Japan
News
24 Sep 2013
Prof. Tamai's latest research examines how orange, apple and grapefruit juices affect the absorption of prescription drugs into the body. As Kanazawa's most cited professor, he has dedicated his career to study molecules and genes responsible for cardiomyopathy, muscle weakness, and Reye’s syndrome.
24 Sep 2013
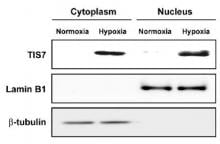
(Kanazawa, Japan, 25 September 2013) Researchers at Kanazawa University have identified the role of the protein TIS7 in processes that regulate adipogenesis, whereby non-specialised cells become adipose or fat cells.
24 Sep 2013
(Kanazawa, Japan, 25 September 2013) Researchers at Kanazawa University have demonstrated a technique that allows direct functionalization of alkenes without the need for metallic reagents, photolysis or extreme reaction conditions.
18 Sep 2013
(Okayama, Japan, 18 Sept 2013) Research by Professor Jian-Ren Shen at Okayama University demystifies the reaction mechanisms of photosynthesis and the findings may lead to the development of methods for producing an unlimited source of clean energy.
18 Sep 2013
Okayama University's e-Bulletin is now live where you can read about Japan's oldest votive tablets which shows a monkey leading a horse and a cow, the molecular mechanisms of ice melts and why humans lost their ability to regenerate organs.

11 Sep 2013
Japanese researchers have identified a mutation associated with a higher incidence of lung cancer in Japanese women who do not smoke, but better survival in lung cancer patients.
29 Aug 2013
Shimadzu Corporation will launch a new series of compact turbo molecular pumps with integrated power supplies for semiconductor and flat panel display manufacturing industries. The new TMP-X series will contribute to reducing the costs and downsizing the footprint of manufacturing flat panel displays and semiconductor devices.
26 Aug 2013
(Tokyo, 26 August 2013) The gene mechanism responsible for altering magnesium ion secretion in fish is uncovered by scientists at Tokyo Tech. The details are described in the August 2013 issue of Tokyo Institute of Technology Bulletin
26 Aug 2013
(Tokyo, 26 August 2013) Research covered include - How pufferfish meditate magnesium to survive, DNA-based method enables the identification of a bacterium as an indicator that obstructs methane fermentation and Manipulating a single nuclear spin qubit of a laser cooled atom

02 Aug 2013
By exploiting the full computational power of the Japanese supercomputer, K Computer, researchers from the RIKEN HPCI Program for Computational Life Sciences, the Okinawa Institute of Technology Graduate University (OIST) in Japan and Forschungszentrum Jülich in Germany have carried out the largest general neuronal network simulation to date.

30 Jul 2013
RIKEN is pleased to announce the launch of a pilot study to assess the safety and feasibility of the transplantation of autologous induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell sheets in patients with exudative (wet-type) age-related macular degeneration
21 Jul 2013
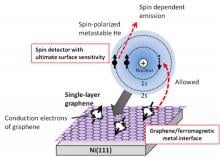
Opens the Way to Research on Spin Properties and Device Applications of Graphene and Other 2-Dimensional Materials
18 Jul 2013
Researchers have developed nano-adhesive plasters that can easily be applied to lacerated vessel walls with no adhesive, and succeeded in arresting massive bleeding from the inferior vena cava in rabbits.
15 Jul 2013
MANA researchers report that incorporating magnetic nanoparticles and an anticancer drug into crosslinked polymer nanofibers presents a twofold treatment for fighting cancer with diminished side effects.

10 Jul 2013
People composed of biotechnology are cyborgs, an amalgam of human being and technology. What direction are human beings, or should I say cyborgs, headed in? Opinion article by Prof. Toru Takahashi of Waseda University
09 Jul 2013
A team of researchers from Japan has finally solved the riddle of the origin of the turtle shell.

04 Jul 2013
As the upper house election date advances, concerns are raised about Japan's Liberal Democrats' policy to make changing the constitution easier for the Diet - Opinin article by Toru Nakajima

04 Jul 2013
Accuracy and precision of robots can give advantage to medical treatment - opinion article by Yo Kobayashi of Waseda University
04 Jul 2013
NIMS researchers have solved a 20 year old riddle concerning the reaction mechanism of aluminium surface oxidation
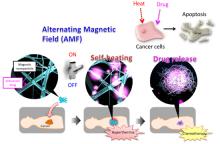
02 Jul 2013
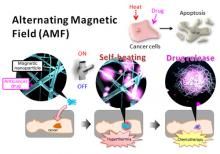
A MANA research team has developed a new nanofiber mesh which is capable of simultaneously realizing thermotherapy (hyperthermia) and chemotherapy (treatment with anticancer drugs) of tumors. They succeeded in efficiently inducing natural death (apoptosis) of epithelial cancer cells.
27 Jun 2013
Biomaterials are increasingly replacing human organs and tissues and silver is added to reduce the adhesion of bacteria to biomaterials and prevent infections. However, a recent study by researchers in Portugal suggests that – in one material – increasing levels of silver may indirectly promote bacterial adhesion.
26 Jun 2013
(Toyohashi, 26 June 2013) Toyohashi Tech researchers fabricate powerful red light-emitting diodes by codoping GaN with Eu and Mg. The details are described in the June 2013 issue of Toyohashi Tech e-Newslette

26 Jun 2013
(Toyohashi, 26 June 2013) Growing plants in factories: the June 2013 issue the Toyohashi Tech e-Newsletter contains the latest research-news and views from one of Japan's most innovative and dynamic science and technology-based academic institutes.
25 Jun 2013
(Kanazawa, Japan, 25 June 2013) One of Kanazawa University’s leading professors has spent the last 15 years investigating the role of orexin neuropeptides in the brain. Takeshi Sakurai’s work is furthering understanding of sleep and wakeful states and leading to the development of new therapies for insomnia and narcolepsy.
25 Jun 2013
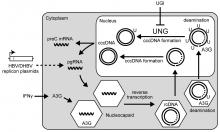
(Kanazawa, Japan, 25 June 2013) Researchers at Kanazawa University Graduate School of Medical Science in Japan have determined how APOBEC proteins mediate hypermutations that inhibit viral replication. They also identify the host factor protein UNG that can repair these mutations.
25 Jun 2013
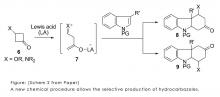
(Kanazawa, Japan, 25 June 2013) A new chemical process developed by researchers at Kanazawa University provides an efficient way of synthesizing diverse organic compounds. Such an efficient, flexible route to these useful compounds could greatly benefit pharmaceuticals and other industries.
22 Jun 2013
A research team headed by Dr. Takashi Nakanishi, a Principal Researcher of the NIMS Organic Materials Group, Polymer Materials Unit, developed a full-colour tunable luminescent liquid material with excellent light stability based on an anthracene molecule, which is a general organic fluorescent dye.

22 Jun 2013
Opinion article by Jinshi Fujii of Waseda University – “How far can these ties be restored given the current state of Japanese cinema, which has become about as individualist and fragmented as it can get?”
19 Jun 2013
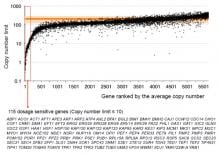
(Okayama, Japan, 19 June 2013) Professor Hisao Moriya and colleagues at Okayama University used their ‘tug of war method to measure the copy number limits of all protein-coding genes in yeast—the first time ever for any organisms.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater