total meniscectomies were more likely to show cartilage degeneration, being worst in lateral disc meniscus injuries. In addition, they found that even with higher levels of meniscus damage, preserving the meniscus with sutures was more effective in protecting the cartilage in young patients.
28 Mar 2023
· Duke-NUS sleep scientists’ analyses show associations between early classes, less sleep, poor attendance and reduced grade point average.
· Studies in secondary and junior college students have shown that later start times can have positive impacts on grades.
27 Mar 2023
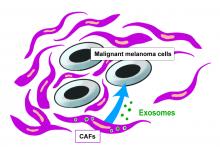
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are key factors in the tumor microenvironment, which have been implicated in cancer cell progression. It has also been reported that vesicles called exosomes produced by these CAFs play an important role in cancer progression. An Osaka Metropolitan University research group investigated the effect of CAF-derived exosomes on the growth of malignant melanoma cells. They found that CAF-derived exosomes express CD9 and CD63 transmembrane proteins, and that the CD9-positive exosomes may inhibit the growth of malignant melanoma cells.
27 Mar 2023
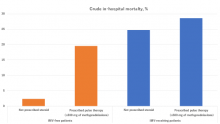
Researchers from Osaka University have found that repeated high-dose treatment, known as pulse therapy, with the steroid methylprednisolone reduces in-hospital deaths in COVID-19 patients who receive invasive mechanical ventilation, but not in patients who don’t receive invasive mechanical ventilation. These findings were only possible using appropriate statistical methods to remove bias from the data, which originally seemed to show that the opposite was true. These results can improve patient treatment and reduce COVID-19-related deaths worldwide.
24 Mar 2023
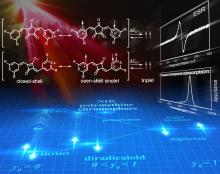
An Osaka Metropolitan University joint research group has discovered that near-infrared absorbing dyes, which had previously been considered to have closed-shell electronic structures, have an intermediate electronic structure, between closed- and open-shell structures. They also found that as the wavelength of near-infrared light that can be absorbed becomes longer the contribution of open-shell forms increases within the dye. These newly discovered characteristics are expected to be utilized to develop new near-infrared absorbing dyes that can absorb longer wavelength near-infrared light.
24 Mar 2023
Hailey-Hailey disease is a rare, inherited condition characterized by patches of blisters appearing mainly in the skin folds of the arm pits, groin and under the breasts. It is caused by a mutation in the gene that codes for a specific protein. Tohoku University scientists have uncovered some critical details of this protein’s structure, and the findings could build the foundation for developing treatment for Hailey-Hailey disease and other neurodegenerative conditions.
23 Mar 2023
A research group from Osaka Metropolitan University investigated the relationship between tobacco use, including heated tobacco products, with the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19. The researchers administered an online survey of living conditions in February 2022 to 30,130 participants aged 16-81 years, finding that heated tobacco product users had significantly higher rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to non-tobacco users. Furthermore, the research group found that among all tobacco users, those who used both heated tobacco products and traditional cigarettes had the highest incidence of requiring hospitalization or oxygen due to COVID-19.
23 Mar 2023
Researchers at The University of Tokyo develop a gate driver for circuit bipolar transistor electronic switches with a timing function robust to changes in current and temperature, which can be used in many industrial control applications
23 Mar 2023
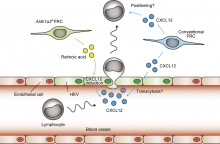
Researchers from Osaka University identified a subset of fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) that simultaneously express two proteins, Aldh1a2 and Tie2, making them unique to areas of the omentum called milky spots. Genetic depletion of these cells caused structural disruption of milky spots. The FRCs were critical to the abdominal immune system as they regulated CXCL12 levels, a molecule necessary for lymphocyte recruitment from blood circulation. These insights can help develop novel treatments for intra-abdominal infections.
22 Mar 2023
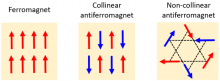
A research team has highlighted recent achievements in antiferromagnetic spintronics in a review article, unearthing a new frontier in the field.
22 Mar 2023
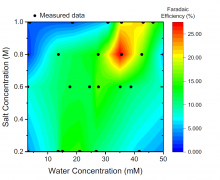
Researchers from SANKEN (The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research), at Osaka University in collaboration with researchers from Imperial College London (UK) have improved the Faradaic efficiency of the nitrogen reduction reaction into ammonia by straightforward optimization of chemical process parameters. They found that trace water was the probable source of the high selectivity by facilitating incorporation of lithium oxide into the solid electrolyte interphase. These findings will also aid optimization of other analogous reactions, and thus help the chemicals industry optimize the sustainability of one of the most carbon-intensive reactions globally.
21 Mar 2023
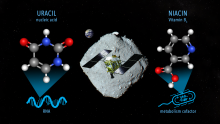
Samples from the asteroid Ryugu collected by the Hayabusa2 mission contain nitrogenous organic compounds, including the nucleobase uracil, which is a part of RNA.
20 Mar 2023
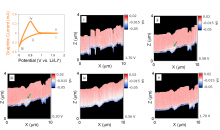
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in JACS Au how they have developed operando scanning ion conductance microscopy to allow simultaneous measurements of changes in the anode surface topography of a lithium ion battery during use, as well as the varying ion concentration with depth. Combining both types of information should help researchers evaluate the correlation between the two to design better batteries.
20 Mar 2023
Parasitic infections in salmonid fish can increase or decrease their vulnerability to angling, depending on their body condition.
17 Mar 2023
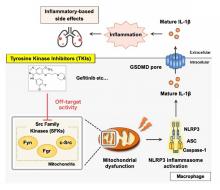
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) are employed to attack specific types of cancer cells. The downside to using TKs is that they can cause serious inflammation. A team of researchers has discovered the underlying mechanism that causes this inflammation.
15 Mar 2023
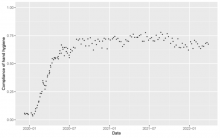
An Osaka University study investigated how the COVID-19 onset and media coverage affected hand hygiene compliance. Voluntary use of hand sanitizer in a hospital rose from 5% in December 2019 to 70%+ by August 2020. In the same period, TV coverage reached 7.7 hours/day on a national broadcaster. The study’s simulations found a significant relation between TV coverage and hand hygiene compliance, though no correlation between compliance and newly confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths.
15 Mar 2023
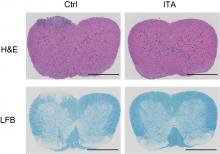
Researchers have revealed the modulatory effect of the anti-inflammatory metabolite itaconate on T helper and T regulatory cells, which may lead to new therapeutic approaches to treating some autoimmune diseases.
14 Mar 2023
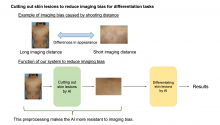
Atopic dermatitis skin lesions and the lesions produced by infectious complications of the disease look so similar that it makes it impossible for patients to spot the difference and know when to visit their doctor for treatment. But an AI-powered mobile app developed by dermatologists now puts the power of diagnosis in the hands of patients.
13 Mar 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists succeeded in directly observing how LECs—which are attracting attention as one of the post-organic LEDs—change their electronic state over time during field emission by measuring their optical absorption via lamp light irradiation for the first time. This research method can be applied to all light-emitting devices, including not only LECs but also organic LEDs. This method is expected to reveal detailed electroluminescence processes and lead to the early detection of factors that reduce the efficiency of electroluminescence.
13 Mar 2023
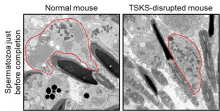
Researchers from Osaka University identified the role of a protein known as testis-specific kinase substrate (TSKS) in the process of spermiation, the release of mature sperm. Analysis of a gene-modified mouse model in which TSKS is disrupted revealed that TSKS is necessary for sperm to eliminate cytoplasm and become streamlined. These findings may lead to the development of diagnostic tests and male contraceptives.
10 Mar 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists successfully quantified the total reactive polysulfide content of 22 different types of vegetables, including onions and garlic. They also revealed that reactive polysulfides are not only found in the leek genus (Allium), such as onions and garlic but also in the cruciferous family of vegetables (Brassicaceae), such as broccoli and cabbage.
10 Mar 2023
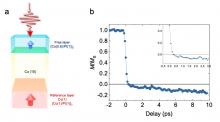
Researchers from the Université de Lorraine and Tohoku University have demonstrated sub-picosecond magnetization reversal in rare-earth-free spin valves. To date, ultra-fast magnetization control without using magnetic fields was only seen in material systems using rare-earth materials. But the recent breakthrough is expected to open up new pathways for developing ultra-fast and energy efficient applications.
10 Mar 2023
The first-ever molecular catalyst specifically tailored for mechanochemical reaction conditions enables high-efficiency transformations at near room temperature.
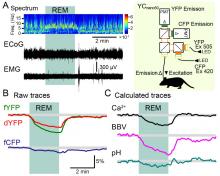
03 Mar 2023
Changes in our REM sleep patterns could potentially be used to diagnose the severity of epilepsy, a new study by Tohoku University researchers has suggested. They showed that astrocytes - star-shaped glial cells that control the local ionic and metabotropic environment of the brain - exhibit an acid response with REM sleep in mice. They theorize that the acid response could be the underlying drive for specific information processing and generating plasticity during sleep.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.