Japan
News
16 Aug 2023
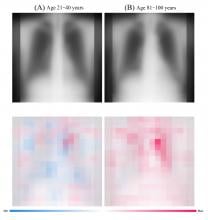
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have developed an AI model that accurately estimates a patient’s age, using chest radiographs of healthy individuals collected from multiple facilities. Furthermore, they found a positive relationship between differences in the AI-estimated and chronological ages and a variety of chronic diseases, such as hypertension, hyperuricemia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In the future, it is expected that AI biomarkers will be developed to predict life expectancy, estimate the severity of chronic diseases, and forecast surgery-related risks.
10 Aug 2023
Hokkaido University researchers found that tiny nematode worm larvae surf electric fields to hitch rides on passing insects.
09 Aug 2023
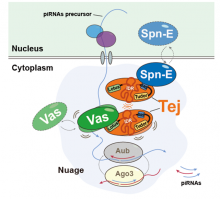
Researchers from Osaka University clarified the interactions of the proteins Tejas (Tej), Vasa (Vas), and Spindle-E (Spn-E) in the formation of cellular compartments known as nuage and the processing of PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) precursors in Drosophila melanogaster ovaries. piRNAs help prevent the transmission of genetic mutations through reproductive cells, and insight into the dynamics of piRNA formation and processing may contribute to our understanding of the mechanisms underlying reproductive disorders, including infertility.
09 Aug 2023
A team led by researchers at Osaka University and University of California, San Diego has conducted simulations of creating matter solely from collisions of light particles. Their method circumvents what would otherwise be the intensity limitations of modern lasers and can be readily implemented by using presently available technology. This work might help experimentally test long-standing theories such as the Standard Model of particle physics, and possibly the need to revise them.
09 Aug 2023
Rheology of hexagonal close-packed iron determined by high-pressure and high temperature deformation experiments
08 Aug 2023
Researchers at the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo use computer simulations of glass-forming particles to discover a new type of exotic ordering impacting the fate of the material.
08 Aug 2023
Researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, provide physical insights into ion hydration in water-based solutions, which will aid electrolyte design for energy storage technologies.
07 Aug 2023
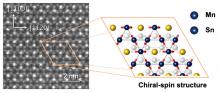
Researchers at Tohoku University and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have unveiled new information about the anomalous dynamics at play when an electric current is applied to a new class of magnetic materials called non-collinear antiferromagnets.
04 Aug 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists tested the antiobesity effects of Mallotus furetianus extract native to Hainan Island, China, using obesity model mice. As a result, body weight and adipose tissue weight of obesity model mice were significantly reduced by the intake of Mallotus furetianus extract. Fatty liver was suppressed and adipocyte size reduction in adipose tissue was observed. Further investigation into the mechanism revealed that fat synthesis is inhibited by suppressing the expression of several transcription factors involved in differentiation into adipocytes.
04 Aug 2023
Tohoku University geophysicist Yuto Katoh led a study into the activity of high energy electrons and clarified the unexpected role of the geomagnetic field surrounding the Earth in protecting.
04 Aug 2023
A research team from the Graduate School of Rehabilitation Science at Osaka Metropolitan University investigated the electrophysiological benefits of working in the presence of others from the perspectives of brain and autonomic nervous system activity. The researchers found that parasympathetic activity—which indicates relaxation—was significantly higher when two individuals were working separately than when one individual was working alone. This suggests that arranging the former condition in occupational therapy for individuals with high levels of tension or anxiety in clinical settings may potentially help alleviate these feelings.
03 Aug 2023
The researchers from Osaka University showed how bone erosion caused by cholesteatoma occurs. This study showed that a subset of cells called osteoclastogenic fibroblasts expresses a protein, activin A, which causes the breakdown of the bones. Because of this discovery, novel medical treatments can be developed as first-line management for cholesteatomas.
02 Aug 2023
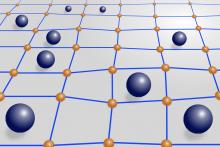
Soft metal-organic polymer networks can adsorb selected molecules from gas mixtures by opening pores when the molecules bind.
02 Aug 2023
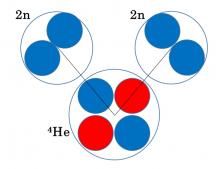
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have shown that within the helium-8 nucleus (with two protons and six neutrons), there are two clusters of two neutrons each, existing around the helium-4 core. Furthermore, they demonstrated the shape these clusters take. Nuclei with an imbalance of protons and neutrons, such as in helium-8, do not naturally exist on Earth but are believed to be abundantly generated in cosmic environments like the interiors of stars through the process of nucleosynthesis. This study’s findings provide new insights into the still largely unknown binding forms of neutrons and deepen our understanding of the origins of the elements that surround us.
02 Aug 2023
Molecules that act as connected wheels can hold long molecular chains together to modify the properties of soft polymers.
01 Aug 2023
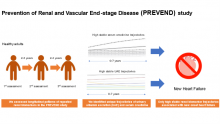
Researchers from Osaka University found that patients with persistently high levels of urinary albumin excretion in the long term are at high risk of new-onset heart failure. Preventive treatment associated with the lowering of urinary albumin excretion levels in these patients could reduce the risk of later heart failure or mortality.
31 Jul 2023
Researchers from Osaka University have demonstrated a proof-of-concept for identifying single nucleotides by using quantum computing. Molecular rotation patterns—and the corresponding variations in conductance—within the nanoscale gap between two electrodes enabled the development of a quantum gate for the nucleotide adenosine monophosphate. Developing quantum gates for the other three nucleotides, and incorporating this technology into DNA sequencing workflows, could revolutionize genome analysis.
27 Jul 2023
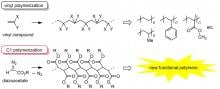
succeeded in preparing atactic C1 polymers with a high melting point of up to 130 ℃ by utilizing a hydrogen-bonding interaction among amide-linkages incorporated into the polymer side-chains.
27 Jul 2023
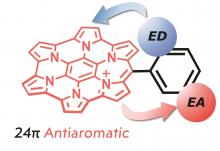
Elucidation of global anti-aromaticity (aromaticity) in homoHPHAC+ (homoHPHAC3+) with electron-accepting to electron-donating substituents
27 Jul 2023
What does healthy aging look like? For answers, Hiroshima University environmental health expert Dr. Saori Kashima taps into a new science dedicated to Earth’s longevity.
26 Jul 2023
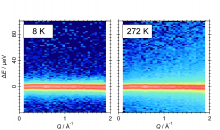
Researchers from Osaka University use quasi-elastic neutron scattering to get a close look at the behavior of water molecules in a semiclathrate hydrate crystal. They found that the molecules showed fast reorientation with an activation energy similar to that of cleaving a hydrogen bound. This rapid relaxation time in the solid electrolyte is expected to lead to efficient, cost-effective, and safe applications for semiclathrate hydrates in batteries and thermal storage materials.
21 Jul 2023
An exquisitely preserved fossil forest from Japan provides missing links and helps reconstruct a whole Eurasia plant from the late Miocene epoch.
20 Jul 2023
Researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, provide physical insights into porous soft materials, which will facilitate the design of many energy, medical, and other technologies.
19 Jul 2023
A joint research group at Osaka Metropolitan University conducted a survey on prevalence of obesity and factors associated with low obesity among 423 adolescents between the ages of 14 and 19 living in Harare, Zimbabwe. The results revealed that 15.8% were obese or overweight. The study also revealed that 27.1% of the participants had low obesity awareness, which was significantly related to parents/guardians' lack of formal education and insufficient knowledge about eating habits.
18 Jul 2023
RNases have been proposed as a treatment against systemic autoimmune diseases. Researchers from Osaka University showed that RNases have a dual action. In some cases, RNases are detrimental and stimulate the immune response by promoting the binding of antibodies to their targets. These findings will improve the understanding and treatment of systemic autoimmune disorders.
14 Jul 2023
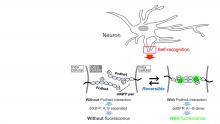
Researchers from Osaka University have developed a fluorescent sensor that may be useful for understanding how cells recognize themselves versus other cells when making connections in the brain. Specifically, their sensor can be used to visualize not only connections between cells, but also the disassociation of these interactions. Because neuronal self-connectivity has been implicated in brain disorders like epilepsy and autism, a better understanding of this process may result in improved therapies.
14 Jul 2023
Researchers from Northwestern University and recently joining the Institute for Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo develop a high-throughput approach to evaluate protein folding stability in thousands of proteins .
11 Jul 2023
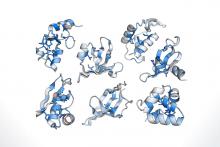
A research team has discovered an astounding array of unexplored protein folds. This research will expand our understanding of the depth of the protein universe and the possibilities for de novo design of functional proteins.
11 Jul 2023
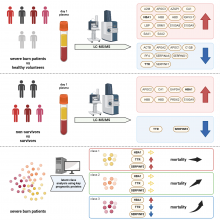
The physiological mechanisms underlying severe burns are not well understood. Researchers at Osaka University used mass spectrometry to identify key blood proteins associated with burn mortality. Ultimately, three proteins (HBA1, TTR, SERPINF2) were very highly correlated with morality rates. Further research into these proteins and their pathways may lead to better drugs to treat people with life-threatening burns.
11 Jul 2023
The entire biosynthetic pathway of actinopyridazone has been unveiled, revealing that an unprecedented carrier protein-mediated ring-forming step is key to its synthesis.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater