Japan
News
29 Sep 2023
Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have succeeded in printing uniformly sized droplets with a diameter of approximately 100 µm using a liquid film of fluorescent ink. This ink, with a viscosity roughly 100 times that of water, was irradiated with an optical vortex, resulting in prints of exceptional positional accuracy at the micrometer scale.
29 Sep 2023
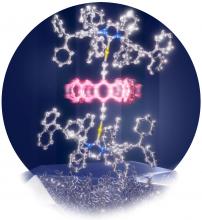
Concave, umbrella-like metal complexes provide space to enable the largest molecular rotor operational in the solid-state.
21 Sep 2023
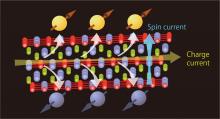
A recent discovery in spintronics could potentially transform future electronics. A group of researchers have revealed the key role of cobalt-tin-sulfur in reducing energy consumption, unlocking new possibilities for high-speed, low-power spintronic devices.
20 Sep 2023
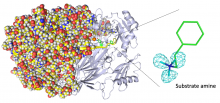
A team led by researchers at SANKEN (The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research), at Osaka University has used neutron crystallography to image all of the atoms in a radical intermediate of a copper amine oxidase enzyme. They disclosed previously unknown details, such as precise conformational changes, that help to explain the enzyme's biochemistry. This work might help researchers engineer enzymes that facilitate unusual chemistry or are highly efficient at room temperature that are useful in chemical industry.
15 Sep 2023
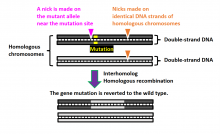
Researchers led by Osaka University developed a novel genome editing technique known as NICER, which results in significantly fewer off-target mutations than CRISPR/Cas9 editing. The technique uses a different type of enzyme that makes single-stranded “nicks” in the DNA. Repair of these nicks is more efficient and accurate than repair of double-strand breaks caused by the current CRISPR/Cas9 editing. This technique represents a novel approach for the treatment of genetic diseases caused by heterozygous mutations.
15 Sep 2023
A reanalysis of studies on night shift naps reveals the ideal snoozing schedule that may help combat fatigue and drowsiness when staying up all night.
14 Sep 2023
Lab-based studies reveal how carbon atoms diffuse on the surface of interstellar ice grains to form complex organic compounds, crucial to reveal the chemical complexity in the universe.
14 Sep 2023
Scientists have found that extracellular calcium mediates the activation of a membrane protein that waves the flag signalling cell death
14 Sep 2023
To address the lack of suitable training data for deep-learning semantic segmentation models in urban landscaping, researchers from Osaka University developed a method that generates a training dataset without the need for real images or a model of an existing city. The method, which is based on procedural modelling and image-to-image techniques, enables segmentation models to achieve comparable performance under some conditions at a fraction of the cost of real dataset generation.
13 Sep 2023
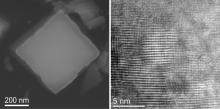
Systematic copper doping boosts all-solar utilization in tungstic acid nanocrystals.
11 Sep 2023
An international team of scientists has successfully conducted large-scale helicopter-based observations along the coast of East Antarctica and has identified pathways through which warm ocean water flows from the open ocean into ice shelf cavities for the first time.
11 Sep 2023
Patients with a specific form of chronic indigestion react differently to images of food, compared to healthy control subjects or patients with irritable bowel syndrome.
11 Sep 2023
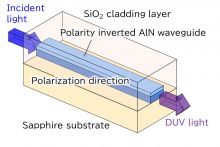
A research team led by researchers from Osaka University created an aluminum-nitride device that can convert visible light into deep-ultraviolet light through the process of second harmonic generation. This work can lead to the development of practical devices that can sterilize surfaces with ultraviolet radiation while using less energy.
11 Sep 2023
Elusive fundamental particles called neutrinos are predicted to interact unexpectedly with photons under extreme conditions.
11 Sep 2023
Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a measurement technique that rapidly measures the number of viable bacteria in food products. They have succeeded in drastically reducing the inspection time from 2 days to about 1 hour. With this technology, it will be possible to confirm food safety before shipment from factories and prevent food poisoning.
10 Sep 2023
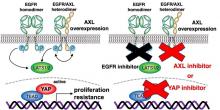
AXL and EGFR inhibitors combined hold promise in fighting certain head, neck, and lung cancers
04 Sep 2023
Researchers from Osaka University have revealed that the expression of a specific isoform of GREB1 Is4 is induced in malignant melanoma cells by the melanocyte-specific transcription factor, MITF. They revealed that GREB1 Is4 stimulates pyrimidine biosynthesis and promotes cancer cell proliferation. Furthermore, the anti-tumor effect of antisense nucleic acids against GREB1 showed a potential new modality for malignant melanoma.
04 Sep 2023
In recent years, an emerging zoonotic pathogen called E. albertii, transmitted by wild animals such as raccoons, has garnered attention due to its remarkable similarities to several strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli), including O157, and its potential to cause severe illness, particularly in children. A research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has developed a novel culture medium that allows for the selective cultivation of E. albertii from raccoon fecal samples. This enabled the successful isolation of E. albertii even from samples with very low quantities of this bacterium. Their findings are expected to further elucidate the bacteriological characteristics of E. albertii and to contribute to the control of foodborne illnesses.
01 Sep 2023
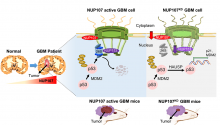
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in Cell Reports how alterations in the nuclear pores lead to the degradation of anti-tumor proteins.
01 Sep 2023
Survey observations with the Subaru Telescope have led to the discovery of 22 quasars in the very distant universe. Their space density indicates the rapid emergence of supermassive black holes soon after the Big Bang, providing strong constraints on models of when, where, and how they formed and grew in cosmic space-time. The results also indicate a small quasar contribution to cosmic reionization, a major phase transition of the early universe.
29 Aug 2023
Machine learning model provides quick method for determining the composition of solid chemical mixtures using only photographs of the sample.
29 Aug 2023
A long-lived monocarpic species of bamboo, Phyllostachys nigra var. henonis, only flowers once every 120 years before it dies. The upcoming flowering event for this species does not bode well for its continued long-term survival, as most flowers are not producing viable seeds.
25 Aug 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have verified the anticancer effects of Kencur, a tropical plant of the ginger family, mainly grown in Southeast Asia, in cell and animal experiments. They found that Kencur extract and its main active components significantly inhibit cancer cell growth at the cellular and animal levels. Furthermore, the involvement of TFAM in the mechanism of action was confirmed.
23 Aug 2023
The search for innovative materials will be greatly assisted by software that can suggest new experimental possibilities and also control the robotic systems that check them out.
23 Aug 2023
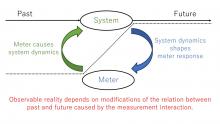
Quantum physicists have found that the outcomes of measurements are shaped by the complex dynamics of measurement interactions, questioning our usual understanding of observable reality.
23 Aug 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers conducted a 5-year claims-based study of 655 non-frail or pre-frail older adults who were certified as having low care needs to investigate the relationship between the risk of frailty and two types of care services. The results showed that users of community-based adult care services had a 40% reduced risk of developing frailty compared to non-users. This suggests that utilizing appropriate support and services can prevent the progression of frailty.
22 Aug 2023
Researchers from SANKEN (The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research) at Osaka University and two other universities used topological data analysis to improve the predictions of physical properties of amorphous materials by machine-learning algorithms. This may allow for cheaper and faster calculations of material properties.
21 Aug 2023
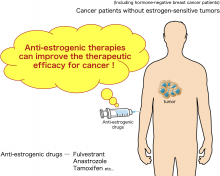
Anti-estrogenic therapies can suppress the growth of cancer that does not express estrogen receptors; when combined with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies, they halt tumor progression in mice models.
19 Aug 2023
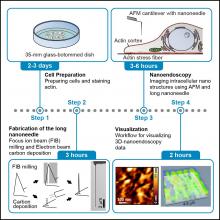
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in STAR Protocols procedural details and tips for nanoendoscopy-AFM, for capturing images of nanoscale structures inside living cells.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater