Japan
News
28 Sep 2022
Research performed on human blastoids, a research model of an early embryo built out of stem cells, may allow scientists to understand better what causes birth defects and lost pregnancies, and so prevent them. But such research is also ethically fraught, warn bioethicists, due to differing beliefs on whether the blastoid possesses sentience or has the potential to do so.
28 Sep 2022
Researchers analyzed how the specific components of peace and environmental sustainability — concepts known to be intrinsically related but often investigated separately — influence each other to better inform policy and decision-making.
27 Sep 2022
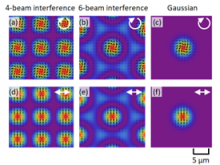
Osaka University researchers showed how to use laser beam interference to construct chiral structures. By using computer simulations, they were able to predict the final light pattern and optical radiation force distribution of any collection of light sources. This work may lead to cheaper optical devices and sensors.
26 Sep 2022
Hokkaido University researchers find a new way of producing the industrially important propylene that is more energy efficient than existing approaches—and in the process turns carbon dioxide into another usable resource. Their pioneering catalyst design thus contributes to the carbon neutralization of the petrochemical industry.
23 Sep 2022
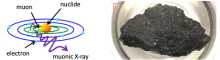
A team of researchers have analyzed the elemental composition of asteroid Ryugu using an artificially generated muon beam from a particle accelerator.
22 Sep 2022
Chaos theory improves understanding of Arctic narwhal behavior, with the aim of helping efforts to protect this vulnerable species.
22 Sep 2022
Researchers led by Osaka University developed a novel fluorescent sensor to detect and monitor levels of the neuropeptide oxytocin, also known as the “happy hormone.” The OT sensor facilitated the successful measurement of OT dynamics in the brains of living animals and may serve as a foundation for the development of therapeutics for the treatment of neurological disorders such as autism and schizophrenia.
22 Sep 2022
Researchers at The University of Tokyo grow a nanoscale layer of a superconducting material on top of a nitride-semiconductor substrate, which may help facilitate the integration of quantum qubits with existing microelectronics
20 Sep 2022
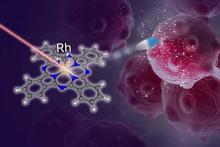
Researchers from The Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo have developed a streamlined photo-uncaging system for photodynamic cancer therapy, using a pulse of light for tumor-specific activation of a cancer-fighting agent
20 Sep 2022
A research group led by the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, finds that sensory neurons in human skin modulate melanocytes via the secretion of Repulsive Guidance Molecule B
20 Sep 2022
The activity of deep-focus earthquakes, which increases with depths from ~400 km to a peak at ~600 km, is enigmatic because conventional brittle failure is unlikely to occur at elevated pressures. Our experiments showed that formation of thin weak layers filled with nano-crystalline olivine/wadsleyite, upon the pressure-induced phase transition of olivine, is the major cause of deep-focus earthquakes on the metastable olivine wedge in deep slabs.
16 Sep 2022
Researchers found a new way to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by wrapping copper nanocubes with an organic layer, solving instability and selectivity problems with copper nanocubes in catalysis, and improving how this electrocatalyst converts CO2 into organic molecules.
16 Sep 2022
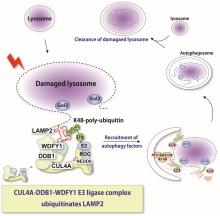
Osaka University researchers identified the specific protein complex that recognizes when cellular organelles called lysosomes become damaged. When this occurs, the CUL4A protein complex transfers a molecular tag, called polyubiquitin, to a lysosomal protein known as LAMP2. WDFY1, another protein in the complex, is able to recognize and interact with LAMP2. These initial steps are critical to beginning a process called lysophagy, in which these damaged lysosomes are cleared away by the cell.
16 Sep 2022
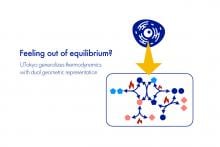
Scientists from The University of Tokyo formulated nonlinear, nonequilibrium energy dissipation relationships using methods from geometry to better understand the kinetics of irreversible chemical processes
15 Sep 2022
Researchers develop a new integrated framework that factors in the many variables relevant to accurate carbon emissions modeling in the transportation sector, allowing for policymakers to choose the best path to achieve carbon neutrality.
15 Sep 2022
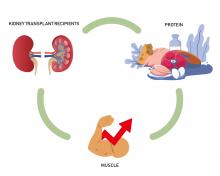
It is commonly believed that patients with chronic kidney disease should limit their protein intake given that excessive protein worsens kidney function. However, a new study by Osaka Metropolitan University scientists indicates that changes in skeletal muscle mass are positively correlated with protein intake, suggesting the necessity of adequate protein intake to improve muscle mass after kidney transplantation.
14 Sep 2022
A team of researchers including Kavli IPMU has found people in Japan, US, and Germany show different concerns regarding Artificial Intelligence (AI) being used in entertainment, shopping services, or to help find criminals.
13 Sep 2022
Demonstration of embodied cognition mechanisms in the brain could have implications for artificial intelligence.
13 Sep 2022
An estimated 1208 excess suicide deaths for men and 1825 for women were recorded during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Japan through December 2021, with the impact being greatest in women and younger age groups.
13 Sep 2022
Research shows that natural catastrophes may trigger or exacerbate attacks of incapacitating migraine in disaster victims.
12 Sep 2022
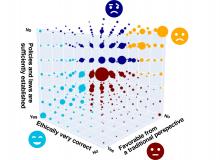
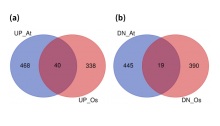
An international research team led by scientists from Osaka Metropolitan University has developed a method to identify symmetries in multi-dimensional data using Bayesian statistical techniques. Bayesian statistics has been in the spotlight in recent years due to improvements in computer performance and its potential applications in artificial intelligence. However, this statistical approach requires complex calculations of integrals, which are often considered approximations only. In their new study, the research team successfully derived new exact integral formulas. Their findings contribute to improving the accuracy of methods to identify data symmetries, possibly extending their applications to wider areas of interest, such as genetic analysis.
12 Sep 2022
Researchers at The University of Tokyo create a geometric representation of thermodynamic systems and apply it to self-replicating processes, which may help improve our understanding of the physical constraints of living organisms
09 Sep 2022
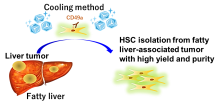
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists developed a new method to isolate hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which play a significant role in liver cancer progression. With enzymatic cold perfusion and utilization of an antibody against CD49a, a reliable HSC surface marker, the new method allows HSC isolation with high yield and purity from livers with various conditions, be they normal or fatty tumor-prone, from both mice and humans. The findings are expected to contribute to the development of efficient tools for characterizing NASH- or fatty liver-based liver cancer.
08 Sep 2022
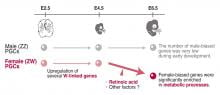
Researchers study sex-determination in birds using primordial germ cells and RNA-sequencing analysis.
08 Sep 2022
Researchers at Hiroshima University are closer to identifying the molecular processes underlying how floods deprive plants of oxygen — and how to engineer hardier crops.
07 Sep 2022
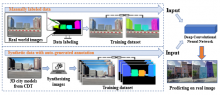
To automatically generate data for training deep convolutional neural network models to segment building facades, researchers from Osaka University used a three-dimensional model and game engine to generate digital city twin synthetic training data. They found that a model trained on these data mixed with some real data was competitive with a model trained on real data alone, revealing the potential of digital twin data to improve accuracy and replace costly manually annotated real data.
07 Sep 2022
Scientists have quantified the glacier mass loss on the Kamchatka Peninsula; the accelerated loss in the region since the turn of the millennium is likely to increase in the short term.
06 Sep 2022
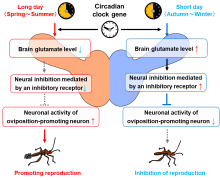
Researchers from Osaka University have found that photoperiod variation in bean bugs is regulated by genes involved in maintaining circadian rhythm via the neurotransmitter glutamate. The discovery of this mechanistic link between the biological clock and seasonal variation may have important implications for seasonal adaptation in other animals, given the conservation of glutamate across many species.
06 Sep 2022
Researchers have used giant lobes of gamma radiation to find that a small satellite galaxy of the Milky Way filled with dark matter, but whose emissions are more likely the result of millisecond pulsars blasting out cosmic particles.
02 Sep 2022
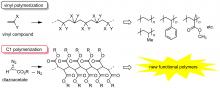
The research team directed by H. Shimomoto and E. Ihara in Ehime University successfully developed a new Pd-based initiating system affording carbon–carbon main-chain polymers bearing end-functional groups. This achievement will contribute to progress in the field of polymer chemistry and will allow us to develop new types of functional polymers.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater