Japan
News
28 Aug 2010
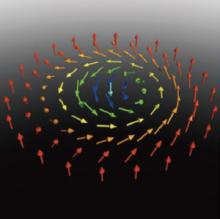
The first direct observation of an unusual magnetic structure could lead to novel electronic and magnetic memory devices
28 Aug 2010
Powerful synchrotron light captures never-before-seen electronic interactions of molecules dissolved in liquids

22 Aug 2010
Producing isolated laser pulses in just attoseconds made easier using a two-color laser field

22 Aug 2010
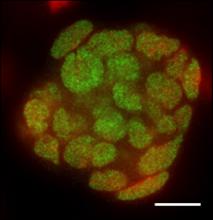
A pair of molecular biology techniques enables detailed characterization of the gene expression of small numbers of cells

22 Aug 2010
Information engineering at RIKEN extends the evolution of life into the digital realm
18 Aug 2010
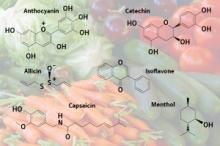
Tokyo, 18 August - Researchers at the RIKEN Plant Science Center have illuminated mechanisms underlying the genetic robustness of metabolic effects in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Their findings reveal a key balance between the roles played by duplicate genes and metabolic network connectivity in functional compensation.
15 Aug 2010
Tokyo, 15 August - A nuclear protein of previously unknown function has been shown to regulate the migration of tumor cells in the spread of melanoma, the most deadly form of skin cancer.
13 Aug 2010
The RIKEN Science Lectures are a series of annual events bringing together pioneering researchers at RIKEN and leading scientists in related fields to share their findings with the public.
13 Aug 2010
Building on pioneering work in metabalomics and omics analyses, researchers at the RIKEN Plant Science Center are gearing up for a new era of functional plant development with clinical applications.

13 Aug 2010
A comparative study of two closely related organic insulators highlights the unusual properties of quantum spin liquids
13 Aug 2010
Cancer may be kept in check by a method for generating patient-specific immune cells with antitumor activity
12 Aug 2010
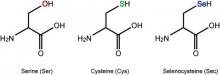
The findings deepen our understanding of protein synthesis and lay the groundwork for advances in protein design.
10 Aug 2010
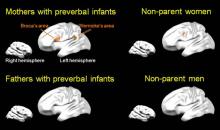
Neural processing in the brains of parents talking to their babies may reveal secrets about early stages of language acquisition in infants.

06 Aug 2010
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology have unraveled the mystery of why human embryonic stem (ES) cells and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells undergo programmed cell death (apoptosis) when cultured in isolation.
06 Aug 2010
Many of Earth’s resources, from copper to more precious metals, are often taken for granted, but the only place to make more of these elements lies at the interior of stars.
06 Aug 2010
Modifying a familiar class of dye molecules with optically active carbon rings creates new possibilities for light-based medical therapies

06 Aug 2010
Secretary-General of the United Nations Ban Ki-moon delivered a special speech entitled "Peace and Disarmament" on Aug. 4 at International Conference Center in Waseda University.

02 Aug 2010
A genome-wide study on Japanese subjects has identified 5 new genetic variations associated with prostate cancer and revealed differences and similarities between Europeans and Asians in susceptibility to the disease.

30 Jul 2010
Claire Marrache-Kikuchi writes to Kimitoshi Kono at the Low Temperature Physics Laboratory, RIKEN Advanced Science Institute
30 Jul 2010
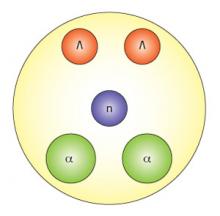
Calculating the binding energy between hyperon particles contributes to understanding a new type of neutron star
30 Jul 2010
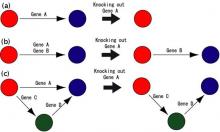
By bolstering a sophisticated computational model with quantitative experimental data, researchers begin to decipher the workings of a complex signaling network
30 Jul 2010
Genetic data help scientists close in on the immunological malfunctions underlying a mysterious pediatric disorder

29 Jul 2010
Tokyo, 29 July - A team of researchers at the RIKEN Plant Science Center and the Institute of Cancer Research has uncovered details of a protein complex governing innate immune response in plants and animals, with applications in the development of disease-resistant crops and treatment of human diseases.
23 Jul 2010
Unusual properties predicted in superconducting thin films could deliver perfect lenses and other novel applications

23 Jul 2010
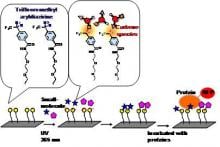
Surface-selective fluorescent labeling enables cell tracking in the body while preserving initial cell function
23 Jul 2010
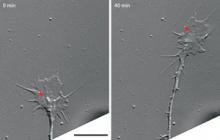
Inward flow of membrane material is critical for repulsive growth cone turning
20 Jul 2010
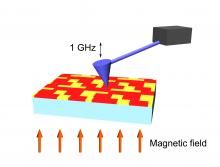
Tokyo, 20 July - Scientists at Stanford University and RIKEN have revealed new clues on the microscopic processes by which resistance in certain materials is dramatically altered by the presence of magnetic fields.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
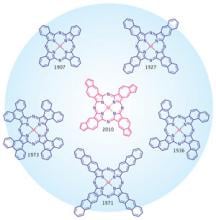
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater