Japan
News
01 Oct 2010
A porous polymer network that researchers can make reactive at will can store gases and hasten chemical reactions
01 Oct 2010
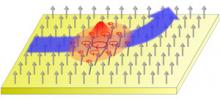
A fundamental effect associated with electrons also occurs in non-charged particles—a potential boon for spintronics

01 Oct 2010
New functions of the plant hormone strigolactone, discovered by researchers at the RIKEN Plant Science Center and University of Toronto, have provided first-ever clues on the germination mechanism for the world’s most destructive species of parasite weeds.

24 Sep 2010
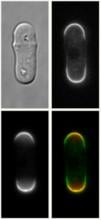
The dynamic activity of electrical signals in neuronal populations can now be visualized with a powerful tool
24 Sep 2010
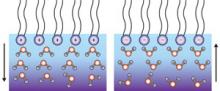
Advanced laser spectroscopy exposes the unique organization of water molecules under model membrane surfaces

17 Sep 2010
Kathrin Goldammer writes to Tsumoru Shintake, Technical Director and
Construction Leader at the XFEL/SPring-8 Accelerator
17 Sep 2010
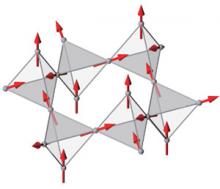
Theoretical physicists find evidence of a new state of matter in a simple oxide
17 Sep 2010
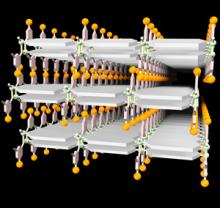
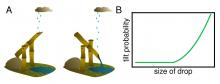
The degree of interconnectivity of molecular frameworks in microporous materials influences their structural flexibility and gas sorption
11 Sep 2010
The Waseda University Library came into existence in 1882. The library was established together with the founding of Tokyo Senmon Gakko, a school which was the precursor to Waseda University.
11 Sep 2010
Kaoru Nakao of Waseda's Tsubouchi Memorial Theatre Museum writes about Kyuen Kawasaki (1874-1961) who was praised and revered as a master during his performances in the Meiji, Taisho and Showa periods.

11 Sep 2010
Rikuo Takagi from Waseda University Library writes on Qing dynasty diplomat, Qian Xun, (1853-1927) who said “Waseda University is liberal and broad-minded, akin to schools in America”

11 Sep 2010
Prof. Hisao Takamatsu writes on the 120th anniversary of the establishment of the Literature Department at the Tokyo Technical School, the forerunner of Waseda University.

11 Sep 2010
Prof. Yasuaki Muto writes on reform of the Japan Sumo Association.
11 Sep 2010
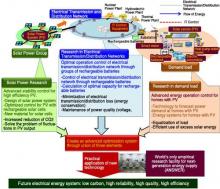
In order to solve the energy issues of the 21st century, it is essential to achieve a harmony of the “three Es”; namely, energy security, environmental protection and economic growth - Interview of Professor Yasuhiro Hayashi, RIANT Director.

11 Sep 2010
Being a biologist who likes bugs, the thing that brought me to write an essay on evolutionary biology was that I thought the “sociobiology,” the theory of evolution that pushed Neo-Darwinism to extremes, was a sham - by Prof. Kiyohiko Ikeda.

11 Sep 2010
Prof. Okauchi reflects on an international meeting in Cairo, Egypt concerning the “Return and Protection of Cultural Property”. A total of 21 countries participated in a discussion which pressed for the return of such famous antiquities as the bust of Queen Nefertiti and the Rosetta Stone.
10 Sep 2010
The EuroScience Open Forum (ESOF) is one of Europe’s most important scientific gatherings. The 2010 forum was held in Torino, Italy, the third in the biennial ESOF series.
10 Sep 2010
The ability to observe individual proteins as they react and combine provides remarkable insights into the complex world of cell signaling
10 Sep 2010
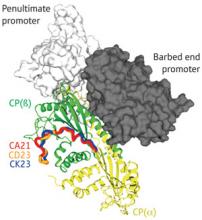
Two regulators of protein filament assembly use dramatically different—and competing—methods to inhibit a common target
10 Sep 2010
Chemical-genomic profiling of bioactive therapeutic compounds reveals therapeutically exploitable signaling activity at fungal cell membranes
09 Sep 2010
Press Release - Reported in PLoS Computational Biology, the findings offer fundamental insights relevant to a wide range of biological, physical and technical systems.

09 Sep 2010
Language change involves changes in power relationships, and groups whose vested interest of the language they have used up to the present is threatened would attempt to reject it completely, because language skill cannot be easily acquired or replaced, and it represents people’s identity.

09 Sep 2010
Shanghai has achieved significant growth over the last twenty years and it is now the richest region in China. It is quite fitting that the Expo, an engine for further economic development, be held in Shanghai.

09 Sep 2010
The sight of the newborn state of East Timor, together with Indonesia leading the way for the democratization of Southeast Asia reflects a bizarre twist of fate.

09 Sep 2010
As a backdrop to these times, I think the key to the welfare state getting past the barriers to realize minimal state (re)distribution and free equality is destined to be found in Basic Income.

09 Sep 2010
A supermarket is a veritable battleground, where consumers who have a strong desire to seek out quality food face a daunting array of products to choose from.

09 Sep 2010
With headlines such as "the shock of E-books", "the truth about electronic books", "Amazon's true character" and "The yin and yang of E-books," expectations and concerns about E-books have been a dominant theme in business magazines during 2010.
03 Sep 2010
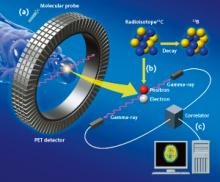
Advances in molecular imaging reveal startling insights into the workings of the brain and could make it possible to diagnose migraine definitively for the first time
03 Sep 2010
A network of filamentary conducting paths is behind the transition between insulating and conducting states in complex oxides
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater