Japan
News

30 Mar 2012
On March 11, 2011, on the campus of Waseda University in Shinjuku, Tokyo, those in laboratories and study rooms on some floors experienced such incredible shaking that they could not stay on their feet. We, on the staff of the Science Media Centre (SMC), also evacuated outdoors.
30 Mar 2012
Nano Characterization Unit of Advanced Key Technologies Division in NIMS and the State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Zhejiang University, have agreed to a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) on the research and development in the field of novel low-dimensional nanomaterials.
30 Mar 2012
On 5th Mar, 2012, The High Temperature Materials Unit at Japan's National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), concluded a Memorandum of Understanding MOU concerning "Protection of materials against oxidation and hot corrosion" with DECHEMA Forschungsinstitut (DFI), Germany.
30 Mar 2012
A central regulator of the inflammatory response shows signs as an appealing target for therapies against autoimmune disease
30 Mar 2012
Human attention to a particular portion of an image alters the way the brain processes visual cortex responses to that image
30 Mar 2012
A newly discovered enzyme brings scientists one step closer to understanding how plants manufacture a molecule with potent medicinal properties

27 Mar 2012
Professor Daisuke Kitamura of Tokyo University of Science and his research group have developed a new culture system in which B cells undergo massive expansion and generate germinal centre B cells, which can then differentiate into cells responsible for immunological memory.
27 Mar 2012
Yoshikuni Edagawa from Waseda University examines the bright and dark sides of dietary supplements.
23 Mar 2012
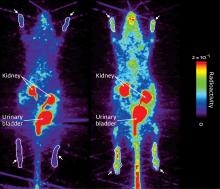
Detecting imminent attacks of gout is now possible using a new modification to an established medical imaging technique
23 Mar 2012
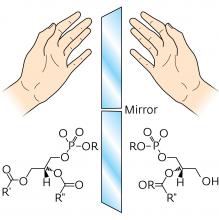
Spectroscopic evidence for the unusual handedness of a mammalian lipid may advance our understanding of evolution
23 Mar 2012
Mutations in people with cancerous Lynch syndrome prevent a DNA mismatch repair protein from doing its job properly
22 Mar 2012
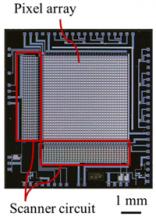
The pH image sensor was invented by Kazuaki Sawada of Toyohashi University of Technology (Toyohashi Tech). The device enables two dimensional visualization of both the pH and optical imaging of chemical activity of solutions and cell activity.
21 Mar 2012
At Toyohashi University of Technology the intriguing properties of graphene—a single atomic-layer of carbon—such as high electron mobility and fluorescence quenching are being exploited for biosensing and analysis of nucleotides, peptides, and proteins.
21 Mar 2012
Researchers at Toyohashi University of Technology have developed a new multimodal bio-image sensor.

21 Mar 2012
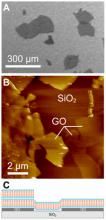
Here the Graphene Research Group at Toyohashi University of Technology report on the synthesis of graphene by reducing graphene oxide using microorganisms extracted from a local river.
21 Mar 2012
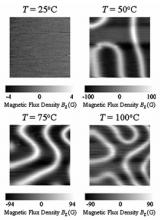
Researchers at Toyohashi University of Technology have invented Hall effect magnetic field sensors that are operable at high temperatures and harmful radiation conditions. The sensors will find applications in space craft and nuclear power stations.
21 Mar 2012
The National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) in Japan has concluded a Comprehensive Collaborative Agreement (a sister institute agreement) with Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI) in Republic of China (Taiwan).

19 Mar 2012
The Research Center for Agrotechnology and Biotechnology at Toyohashi University of Technology have made the university's original Japanese Sake (rice wine) again this year.

19 Mar 2012
Waseda University's Tadahiko Abiko argues that formal and informal education should be differentiated in discussion.

16 Mar 2012
On 21 February 2012, RIKEN President Ryoji Noyori visited the Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU) in China to attend the opening ceremony for the RIKEN-XJTU Joint Research Center.
16 Mar 2012
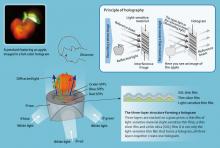
Researchers at the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute have developed a unique way to create full-color holograms with the aid of surface plasmons
16 Mar 2012
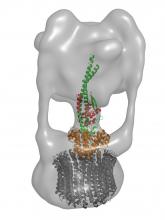
Structural data bring researchers one step closer to understanding the detailed mechanism underlying a complicated molecular machine
16 Mar 2012
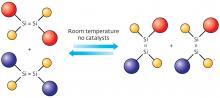
The dynamic equilibrium between two reactive silicon compounds provides chemists with improved tools for synthesizing optically and electronically active molecules
16 Mar 2012
By temporarily silencing a hyperactive gene, scientists dramatically boost the efficiency of mouse cloning

15 Mar 2012
Last week more than 150 international students and regional supporters for Toyohashi Univeristy of Technology's international students gathered in Toyohashi Chamber of Commerce, to have an annual meeting and the buffet party for Toyohashi Tech's International Students.
14 Mar 2012
Dr. Masanori Kohno, a MANA Scientist at the International Center for Materials Nanoarchitectonics, National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), theoretically clarified the nature of the metal-insulator transition due to electronic correlation (Mott transition).

14 Mar 2012
Researchers at the RIKEN Omics Science Center (OSC) have successfully developed and demonstrated a new experimental technique for producing cells with specific functions. As an alternative to induced pluripotent stem cells, the technique promises to enable faster production of functional cells for use in cancer therapy and other areas.
13 Mar 2012
By Yoshihiro Kanno, Composer and Professor at Waseda University, Faculty of Science and Engineering, School of Intermedia Art and Science

12 Mar 2012
Comment on one year anniversary by Waseda University President Kaoru Kamata

12 Mar 2012
Mathematical Model Describes the Collaboration of Individual Neurons
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater