Japan
News
20 Mar 2023
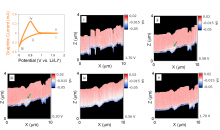
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in JACS Au how they have developed operando scanning ion conductance microscopy to allow simultaneous measurements of changes in the anode surface topography of a lithium ion battery during use, as well as the varying ion concentration with depth. Combining both types of information should help researchers evaluate the correlation between the two to design better batteries.
20 Mar 2023
Parasitic infections in salmonid fish can increase or decrease their vulnerability to angling, depending on their body condition.
20 Mar 2023
By adapting technology used for gamma-ray astronomy, researchers has found X-ray transitions previously thought to have been unpolarized according to atomic physics, are in fact highly polarized.
15 Mar 2023
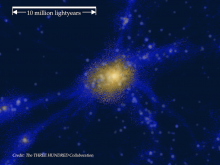
A team led by Kavli IPMU researchers have found the earliest evidence of parts of the universe that were heated to temperatures more characteristic to the intergalactic gas medium where most atoms reside in the universe today.
15 Mar 2023
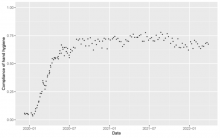
An Osaka University study investigated how the COVID-19 onset and media coverage affected hand hygiene compliance. Voluntary use of hand sanitizer in a hospital rose from 5% in December 2019 to 70%+ by August 2020. In the same period, TV coverage reached 7.7 hours/day on a national broadcaster. The study’s simulations found a significant relation between TV coverage and hand hygiene compliance, though no correlation between compliance and newly confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths.
15 Mar 2023
Researchers have revealed the modulatory effect of the anti-inflammatory metabolite itaconate on T helper and T regulatory cells, which may lead to new therapeutic approaches to treating some autoimmune diseases.

14 Mar 2023
In a study recently published in the journal ACS Nano, published by American Chemical Society, researchers from Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, collaborating with University of Washington, Seattle, USA, used frequency modulated atomic force microscopy to reveal the molecular architecture of a genetically designed peptide and its self-organization that forms single-molecule thick crystals on atomically flat graphite surfaces, that offer a potential platform for hybrid technologies such as bioelectronics, biosensors, and protein arrays.

13 Mar 2023
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in ACS Nano how high-speed atomic force microscopy can be used to study the biomolecular mechanisms underlying gene editing.
13 Mar 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists succeeded in directly observing how LECs—which are attracting attention as one of the post-organic LEDs—change their electronic state over time during field emission by measuring their optical absorption via lamp light irradiation for the first time. This research method can be applied to all light-emitting devices, including not only LECs but also organic LEDs. This method is expected to reveal detailed electroluminescence processes and lead to the early detection of factors that reduce the efficiency of electroluminescence.
13 Mar 2023
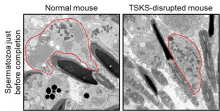
Researchers from Osaka University identified the role of a protein known as testis-specific kinase substrate (TSKS) in the process of spermiation, the release of mature sperm. Analysis of a gene-modified mouse model in which TSKS is disrupted revealed that TSKS is necessary for sperm to eliminate cytoplasm and become streamlined. These findings may lead to the development of diagnostic tests and male contraceptives.
10 Mar 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists successfully quantified the total reactive polysulfide content of 22 different types of vegetables, including onions and garlic. They also revealed that reactive polysulfides are not only found in the leek genus (Allium), such as onions and garlic but also in the cruciferous family of vegetables (Brassicaceae), such as broccoli and cabbage.
10 Mar 2023
The first-ever molecular catalyst specifically tailored for mechanochemical reaction conditions enables high-efficiency transformations at near room temperature.
08 Mar 2023
Finding extra-terrestrial life would transform how we view our place in the Universe, but reporting on the search for it poses challenges for scientists and the media.
08 Mar 2023
A science communication course at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) in Japan provides graduate students with practical skills to communicate research to a diverse audience.
08 Mar 2023
One astronomer never thought of leaving Japan, but then he did and became a world best.
07 Mar 2023
Asia Research News met five female researchers to learn about their research, what drew them to Kavli IPMU, and their experiences there. These women, from diverse backgrounds, excel in their fields and show what can be achieved when women are not held back.
04 Mar 2023
Scientists have shown that swarming molecular robots can deliver cargo five times more efficiently than a robot working on its own.
03 Mar 2023
An international collaboration is developing coating materials that could make windows better insulators.
03 Mar 2023
Hi-tech electrocatalysts made from seashells and waste animal blood could help build sustainable batteries, fuel cells and other electrochemical systems.
03 Mar 2023
Machine learning algorithms allow analysis and characterization of the atomic arrangement of silicon surface superstructures without the need for human expertise.
02 Mar 2023
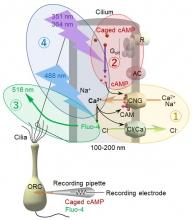
Researchers from Osaka University found that Ca2+ signaling simultaneously performed signal amplification and olfactory adaptation. The results demonstrated that this mysterious phenomenon was segregated inside the cilium. A novel system was used to observe changes in Ca2+ dynamics inside the thin structure of a cilium. Unveiling the mystery of Ca2+ signaling segregation further clarifies the mechanisms underlying the human sense of smell.
02 Mar 2023
Bioengineers formulated a mathematical model that clarified the importance of bat ear motions in direction detection, making way for lean, mean sonar navigation machines.
02 Mar 2023
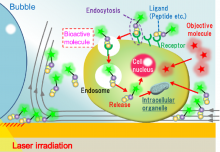
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have used 100 seconds of laser irradiation to generate convection currents that selectively accelerate biochemical reactions—due to the photothermal effect—by concentrating biofunctional molecules at the cell surface. Using this method, useful molecules can be transported into cells at concentrations a hundred to a thousand times lower than with conventional methods. Furthermore, they also succeeded in selectively introducing small molecules into intracellular organelles usually impossible at low concentrations (hundreds of pmol/L) as well as inducing cell death in targeted cells by concentrating anticancer active peptides into them at concentrations so low that they would not be conventionally effective (several tens of nmol/L).
02 Mar 2023
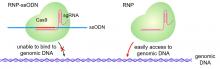
Lipid nanoparticles have been used to encapsulate CRISPR-Cas9 and deliver it to cells in mice, where it was highly effective at knocking down expression of a target protein.
01 Mar 2023
Brain shrinkage patterns tied to low trust have links to depression vulnerability that can alert to its early detection even before symptoms appear.
01 Mar 2023
An international research team has discovered the first example of a supernova, known as SN 2018ivc, showing an unprecedented rebrightening at millimeter wavelengths about one year after the explosion.
With the help of the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array -- or ALMA -- the analysis revealed that the dying massive star ejected a large amount of its envelope due to a strong binary interaction with a companion star that took place about 1500 years before the explosion.
In a paper published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, the team posits that this rebrightening event in SN 2018ivc provides a missing link between supernovae -- or SN -- that occur in binary star systems and those that involve solitary massive stars.
28 Feb 2023
A model that rapidly searches through large amounts of materials could find sustainable alternatives to existing composites.
28 Feb 2023
2.5-dimensional materials promise new applications for artificial intelligence, electronics, automobiles and the energy sector.
28 Feb 2023
Two novel hypotheses address the “two-fold cost of sex”: one of the biggest enigmas in the evolution of sexual reproduction.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater