Japan
News
09 Nov 2010
This agreement will not only reinforce the existing collaboration between UCL and NIMS in the field of computational materials science, organic nanomaterials and photocatalytic materials, but also envisage new collaboration and exchange of researchers.
09 Nov 2010
Tokyo, 8 Oct - The Inter University Accelerator Centre (IUAC), India, and the Quantum Beam Center, NIMS, signed a MOU on collaborative research for "the Fabrication and modification of nano-materials by ion beams"
09 Nov 2010
This dramatic improvement in thermal agglomeration resistance opens the road to a large reduction in the amount of rare metals used in exhaust gas purification technologies.
08 Nov 2010
Tokyo, 8 Nov - C.N.R. Rao and colleagues have published a timely review analyzing the correlation of synthesis methods and physical properties of single-layer and few-layered graphene flakes. The paper was published in Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
05 Nov 2010
Cloning efficiency is undermined by widespread disruption of genomic regulation resulting largely from defective expression of a single gene
05 Nov 2010
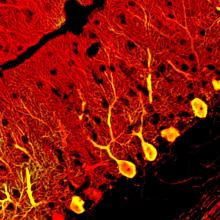
An effective method for generating cerebellar neurons could lead to new treatments for movement disorders
05 Nov 2010
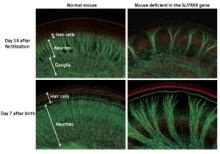
A specific genetic variant puts individuals of Asian ancestry at risk of developing diabetes—but not their European counterparts
05 Nov 2010
Tokyo, 5 Nov - A new analysis technique for the design and optimization of beam optics has successfully been used to model the group behavior of electron beams over a linear accelerator, paving the way for its use at linear accelerator based light source facilities around the world.
04 Nov 2010
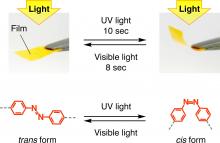
Tokyo, 4 Nov- Researchers at RIKEN have successfully developed a revolutionary new polymer film that changes shape upon irradiation with UV and visible light.
29 Oct 2010
A small-molecule screening method helps scientists probe mysteries of protein function

29 Oct 2010
A naturally occurring back-up system in plants to produce metabolites compensates for experimentally induced gene loss
29 Oct 2010
Close collaboration between developmental neurologists and clinical researchers could one day find the genetic answer to what it means to be human.
25 Oct 2010
Shigeki Nakauchi at Toyohashi Tech in collaboration with Kanebo Cosmetics Inc., Japan, has developed a technology enabling the quantification and visualization of the ‘quality’ and finish of foundation applied to the face.
25 Oct 2010
Dr Tsetserukou and Dr Neviarouskaya have designed iFeel_IM! to intensify the communicators' own feelings or simulate the partner's emotions in order to enhance social interactivity and provide an emotionally immersive experience for real-time messaging.
25 Oct 2010
Using state of the art microfabrication technology to create periodic structures with high accuracy, Dr Baryshev and colleagues report the existence of so-called optical surface (Tamm) states at the interfaces of magnetophotonic crystals.
25 Oct 2010
Dr Kawano and colleagues successfully demonstrate the neural recording capability of micrometer sized VLS-silicon wires—'Toyohashi Probe' using the retina of a fish (Fig.1 and Animation).
25 Oct 2010
Using monkey electrophysiology, Dr Koida and Dr Komatsu found that task demand altered the response of the inferior temporal neurons.
25 Oct 2010
Dr Minami and colleagues investigated the P3 component using an oddball paradigm.
25 Oct 2010
Dr Misawa and colleagues focused on a chemical sensor composed of living cells from frog eggs and compact fluidic devices integrated with glass capillary electrodes.
25 Oct 2010
Dr Numano and colleagues have been investigating the dynamics of ion channels and efficiently manipulating them for optical control of neural activity.
25 Oct 2010
Dr Park and colleagues report on a new biosensing protocol based on monitoring changes in optical transmittance of a solution containing self-assembled chains of functionalized magnetic beads being rotated by an external magnetic field.
25 Oct 2010
Dr Tero and colleagues found unique phase separation forming triangular domains to occur in a supported lipid bilayer (SLB) consisting of GM1, sphingomyelin (SM) and cholesterol (Chol) at 20:40:40 molar ratio.
25 Oct 2010
This inaugural Toyohashi Tech e-Newsletter includes an interview with President Yoshiyuki Sakaki—internationally renowned molecular biologist who led Japan’s International Human Genome Project—about his ambitious plans on enhancing the university’s research and education infrastructure.
24 Oct 2010
Tokyo, 24 Oct - Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Genomic Medicine (CGM) have uncovered hundreds of thousands of previously unknown variations in the human genome using new massively parallel sequencing technology.

15 Oct 2010
Rungaroon Waditee-Sirisattha writes to Masafumi Tsujimoto, Laboratory Head (former) at the Laboratory of Cellular Biochemistry, RIKEN Advanced Science Institute
15 Oct 2010
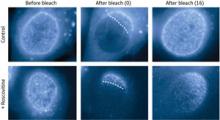
The formation of nuclear pores in dividing human cells is being illuminated by new visualization techniques
15 Oct 2010
A versatile formula describes the energetic conditions needed to transport molecules laterally on surfaces

12 Oct 2010
A new study on Japanese and French infants by researchers at the RIKEN Brain Science Institute and their collaborators has provided first-ever clues on the development of mechanisms governing how people perceive the words of a foreign language.
10 Oct 2010
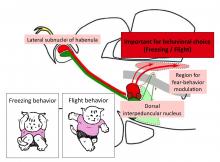
Press release - A new study on the behavior of the zebrafish has uncovered a key role for a region of the brain on the development of fear responses. The discovery provides valuable insights applicable to the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other mental illnesses.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater