Nature Communications
News
27 Sep 2021
The missing link isn’t a not-yet-discovered fossil, after all. It’s a tiny, self-replicating globule called a coacervate droplet, developed by two researchers in Japan to represent the evolution of chemistry into biology.
24 Sep 2021
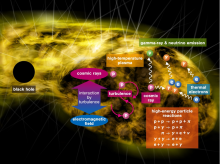
Energetic particles are ubiquitous across the universe but their origins are unexplained. Now, a research team has proposed that mellow black holes act as the source of high-energy cosmic particles.
16 Sep 2021
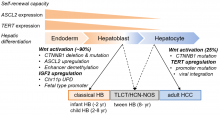
Genetic and epigenetic profiling of hundreds of hepatoblastoma tumors have revealed many of its secrets, long unknown to those researching and treating what is the most common type of liver tumor in children.

14 Sep 2021
Similar to a magnet that always has both south and north poles, a kind of special quasiparticles in condensed matter called “Weyl Fermions” always appear in pairs with opposite chirality. There had been no experimental report that unpaired Weyl points exist in condensed matter until recently, a City University of Hong Kong (CityU) physicist observed the first unpaired singular Weyl magnetic monopole in a specific kind of single crystalline solid.
12 Jul 2021
Scientists in Singapore are calling for revisions in planned hydropower expansions in light of the rapidly decreasing cost of solar photovoltaic systems
07 Jul 2021
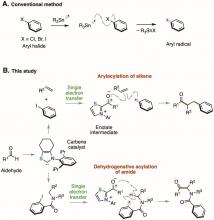
We have developed a groundbreaking chemical reaction using an N-heterocyclic carbene catalyst that has a low environmental impact to cleave the bond between the benzene ring of an aryl halide and a halogen atom to generate an aryl radical. Since aryl radicals can thus be easily generated from aryl halides that are widely used in organic synthesis, this is expected to be a powerful technology for precisely synthesizing medical and agricultural drugs and chemical materials.
05 Jul 2021
Scientists used digital circuitry to manipulate and store label-free matters in order to study their unique characteristics
01 Jul 2021
Scientists show that an ocean-bottom seismometer deployed close to the calving front of a glacier in Greenland can detect continuous seismic radiation from a glacier sliding, reminiscent of a slow earthquake.
30 Jun 2021
Researchers from The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science and Fudan University experimentally interrogate a phenomenon that bridges diverse fields of science and engineering
28 May 2021
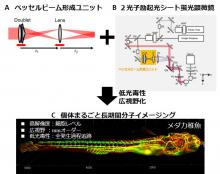
Contributing to embryogenesis and pathogenesis through long-term in vivo molecular imaging
1. Development of a two-photon excitation light-sheet microscope which achieves low phototoxicity, an extended field of view, and high resolution for the observation of the growth of living organisms
2. Applications of the microscope demonstrate long-term time-lapse observations for a three-day span of the embryonic development of medaka fish
27 May 2021
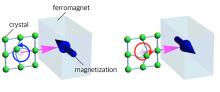
Schematic illustrations of magnetization control by the injection of phonon angular momentum.
21 May 2021
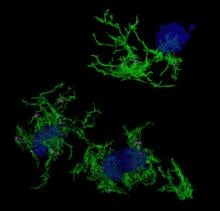
Single-cell gene studies are clarifying the roles of the brain’s specialised immune cell in Alzheimer’s disease and offer new avenues for treatment of this incurable condition.
19 May 2021
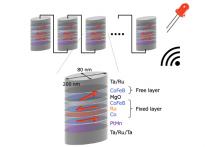
Researchers at the National University of Singapore and Tohoku University have demonstrated that an array of electrically connected spintronic devices can harvest a 2.4 GHz wireless signal, which can be used to power and charge small electronic devices and sensors.
12 May 2021
Printing electronic circuits could soon get easier and cheaper.
10 May 2021
Ice is melting at a surprisingly fast rate underneath Shirase Glacier Tongue in East Antarctica due to the continuing influx of warm seawater into the Lützow-Holm Bay.
22 Apr 2021
A mitochondrial peptide called MOCCI has a surprising sidekick, and they work together to regulate inflammation and immunity, Singapore researchers reveal.

15 Apr 2021
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive type of breast cancer with a high fatality rate. Currently, chemotherapy is the major treatment option, but the clinical result is unsatisfactory. A research team led by biologists at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has identified and characterised a set of specific super-enhancers that stimulate the activity of the related critical cancer genes. The research has also discovered that the deletion of certain specific super-enhancers could reduce tumour cell growth. The latest findings may help discover new effective drug targets for TNBC patients to improve their survival chance.
19 Mar 2021
Through a series of prosocial choice tasks, researchers reveal prosocial and antisocial characteristics in male convict cichlid fish. The fish distinguish between female breeding partners, unknown females, and rival males by adjusting their actions to either provide food for both them and the females or avoid providing food for the rival males.

10 Mar 2021
Energy-efficient light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have been used in our everyday life for many decades. But the quest for better LEDs, offering both lower costs and brighter colours, has recently drawn scientists to a material called perovskite. A recent joint-research project co-led by the scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has now developed a 2D perovskite material for the most efficient LEDs.
25 Feb 2021
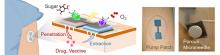
Researchers from Tohoku University have developed a biobattery-powered device capable of both delivering large molecule pharmaceuticals across the skin barrier and extracting interstitial fluid for diagnostic purposes.
12 Feb 2021
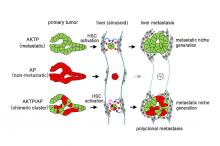
In a study published in Nature Communications, cancer researchers at Kanazawa University identify mechanisms by which malignant tumor cells extend their toxicity to distinct cell types and in turn help them spread.
10 Feb 2021
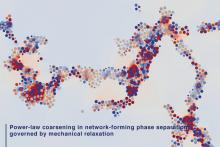
Researchers at The University of Tokyo discover a new law about how the complex network of phase-separated structures grows with time, which may lead to more efficient batteries and industrial catalysts
29 Jan 2021
Although genome sequencing has come leaps and bounds over the past 20 years, there did not exist a reference genome specific to the Japanese. That is until now. Researchers at Tohoku University have completed and released the first Japanese reference genome by analyzing the genomes of three Japanese individuals using high coverage, long-read next-generation sequencing technologies.
20 Jan 2021
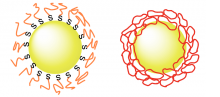
Hokkaido University scientists have found a way to prevent gold nanoparticles from clumping, which could help towards their use as an anti-cancer therapy.
12 Jan 2021
An atomic switch is bringing us closer to highly effective solid-state batteries for electric vehicles.
24 Dec 2020
Tohoku University scientists have, for the first time, provided experimental evidence that cell stickiness helps them stay sorted within correct compartments during development. How tightly cells clump together, known as cell adhesion, appears to be enabled by a protein better known for its role in the immune system. The findings were detailed in the journal Nature Communications.
23 Dec 2020
A joint research team co-led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has developed a novel computational tool that can reconstruct and visualise three-dimensional (3D) shapes and temporal changes of cells, speeding up the analysing process from hundreds of hours by hand to a few hours by computer. Revolutionising the way biologists analyse image data, this tool can advance further studies in developmental and cell biology, such as the growth of cancer cells.
07 Dec 2020
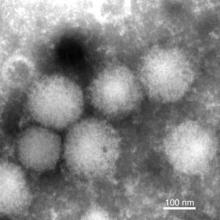
Scientists from Japan and the USA have confirmed the presence in meteorites of a key organic molecule which may have been used to build other organic molecules, including some used by life. The discovery validates theories of the formation of organic compounds in extraterrestrial environments.

02 Dec 2020
“Superbug” resistant to strong antibiotics is a ticking time bomb in global public health. A joint study led by a scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has traced the potential origin of an antibiotic resistance gene and identified a type of bacteria as the possible source. The team also studied the gene’s transmission mechanisms and published their findings recently, in the hope of blocking its transmission.
Events
Sorry, no events coming up for this topic.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.