Japan
News
20 Oct 2022
An Osaka Metropolitan University researcher has provided a review article regarding INSL3, a circulating hormone secreted from the gonads, in domestic animals, in comparison to rodents and humans. In this review article, the author describes his research group’s work that (1) developed immunoassays, for the first time, that can measure circulating INSL3 in multiple domestic mammals, including cattle, goats, sheep, pigs, horses, and dogs, (2) provided evidence in studies with bulls and bucks that INSL3 offers more reliable and stable values by a single blood collection than testosterone, a conventional and well-known testicular hormone, and (3) suggested that blood INSL3 concentrations would be a good biomarker for testicular and reproductive functions in normal and abnormal male domestic animals. These findings suggest that the INSL3 assay might simplify the evaluation of reproductive functions in various male domestic animals. In particular, the assay method may facilitate earlier selection of valuable male animals such as beef sire bulls (Image) with higher reproductive performance, contributing to reductions in the labor and costs required for sire production.
20 Oct 2022
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers interviewed active para-athletes with lower-limb disabilities who compete at an international level, about diet and nutrition. The research team found that what para-athletes considered an ideal diet was not necessarily optimized for improving athletic performance, and even when para-athletes understood diets geared towards athletic performance, characteristics of their disabilities impose barriers to implementing dietary changes. Understanding these concerns and struggles is important for nutritionists who support para-athletes in sports nutrition.
19 Oct 2022
Scientists have uncovered new details of how ice forming below the ocean surface in Antarctica provides cold dense water that sinks to the seabed in an important aspect of global water circulation.
19 Oct 2022
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers conducted a study of human mobility to find effective lifestyle changes that enable people to exist with the novel coronavirus COVID-19, while maintaining social and economic activities. They found that restricting the human mobility in specific areas according to the state of the pandemic, rather than uniformly controlling human mobility, could be effective in reducing the number of new COVID-19 infections.
19 Oct 2022
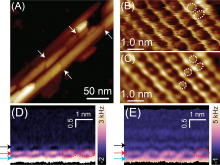
Pyroxenes are a major group of rock-forming minerals. Osaka Metropolitan University scientists investigated the iron ion status of a calcium-rich pyroxene, using Mössbauer spectroscopy on thin sections of single crystals. The study revealed that in pyroxene crystals consisting of roughly 50% calcium, the tensor that determines the ratios of iron ions at the Mössbauer spectral peaks in the M1 sites—one of two types of cation positions in the pyroxene crystal structure—is independent of the iron content but dependent on the calcium content. The research findings have clarified one of the physical properties of pyroxenes, facilitating detailed future analysis of iron using Mössbauer spectroscopy on mineral flakes.
18 Oct 2022
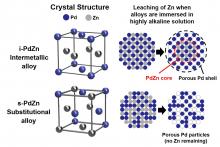
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have created intermetallic alloy nanoparticles of palladium and zinc with an alternating arrangement of zinc and palladium atoms. The intermetallic alloy is more corrosion-resistant than substitutional alloys while retaining the electrocatalytic properties of both metals, which could be useful for developing new non-precious metal electrocatalysts.
18 Oct 2022
Researchers develop a ground-breaking model to estimate bait vaccination effectiveness in wild animals based on the proportion of immunized animals in a population and the number of vaccine applications.
17 Oct 2022
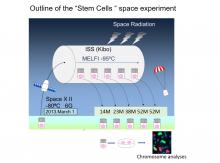
A long-term experiment aboard the International Space Station has tested the effect of space radiation on mouse embryonic stem cells. Their findings will contribute to helping scientists better assess the safety and risks related to space radiation for future human space flights. The findings are published in the journal Heliyon.
17 Oct 2022
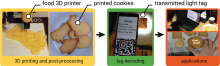
Researchers from Osaka University have developed a way of printing edible QR codes—a kind of barcode—within cookies, meaning that the tag is embedded within the food itself. Crucially, the tag doesn’t change the flavor or outer appearance of the cookie, and can be read using a backlight while the cookie remains intact. This new method has great commercial potential for improving food safety and traceability in an environmentally friendly way.
17 Oct 2022
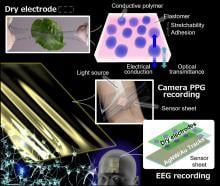
Researchers from Osaka University have developed a skin-like device to measure brain activity via electroencephalography, which uses electrodes to measure electrical activity on the scalp (reflecting underlying brain activity). The device has other useful applications, such as measuring heart rate and blood oxygen levels. Wearable devices that can remotely assess brain health in everyday settings are likely to improve healthcare for millions of people worldwide.
17 Oct 2022
Chemists in Japan, Canada and Europe have uncovered flaws in the surface structure of cellulose nanocrystals—an important step toward deconstructing cellulose to produce renewable nano-materials relevant to biochemical products, energy solutions, and biofuels.
17 Oct 2022
Researchers from Osaka University have shown that deficiency of the protein Favine can lead to accelerated development of atherosclerosis. Loss of Favine in a mouse atherosclerosis model also led to calcification and thrombus development in the blood vessels of the mice. Prior to this, no mouse models for calcification or thrombus formation existed, hindering atherosclerosis research. This work also identifies Favine and its downstream signaling pathway, known as MEF2C-KLF2, as potential therapeutic targets for atherosclerosis.
14 Oct 2022
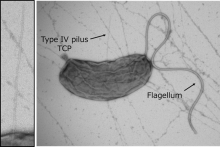
Researchers from Osaka University have found that the Vibrio cholerae colonization factor TcpF forms a flower-shaped trimer to specifically bind to the minor pilus protein TcpB resulting in secretion by the type 4 pilus secretion system into the extracellular space. This finding could help lead to the development of a novel anti-adhesive drug that selectively interrupts the TcpF-TcpB interaction, which may replace antibiotics in the treatment of cholera.
14 Oct 2022
A new material is set to provide us with faster and higher resolution displays. Hokkaido University researchers could explain what makes this material so special, opening the door to its application and further development.
14 Oct 2022
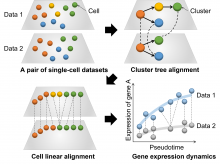
Researchers from Osaka University have developed a computational analysis tool called CAPITAL for comparative analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data with complicated branching trajectories. As cells undergo a dynamic process, they can be placed on a “pseudotime trajectory” to analyze the gene expression changes throughout the process. While previously only straightforward linear trajectories could be compared, CAPITAL is proven to be able to accurately compare branching trajectories, significantly advancing the field of high-throughput single-cell sequencing.
14 Oct 2022
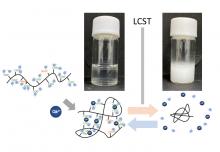
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have created a novel thermoresponsive polymer by adding divalent cations to polymers and water solvents. They also succeeded in controlling thermoresponsive properties by changing the type and mixing ratio of ionic species. This new polymer type is expected to be applied as an analytical reagent for ion-sensing devices and as a material for drug delivery systems.
13 Oct 2022
Giants in History: Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
12 Oct 2022
—For acceleration of social implementation of wastewater-based epidemiology—
12 Oct 2022
A study in Japan finds antibody response to the Moderna COVID-19 mRNA vaccine does not vary depending on the time of day when the dose was received.
12 Oct 2022
Osaka University researchers developed a power generation system based on osmotic flow of ions through a membrane riddled with tiny nanopores. By optimizing the size and distribution of the pores, the team demonstrated a way to obtain clean energy from the oceans.
11 Oct 2022
Researchers at The University of Tokyo simulated fractures in amorphous materials due to both cyclic fatigue and constant stress using course-grained dynamics, and demonstrated various failure modes, which can help improve reliability of materials
11 Oct 2022
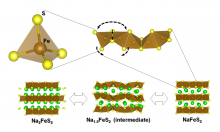
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have successfully developed a new positive electrode material Na2FeS2, consisting of sodium, iron, and sulfur. During testing, batteries using the Na2FeS2 positive electrode had a high energy storage capacity and could be charged and discharged for more than 300 cycles. Because the Na2FeS2 is made of abundant inexpensive elements, it is expected to be used in all-solid-state sodium batteries with higher capacity and lower costs.
07 Oct 2022
Researchers from Hokkaido University and Toppan have developed a method to detect build-up of amyloid β in the brain, a characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease, from biomarkers in blood samples.
06 Oct 2022
Researchers from Osaka University have found that serum albumin interferes with β2m amyloid fibril formation through macromolecular crowding. Monitoring serum albumin concentrations could therefore help prevent patients from developing dialysis-related amyloidosis, a serious complication of long-term dialysis.
06 Oct 2022
Low concentrations of cetylpyridinium chloride, an antimicrobial agent present in mouthwashes, inhibit the infectivity of four variants of SARS-CoV-2.
05 Oct 2022
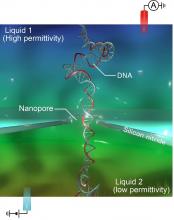
Researchers from Osaka University and collaborating partners enhanced DNA detection in silicon nitride nanopores by means of a water–glycerol viscosity gradient. Use of common chemistry under electrochemical flow enabled straightforward detection of individual DNA molecules. With further development, the results of this work could dramatically speed up and lower the cost of genomic sequencing, and facilitate unprecedented integration with compact electronics.
04 Oct 2022
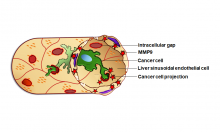
Metastasis—when cancer spreads to form new tumors—causes approximately 90% of cancer-related deaths. Because metastatic cancer cells circulate in the blood, the liver—which filters the blood—is considered the most vulnerable organ, so treatments that prevent liver metastasis are urgently needed. A team of Osaka Metropolitan University researchers discovered a mechanism that allows metastatic cancer cells to infiltrate the liver, and how that infiltration can be blocked by inhibiting a related protein.
03 Oct 2022
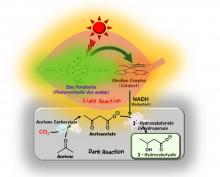
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have successfully synthesized 3-hydroxybutyrate, a raw material for poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB)—a strong, water-insoluble, biodegradable plastic used for packaging materials—from acetone and CO2. With a visible light-driven catalytic system utilizing sunlight and two biocatalysts, the researchers achieved a high conversion yield of about 80%. Mimicking natural photosynthesis, this study artificially reproduced a light reaction involving sunlight and a dark reaction fixing CO2 to synthesize the raw material for PHB. The finding is expected to contribute to solving the plastic waste problem and to reducing CO2.
30 Sep 2022
Researchers from Osaka University revealed that the surface electronic structure of topological insulators varies according to its surface atomic structure, even though it was believed to have been protected by the symmetry of the electronic structure inside the crystal and is therefore unaffected by differences in surface atomic structure. This work offers a new means of minimizing the power consumption and increasing the speed of next-generation technology.
29 Sep 2022
A simple and economical method of detecting SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in wastewater with high sensitivity has been developed, expanding the use of wastewater-based epidemiology for tracking the virus in populations.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater