Japan
News

28 Feb 2023
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Nano Letters the discovery of a biomolecular dynamical process likely relevant to gene expression. The process, revealed by means of high-speed atomic force microscopy, involves DNA and its packaging molecules.
28 Feb 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists identified about 140,000 molecular clouds in the Milky Way Galaxy from large-scale data of carbon monoxide molecules, observed in detail by the Nobeyama 45-m radio telescope. Using artificial intelligence, the researchers estimated the distance of each of these molecular clouds to determine their size and mass, successfully mapping the distribution of the molecular clouds in the Galaxy in the most detailed manner to date.
27 Feb 2023
Scientists at Tokyo Medical and Dental University have discovered a new type of bone repairing material that could be used to more precisely fix bone defects.
24 Feb 2023
A research group from the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Medicine conducted a survey of 285 patients regarding the long-term aftereffects of COVID-19. As a result, they revealed that more than half of COVID-19 patients still had residual symptoms, even close to a year afterward. It became clear that fatigue, abnormalities in senses of taste and smell, hair loss, and sleep disorders could persist, regardless of the severity of the initial COVID-19.
24 Feb 2023
Synthetic hydrogels were shown to provide an effective scaffold for neuronal tissue growth in areas of brain damage, providing a possible approach for brain tissue reconstruction.
21 Feb 2023
An effective, stable solid-state electrochemical transistor has been developed, heralding a new era in thermal management technology.
21 Feb 2023
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have developed principles and technologies of nanofluidic devices to freely manipulate nanomaterials, biomaterials, and molecules at the single-molecule level using fundamental technologies such as nanofluidic processing, functional integration, and fluidic control and measurement, which has pioneered the way to integrate various fields under nanofluidics.

21 Feb 2023
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Angewandte Chemie International Edition how the formation and deformation speed of interlocked molecular structures called rotaxanes can be tuned — a discovery that may lead to an enhanced functionality of rotaxanes as building blocks for molecular machines.
21 Feb 2023
Sifting through sewage for SARS-CoV-2 genetic material could help authorities tailor infection control policies.
16 Feb 2023
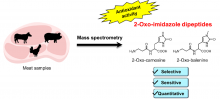
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists found that 2-oxo-imidazole-containing dipeptides (2-oxo-IDPs) exhibit very high antioxidant activity. Furthermore, they established a method to selectively and sensitively detect very small amounts of 2-oxo-IDPs and revealed for the first time that several types of 2-oxo-IDPs are contained in meat, including beef, pork, and chicken.
15 Feb 2023
To clarify the mechanism of serial dependence in number perception, a research team from Osaka Metropolitan University conducted two tests, independently asking subjects to estimate the number of coins, or to estimate the value of those coins, shown on-screen for half a second. The results showed that serial dependence was confirmed in both tasks and that the most significant effect on serial dependence was not caused by the last stimuli, but the subjects last response. These results indicate that higher-order cognitive processing has a greater influence on the occurrence of serial dependence.
13 Feb 2023
Team studies discrimination, mental distress, and work impairment in COVID-19 survivors.
13 Feb 2023
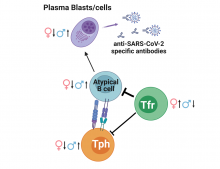
Researchers from Osaka University have shown sex-specific differences in the immune response to COVID-19 infection. By identifying and analyzing the immune cell population in COVID-19 patients, they showed that infection results in a reduced ratio of circulating follicular T regulatory (cTfr) cells to a network of antibody-producing proteins, correlated with dysregulated antibody production. This cTfr cell reduction is more significant in males, providing cellular evidence for the observed association between increased risk and male sex.
13 Feb 2023
A research group from the Graduate School of Engineering at Osaka Metropolitan University has shown that 3C-SiC exhibits high thermal conductivity equivalent to the theoretical value, based on thermal conductivity evaluation and atomic-level analysis, for the first time. They demonstrated that a 3C-SiC film on silicon substrate had a high thermal conductivity and expect that fabricating large-diameter wafers can be achieved at a low cost. The discovery should lead to improved heat dissipation in everyday electronic devices.

12 Feb 2023
In hepatic steatosis, hepatocytes "die," resulting in liver damage. Severe steatosis increases hepatocellular deaths, thus aggravating liver damage. The mechanism is unclear. Using mice, we show that mild steatosis causes apoptosis whereas severe steatosis predominantly causes necroptosis leading to cell rupture. This induces strong inflammation and new cell death, producing further liver damage. We reveal the transcription factor ATF3 to be involved in this process. Our results are expected to contribute to therapeutic method development.
10 Feb 2023
Hydrothermal vents have been identified as a previously undiscovered source of dissolved black carbon in the oceans, furthering the understanding of the role of oceans as a carbon sink.
10 Feb 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have demonstrated that fish can recognize “it’s me” when they themselves in a picture for the first time in non-human animals. Further testing made it clear that the fish recognize their own face in the pictures like humans.
08 Feb 2023
Hokkaido University researchers have developed a novel method to design and develop peptide antibiotics in large numbers, which will prove critical to controlling antibiotic resistance.
07 Feb 2023
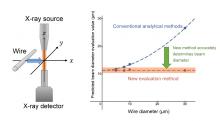
A research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has derived a new evaluation method for the measuring the size X-ray microbeams (diameter) through mathematical analysis. The group then verified the validity of the mathematically derived evaluation method by measuring the diameter of X-ray microbeams using metal wires of various diameters with an X-ray fluorescence analysis system for small areas and found that it was possible to calculate the beam diameter more accurately than the previous conventional evaluation method.
07 Feb 2023
Two catalysts working in tandem enable inexpensive formate salts to perform difficult dearomative reactions, giving products potentially useful for drug development.
06 Feb 2023
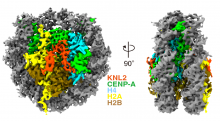
Researchers led by Osaka University used cryogenic electron microscopy to analyze the atomic structure of the centromeric region of the chromosome, essential for cell division. A protein called CENP-A marks the centromere; the researchers showed that during interphase, CENP-A is bound by a protein called KNL2 to maintain the location of the centromere. During mitosis, KNL2 is replaced by CENP-C, allowing correct formation of the kinetochore complex for cell division.
06 Feb 2023
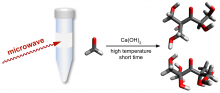
Researchers from Osaka University expanded the synthetic toolkit for preparing valuable chemical precursors from renewable feedstocks. They used microwave irradiation to dramatically improve the selectivity of the formose reaction, forming a simple six- and seven-carbon mixture that can be readily purified. These findings will help the chemicals industry minimize the use of fossil resources and improve the sustainability of manufacturing processes.
03 Feb 2023
Researchers used the James Webb Space Telescope to identify the precise location of a powerful energy source hidden by cosmic dust in the luminous merging galaxy IIZw096.
03 Feb 2023
Researchers used a chemical synthesis robot and computationally cost effective A.I. model to successfully predict and validate highly selective catalysts.
02 Feb 2023
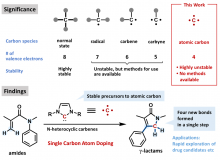
Researchers from Osaka University have used single carbon atom doping to form four chemical bonds in one step. Gamma-lactams (cyclic molecules that are common in antibiotics) were easily synthetically accessible from alpha, beta-unsaturated amides (an important molecule in cancer progression). The team chemically modified an anti-seizure medication in 96% yield, highlighting the work's utility to otherwise synthetically complex aspects of pharmaceutical development. The results of this work could become foundational to drug discovery and development.
02 Feb 2023
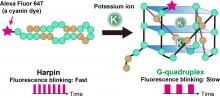
A new microscopic technique allows for the real-time study of RNA G-quadruplexes in living cells, with implications for the fight against amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
01 Feb 2023
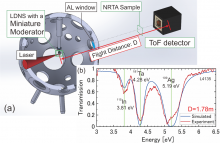
Osaka University researchers investigated the physics of laser-driven neutron sources, and found the relationship between the power and the neutrons generated. They were able to decrease the exposure time needed for neutron absorption experiments, which may be employed in biomedical research.
31 Jan 2023
A research group at the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Informatics has developed a new learning method for artificial intelligence that combines classification performance for data with multiple labels with the ability to learn continually from data. Numerical experiments on real-world multi-label data indicate that the new method outperforms conventional approaches. The simplicity of this algorithm makes it easy to integrate it with other algorithms to devise new ones.
31 Jan 2023
Data stored in ice cores dating back 55 years bring new insight into atmospheric levels of a molecule that can significantly affect weather and climate.
31 Jan 2023
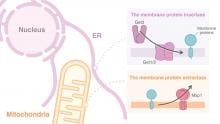
Researchers from Osaka University have shown that a system known as the GET pathway is essential for efficient mitophagy, the process by which mitochondria are removed from cells. The GET pathway targets a protein assembly called the Ppg1–Far complex, which inhibits mitophagy, to the membrane of a part of the cell called the endoplasmic reticulum. When the GET pathway is defective, this complex instead becomes targeted to mitochondria, where it acts to suppress mitophagy.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater