Japan
News

07 Feb 2012
The Japan National Tourism Organization (JNTO) awarded Professor Hitoshi Isahara from Toyohashi University of Technology the "Award for Contribution to Invitation and Organization of an International Conference in 2011" for successful invitations to the 8th International Conference on Natural Language Processing, JapTAL 2012.
06 Feb 2012
Granta Design today announced an agreement with Japan’s National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) to provide searchable access to metals property data from NIMS.
06 Feb 2012
Researchers at the RIKEN Omics Science Center (OSC) have developed a robotic workflow for sample preparation on the HeliScope single molecule sequencer which drastically reduces sample preparation time to from 42 days to only 8 days.

06 Feb 2012
Professor Masahiko Abe, et al. from the Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology at Tokyo University of Science, have succeeded in developing “Technology for the mass production of ceramics micro/nano springs (CMS).”

06 Feb 2012
The Research Institute for Advanced Network Technology (RIANT) at Waseda University has formed the Demand Response Technology Research Program, together with nine companies.
06 Feb 2012
“Jukusui-kun (Mr. Deep Sleep)”, a robot supporting patients with sleep-apnea syndrome etc., on display
06 Feb 2012
Research group headed by Professor Takashi Tsuji demonstrates in “Reinforcement of microfibril rescues microfibril disorder of Marfan’s syndrome”.
Substantial advance in the development of novel strategy of Marfan’s syndrome.

06 Feb 2012
A new diagnosis technique developed by researchers at the RIKEN Omics Science Center (OSC) has succeeded in detecting influenza virus infection in only 40 minutes and with one hundred times the sensitivity of conventional methods.

06 Feb 2012
Miho Namba, an Associate Professor at Waseda University, shares her thoughts on the communication of science and technology in Japan, taking the activities of the Science Media Centre at the time of the earthquake as an example.
06 Feb 2012
Professor Sadahiko Kano from the Faculty of International Research and Education, Waseda University, explores the challenges for international standardization.

06 Feb 2012
Japanese workers are said to be hard working. One of the reasons is the long working hours. So-called full-time employees work some 2,000 hours per year, which is 400 hours longer than their counterparts in Germany or France.

03 Feb 2012
Derivation of equations that describe the dynamics of complex magnetic quasi-particles may aid the design of novel electronic devices

03 Feb 2012
Industrial chemistry is set to improve from novel rare-earth metal catalysts that reduce waste and improve aromatic bond-forming reactions
03 Feb 2012
A ‘gatekeeper’ protein plays a critical role in helping immune cells to sound a warning after encountering signs of tumor growth or infection
27 Jan 2012
Demonstration of a rare combination of electric and magnetic properties in a now readily producible material could improve electronic memory devices
27 Jan 2012
Clarification of metabolite regulation and distribution in a large, freshwater algal cell illuminates important aspects of general cell metabolism
27 Jan 2012
A large-scale study of East Asian individuals reveals a number of previously overlooked genetic variants with potential roles in a number of metabolic diseases
27 Jan 2012
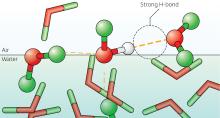
High-level spectroscopy and computer simulations of specially diluted liquids reveal the long-debated structure of air–water interfaces
23 Jan 2012
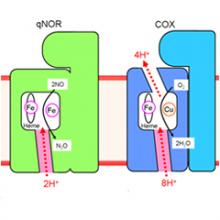
Researchers at the RIKEN SPring-8 Center have clarified the crystal structure of quinol dependent nitric oxide reductase, a bacterial enzyme that offers clues on the origins of our earliest oxygen-breathing ancestors. The findings provide key insights into the production of nitrogen oxide, a greenhouse gas hundreds of times more potent than C02.

20 Jan 2012
Presenters from Japan and Singapore gathered at the National University of Singapore to discuss the latest research in infectious diseases
20 Jan 2012
A chemical probe that can differentiate between chemical tags adorning DNA could provide insights into how nature switches genes on and off
20 Jan 2012
A new model of intracellular signaling via calcium ions will assist in understanding the effects of calcium fluctuations
20 Jan 2012
The draft genome of the Chinese cabbage could underpin genetic improvement of brassica vegetable and oil crops
17 Jan 2012
Prof. Dr. Sherif A. El-Safty, a Principal Researcher of the Materials Recycling Design Group, Research Center for Strategic Materials, National Institute for Materials Science developed a nanomaterial which enables simple detection and removal of arsenic from drinking water.
13 Jan 2012
A particular type of age-related macular degeneration in the Japanese population is linked to four regions of the genome
13 Jan 2012
Fast and sensitive detection and identification of air-borne gases is now possible using a newly developed sensor
13 Jan 2012
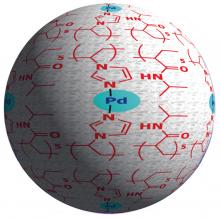
Wrapping palladium nanoparticles inside a self-assembled polymer matrix makes catalysts easier to retain and recycle
12 Jan 2012
NIMS is collecting basic data on natural minerals produced in various regions and inorganic materials with different chemical compositions as a tool for selecting suitable materials, and will make this information available in a NIMS Materials database (MatNavi).
06 Jan 2012
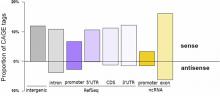
Researchers at the RIKEN Omics Science Center, collaborating with scientists from Italy, Norway, the United States, the United Kingdom and Germany, have found promoters for olfactory receptor genes using nanoCAGE technology, which enables comprehensive analysis of transcription start sites (TSSs) from tiny biological samples.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater