Japan
News
25 Feb 2013
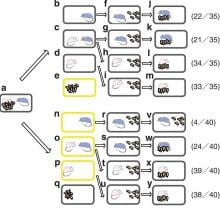
Kanazawa, Japan, 25 Feb - Researchers at Japan’s Kanazawa University have proven the existence of communicative signalling from female mice that induces male parental behaviour. The research was published in Nature and is described in the Feb issue of the Kanazawa University Research Bulletin
25 Feb 2013
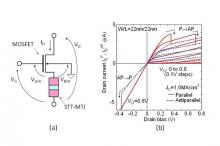
Tokyo, 25 Feb - Non-volatile bistable memory circuits being developed by Satoshi Sugahara and his team at Tokyo Tech pave the way for highly energy-efficient CMOS logic systems. The details are described in the Feb issue of Tokyo Institute of Technology Bulletin
25 Feb 2013
Tokyo, 25 Feb - Helium crystallization under micro-gravity, highly energy-efficient CMOS logic systems, and ham radio for global communication: the Feb issue of the Tokyo Tech Bulletin contains the latest information about cutting edge research projects and related activities at Tokyo Tech.

18 Feb 2013
Opinion article by Assist. Prof. Maho Isono, a cultural anthropologist in medicine. "Medical personnel frequently have feelings and conflicts that are not expressed to their patients, while patients often experience confusion and hesitation that are not told to medical personnel."
18 Feb 2013
In Algeria, education of young researchers and graduate students is also important issue and the Ambassador particularly took a great deal of interest in our graduate school and internship programs with universities both in Japan and overseas.
18 Feb 2013
Prof. Pairash Thajchayapong, Chairman of the Executive Board of NANOTEC, accompanied by Prof. Sirirurg Songsivilai, Executive director of NANOTEC paid a visit to NIMS President Prof. USHIODA.
07 Feb 2013
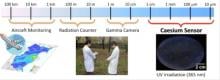
Tsukuba, Japan 7 Feb - Researchers in Japan have developed a way to detect caesium contamination on a scale of millimetres enabling the detection of small areas of radioactive contamination. The research is published in Science and Technology of Advanced Materials today.
07 Feb 2013
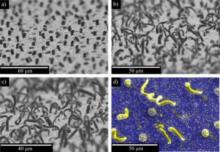
Tsukuba, Japan 7 Feb - Researchers at Ruhr University have used self-assembling techniques to produce gold microwires that have suitable properties for micro-Velcro. The research is published today in Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
30 Jan 2013
(Tokyo, 30 January 2013) Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology have produced a new form of photoactive micelles with potential applications in photofunctional dyes and sensors. The research was published in Angewandte Chemie recently.
22 Jan 2013
A Japanese team led by Kazuhiro Sato of Okayama University participates in the International Barley Sequencing Consortium (IBSC) to produce a high resolution assembly of the majority of barley genes.
22 Jan 2013
(Okayama, Japan, 22 Jan) Pioneering research from Okayama University on surgical treatment of congenital heart disease & inflammation & diabetic nephropathy, to plant activators to protect crops, DNA sequencing of barley & piezoelectric actuator for cryogenic temperature

16 Jan 2013
The Implications of the LDP’s Landslide Victory and the Proliferation of Small Parties - Opinion article by Prof. Masanobu Ido, Professor, Faculty of Education and Integrated Arts and Sciences, Waseda University
15 Jan 2013
World’s First Successful Power Switch Using a Diamond Semiconductor. In the future, this technology may contribute to a new energy strategy in Japan through offshore wind energy, efficient power transmission across the Japanese archipelago, and more.

15 Jan 2013
Professor Oka and his research team at Waseda University have succeeded in developing the world's first conceptual nuclear reactor design of high plutonium breeding by light water cooling.
08 Jan 2013
(Aichi, Japan, 8 January, 2013) – Aisin Seki Co., Ltd welcomes visitors to experience its latest innovative ITS technology on exhibition at North American International Auto Show, Detroit, 14–27 January 2013.
04 Jan 2013
(Kanazawa, Japan, 4 January 2013) High-speed atomic force microscopy (HS-AFM) is providing the means to produce dramatic footage of moving biomolecules, and scientists at Kanazawa University leading the field.

04 Jan 2013
(Kanazawa, Japan, 4 Jan) From atomic force microscopy for moving biomolecules; to the motion of titanium in the mantle; atomically controlled diamond surfaces for next-generation high-power electronics and more— Kanazawa University Research Bulletin an overview of their research.

21 Dec 2012
"Regularly trained athletes often do too much exercise, and they catch a cold more easily than general people." An interview with Takao Akama, Professor at Faculty of Sport Sciences, Waseda University in Japan about how athletes' health and immunity.
20 Dec 2012
(Tsukuba, 21 December 2012) Researchers in Japan and the US propose a nanoionic device with a range of neuromorphic and electrical multifunctions that may allow the fabrication of on-demand configurable circuits, analog memories and digital–neural fused networks in one device architecture.
12 Dec 2012
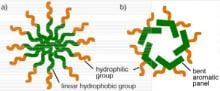
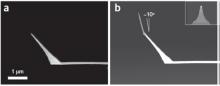
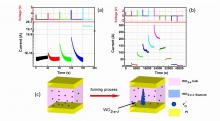
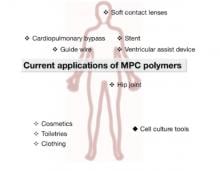
In their recently published review article in the Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, Yasuhiko Iwasaki at Kansai University and Kazuhiko Ishihara at the University of Tokyo describe how developments in synthesis techniques have liberated the polymer MPC’s potential for a huge range of medical and biological applications.
05 Dec 2012
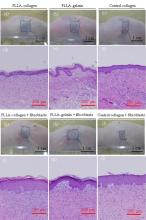
Tsukuba, Japan 5 Dec - Researchers in Japan have created a hybrid scaffold which promotes regeneration of skin in live animals while maintaining mechanical strength making it a promising material for future skin tissue engineering. This research was recently published in the Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
04 Dec 2012
The cortical mechanisms governing speech are not well understood because it is extremely challenging to measure the activity of the brain in action, that is, during speech production. Researchers in Japan have found modulation of mu-rhythms in the cortex related to speech production.

04 Dec 2012
Electric vehicles (EV) have ten times higher energy performance than automobiles powered by gasoline-based engines. However, they are not yet popular with drivers due to the need to store large batteries onboard. Now, Takashi Ohira and colleagues are developing an innovative method for powering EVs that drastically reduces the number of batteries.
04 Dec 2012
Hitoshi Goto and colleagues have developed high performance molecular simulation tools to study the 3D arrangement of molecules, enabling better design of medicinal and agricultural drugs which are more effective and fewer side effects
26 Nov 2012
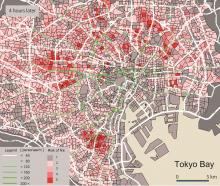
(Tokyo, 26 November 2012) Tokyo Tech ‘s Toshihiro Osaragi and colleagues report on models for evacuation procedures in big cities after massive earthquakes based on the behavior of people in Tokyo after the Tohoku-Pacific Ocean Earthquake on 11 March 2011.
26 Nov 2012
(Tokyo, 26 November 2012) Models for earthquake evacuation procedures, training computer to understand the human brain, and Lewis acid catalysts for industry—the November issue of the Tokyo Institute of Technology Bulletin contains the latest information about cutting edge research projects and related activities at Tokyo Tech.
19 Nov 2012
Aichi, Japan, 19 November 2012 - Over 180 participants attended the IRAGO Conference in Aichi, Japan which aimed to enhance mutual understanding between scientists, engineers and policy makers. Topics tackled ranged from energy and natural resources to public health and disaster prevention.
19 Nov 2012
(Tokyo, 19 November 2012) Researchers at the Tokyo Institute of Technology, NASA’s Johnson Space Center, Lunar Planetary Institute, and Carnegie Institute of Washington report on geochemical studies that help towards settling the controversy that surrounds the origin, abundance, and history of water on Mars.
16 Nov 2012
Researchers have developed a novel technique for controlling the electrical conductivity of graphene.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater