Japan
News
08 Sep 2014
Thousands of potentially bioactive molecules can be made rapidly by mixing 20 or so building blocks together. Researchers at ETH-Zürich (Switzerland) and the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (Japan) have developed a new technique to generate large libraries of novel organic molecules, a method that was inspired by Nature.
27 Aug 2014
A paper published in Science and Technology of Advanced Materials have shown that a synthetic protein mimic called AGMA1 has the potential to promote the adhesion of brain cells in a laboratory setting. It is also cheaper and easier to produce on a large scale. This could help overcome a major challenge in nerve tissue engineering.
26 Aug 2014
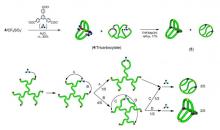
(Tokyo, 26 August 2014) Tokyo Tech scientists synthesize multicyclic type of polymers for the first time offering insights for tailoring polymer properties as well as the mathematics of complex geometries.
20 Aug 2014
Anticipated for applications in the development of "superplants" for radiocesium decontamination

20 Aug 2014
The ACS recognizes Kenichiro Itami with this award for the development of powerful and unique catalysts (in particular for C-H activation) that have significant impact in materials science, pharmaceutical science, and advanced biology.

20 Aug 2014
Opinion article by Prof. Hiroshi Nishihara of Waseda University on the Japan Cabinet's decision to approve the exercise of the right to collective self-defense.
15 Aug 2014
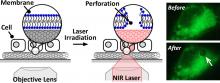
Japanese researchers have developed a new, targeted method for perforating cell membranes in order to deliver drugs to, or manipulate the genes of, individual cells. The paper is published in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.

14 Aug 2014
Waseda university researchers have identified certain chemicals in the brain which regulate downstream reproductive hormones of males.
14 Aug 2014
Waseda researchers have described the earliest example of a true dolphin in the known fossil record.

21 Jul 2014
Prof. Cathleen Crudden (PI of ITbM and Professor at Queen's University) has been awarded the 2014 CIC Fellowship of the Chemical Institute of Canada.
20 Jul 2014
Will Tokyo be able to unveil a disaster-prepared, barrier-free Tokyo at the Olympics where the elderly, disabled, and foreign visitors can live in safety? Opinion article by Prof. Yuji Hasemi of Waseda University.
14 Jul 2014
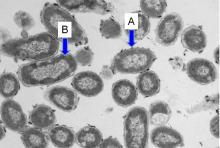
This article published in the Science and Technology of Advanced Materials reports an approach with industrial potential to produce nano-sized composite silicon-based powders as negative electrodes for the next generation lithium ion batteries.
10 Jul 2014
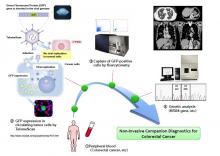
(Okayama, Japan, 10 July) Okayama University researchers seek partners to commercialize a clinically proven non-invasive fluorescence virus-guided capture system of human colorectal circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from blood samples for genetic testing. This non-invasive companion diagnostics is important for personalized targeted cancer therapy.
08 Jul 2014
Biologists at ITbM, Nagoya University have identified for the first time, a key photoreceptor cell deep inside the brain of birds, which takes the role of eyes in humans by directly responding to light and regulates breeding activity according to seasonal changes.
25 Jun 2014
(Okayama, Japan, 25 June 2014) Research highlights in the June issue of the Okayama University e-Bulletin include innovative pendulum dynamo for converting tidal energy to electricity; models for breeding plants; unique insights into photosynthesis and Photosystem II; repairing DNA; and developing lithium-ion baterries with help from bacteria.

25 Jun 2014
A collaboration from RIKEN, the Tokyo Institute of Technology, and University College Dublin won top place in the June 2014 Graph 500 supercomputer ranking using the K computer, which is located in Kobe, Japan.
20 Jun 2014
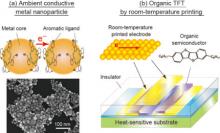
Japanese researchers have established a process for forming organic thin-film transistors (TFTs), conducting the entire printing process at room temperature under ambient atmospheric conditions.
20 Jun 2014
Using a soft X-ray microscope, a Japanese research team has examined the nanostructure of organic solar cells and discovered that different molecules are intermixed in each molecular domain.
20 Jun 2014
Researchers at the University of Tokyo and Japan's National Institute for Materials Science have discovered pure organic substances exhibiting the quantum spin liquid state.
20 Jun 2014
(Tokyo, Japan, 20 June 2014) The June 2014 issue of the University of Electro-Communications e-Bulletin includes research highlights on Raman scattering for laser optical communications; fuzzy control systems; optical signal processing; pharmacophores and future of drug discovery; hybrid dye solar cells.
19 Jun 2014
Researchers at the Synchrotron X-ray Station at Spring-8 and Tohoku University have successfully detected spin-resolved electronic states from a buried ferromagnetic layer, which had been difficult to detect using conventional spin-resolved photoemission spectroscopy.
19 Jun 2014
A Japanese research team has successfully demonstrated a new approach toward a non-precious metal oxygen reduction catalyst for fuel cells.
02 Jun 2014
The 2nd International Symposium on Transformative Bio-Molecules 2014 is an annual event held by ITbM, inviting prestigious speakers from around the world to enhance interdisciplinary research between synthetic chemistry and animal/plant biology.
27 May 2014
Researchers at ITbM developed a new nickel catalyst with a “Kabuto-like” structure that catalyzed the cross-coupling reaction between carbonyl compounds and readily available phenol derivatives, to form α-arylketones, which are found in many biologically active compounds.
26 May 2014
(Tokyo, 27 May 2014) Tokyo Tech scientists and colleagues in Switzerland develop an innovative new model to aid the analysis of financial markets uses the laws of molecular fluid dynamics to describe order-book transactions.
08 May 2014
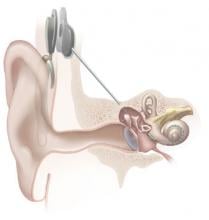
(Kanazawa, Japan, 8 May 2014) Levels of interferon-stimulated genes in the liver and blood could help predict if a patient with hepatitis C will respond to conventional therapy, researchers at Kanazawa University suggest.
08 May 2014
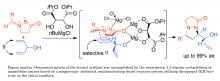
Yutaka Ukaji and colleagues at Kanazawa University have now developed a method for desymmetrising compounds to produce new chiral molecules. The process allows 99% selectivity in the chemicals produced.
08 May 2014
Highlights of Prof. Hayakawa's research who is currently developing methods to identify metabolites of PAHs and NPAHs in urine and blood. Other work include developing the most sensitive method for measuring PAHs and NPAHs, showing that motorcycle engines released more particulate matter than automobiles and more
24 Apr 2014
Researchers at Japan's National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) have synthesized a novel superconductor, SrAuSi3, which contains gold as a principal constituent element.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater