Japan
News
22 Dec 2010
This year marks the 1300th anniversary of the transfer of the national capital to Heijo-kyo in Nara. Also, the regular exhibition of Shosoin, the treasure storehouse built in the eighth century at Todai-ji Temple in Nara, was held at the Nara National Museum until November 11th.
22 Dec 2010
On October 11, 2010, the computer shogi (Japanese chess) system Akara 2010 played a game against the then women’s Osho champion Ichiyo Shimizu with no handicap and defeated her in 86 moves.
22 Dec 2010
The conservation of biodiversity calls for protecting precious living organisms. But it is difficult to explain the true significance of biodiversity conservation.
20 Dec 2010
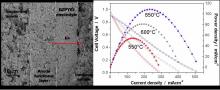
Researchers at National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) have successfully developed two types of novel proton conducting oxide electrolytes for SOFCs, moving towards the commercialization of SOFCs.
17 Dec 2010
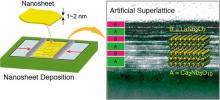
A research group at the National Institute for Materials Science have successfully developed a novel nanoferroelectric by a solution-based bottom-up nanotechnology.
17 Dec 2010
Mathematical equations can now resolve whether electron transport in nanostructures follows classical or quantum mechanical behavior
17 Dec 2010
Fear responses of zebrafish are controlled by brain structures of previously unknown function
17 Dec 2010
Theoretical physicists are working to unlock the secrets of a new class of matter known as topological insulators and topological superconductors.
14 Dec 2010
Researchers at RIKEN have linked a specific type of cellular stress to neuronal cell death leading to brain damage. The findings overturn existing assumptions on the role of a key neuronal protein in cellular stress response, opening up new avenues for research on a range of neurodegenerative diseases.

10 Dec 2010
On September 17–18, the RIKEN Harima Institute hosted the second Noyori Summer School, a retreat for PhD students in the International Program Associate (IPA) and Junior Research Associate (JRA) programs conducting research at RIKEN.
10 Dec 2010
Linking silicon and carbon double bonds into an extended network with bulky molecules produces air-stable and photo-responsive crystals
10 Dec 2010
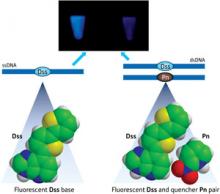
The toolbox for imaging DNA now comes with an artificial DNA fluorescent base that can be ‘switched off’
06 Dec 2010
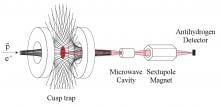
Tokyo, 6 Dec - Researchers at RIKEN, Japan’s flagship research institution, have successfully devised the world’s first experimental technique for measuring ground-state hyperfine transitions of antihydrogen.

06 Dec 2010
Tokyo, 6 December - Researchers in Japan have launched FANTOM5, Functional Annotation of the Mammalian Genome, an international effort to globally map transcription initiation in every human cell type.
03 Dec 2010
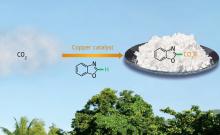
‘Green’ catalysts transform carbon dioxide gas into valuable building blocks for organic synthesis
03 Dec 2010
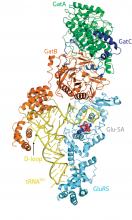
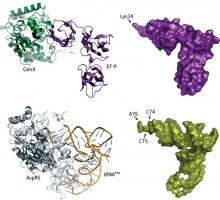
RIKEN biochemists decipher how the precisely choreographed activity of a pair of enzymes helps protein synthesis move forward
03 Dec 2010
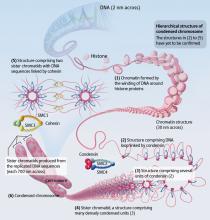
Advances in our understanding of basic biological processes and human disease owe much to the groundbreaking research of scientists at the Chromosome Dynamics Laboratory at RIKEN Advanced Science Institute.
29 Nov 2010
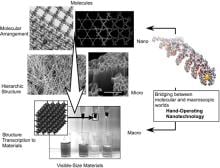
The STAM article titled “Challenges and Breakthroughs in Recent Research on Self-Assembly,” which was published in March 2008 issue by Dr. Ariga, MANA PI, and Dr. Hill, MANA Scientist, et al., was ranked No. 1 Hot Paper in Materials Science by the Essential Science Indicators on November 1 (provided by Thomson Reuters).

26 Nov 2010
Large tree-like sugar clusters provide potential in vivo probes for cancer cells

26 Nov 2010
Frame-by-frame observations of the ionization of argon atoms under extremely bright and energetic illumination could prove a boon to research
19 Nov 2010
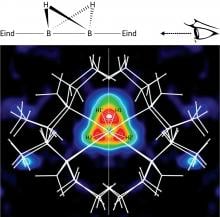
Bulky molecules help trap boron compounds into a never-before-seen structural arrangement
19 Nov 2010
Evolution has left a protein and nucleic acid molecule with remarkably similar structures, allowing them to undergo modification by closely related enzymes
19 Nov 2010
A new molecular simulation technique developed by researchers at RIKEN and Kyoto University has confirmed for the first time the function of the transporter protein AcrB in E. coli multidrug resistance.
15 Nov 2010
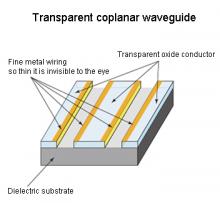
Tokyo, 15 Nov - New findings by researchers at RIKEN and the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) have shed light on the remarkable electrochemical response properties of an elusive class of molecular helix structures, charting a new path in the design of molecular machines and devices.
12 Nov 2010
Scientists discover that a protein with an essential role in controlling gene dosage in female cells has been hiding in plain sight

12 Nov 2010
Tolerating the foreign materials in food that mice and humans need hinges on the presence of B7 proteins
12 Nov 2010
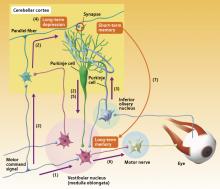
A 40-year debate over the mechanism of long-term motor memory storage in the brain has been settled through pioneering research by researchers at the RIKEN Brain Science Institute.
12 Nov 2010
“We hope our partnership in green chemistry and nanotechology will lead to results that will make significant contributions to resolving pressing global issues and pave the way for a sustainable society.” - RIKEN executive director Yoshiharu Doi
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater